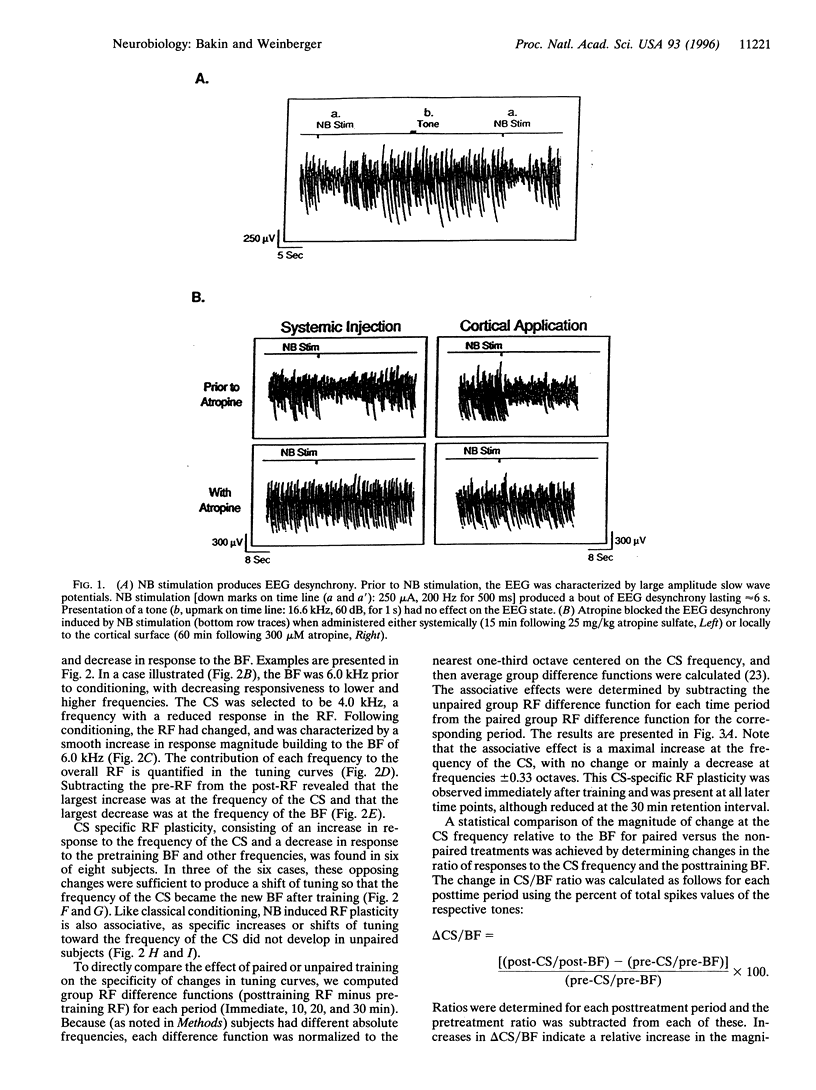
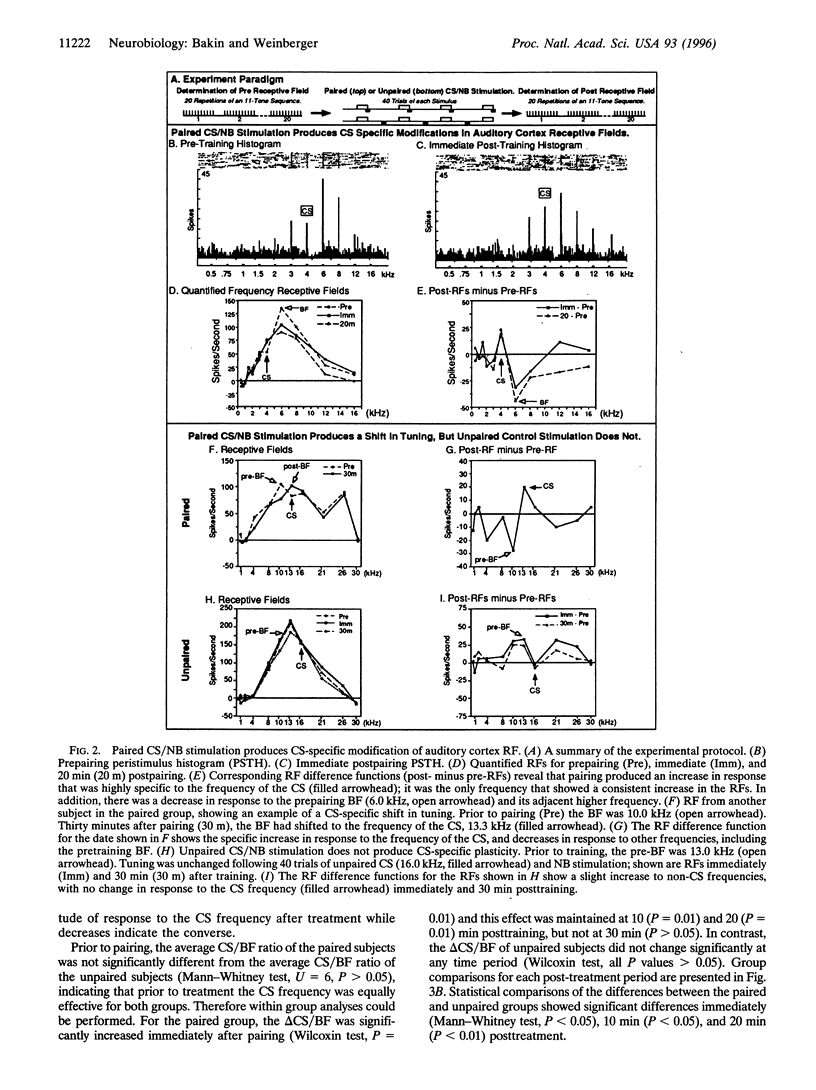
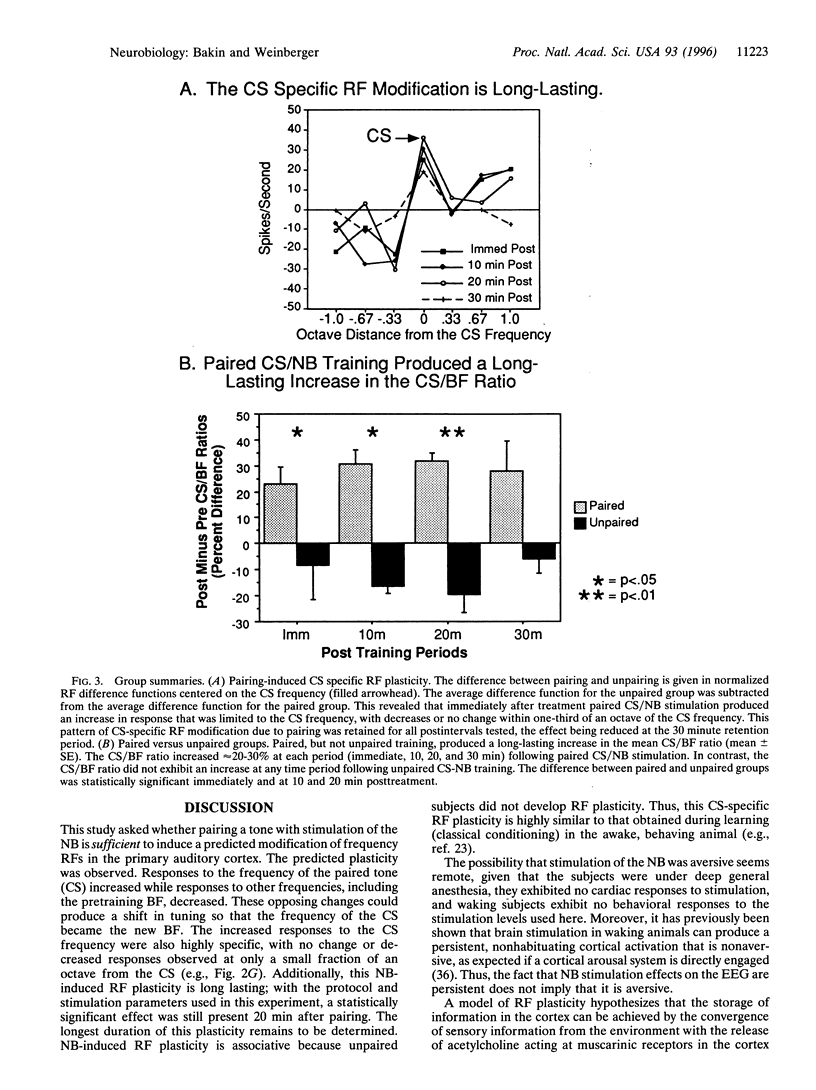
Abstract
Auditory cortical receptive field plasticity produced during behavioral learning may be considered to constitute "physiological memory" because it has major characteristics of behavioral memory: associativity, specificity, rapid acquisition, and long-term retention. To investigate basal forebrain mechanisms in receptive field plasticity, we paired a tone with stimulation of the nucleus basalis, the main subcortical source of cortical acetylcholine, in the adult guinea pig. Nucleus basalis stimulation produced electroencephalogram desynchronization that was blocked by systemic and cortical atropine. Paired tone/nucleus basalis stimulation, but not unpaired stimulation, induced receptive field plasticity similar to that produced by behavioral learning. Thus paired activation of the nucleus basalis is sufficient to induce receptive field plasticity, possibly via cholinergic actions in the cortex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashe J. H., McKenna T. M., Weinberger N. M. Cholinergic modulation of frequency receptive fields in auditory cortex: II. Frequency-specific effects of anticholinesterases provide evidence for a modulatory action of endogenous ACh. Synapse. 1989;4(1):44–54. doi: 10.1002/syn.890040106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakin J. S., Lepan B., Weinberger N. M. Sensitization induced receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex is independent of CS-modality. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 17;577(2):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90278-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakin J. S., Weinberger N. M. Classical conditioning induces CS-specific receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex of the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 17;536(1-2):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90035-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartus R. T., Dean R. L., Pontecorvo M. J., Flicker C. The cholinergic hypothesis: a historical overview, current perspective, and future directions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;444:332–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb37600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigl V., Woolf N. J., Butcher L. L. Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and cingulate cortices: a combined fluorescent tracer and acetylcholinesterase analysis. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jun;8(6):727–749. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collerton D. Cholinergic function and intellectual decline in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacour J., Houcine O., Costa J. C. Evidence for a cholinergic mechanism of "learned" changes in the responses of barrel field neurons of the awake and undrugged rat. Neuroscience. 1990;34(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90299-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch J. A. The cholinergic synapse and the site of memory. Science. 1971 Nov 19;174(4011):788–794. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4011.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edeline J. M., Maho C., Hars B., Hennevin E. Non-awaking basal forebrain stimulation enhances auditory cortex responsiveness during slow-wave sleep. Brain Res. 1994 Feb 14;636(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edeline J. M., Pham P., Weinberger N. M. Rapid development of learning-induced receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex. Behav Neurosci. 1993 Aug;107(4):539–551. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.107.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edeline J. M., Weinberger N. M. Receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex during frequency discrimination training: selective retuning independent of task difficulty. Behav Neurosci. 1993 Feb;107(1):82–103. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.107.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edeline J. M., Weinberger N. M. Thalamic short-term plasticity in the auditory system: associative returning of receptive fields in the ventral medial geniculate body. Behav Neurosci. 1991 Oct;105(5):618–639. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.105.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartgraves S. L., Mensah P. L., Kelly P. H. Regional decreases of cortical choline acetyltransferase after lesions of the septal area and in the area of nucleus basalis magnocellularis. Neuroscience. 1982 Oct;7(10):2369–2376. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S. E., Juliano S. L. The impact of basal forebrain lesions on the ability of rats to perform a sensory discrimination task involving barrel cortex. J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1099–1109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01099.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. V., McKinney M., Coyle J. T. Evidence for a cholinergic projection to neocortex from neurons in basal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. V., McKinney M., Coyle J. T. Neocortical cholinergic innervation: a description of extrinsic and intrinsic components in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1981;43(2):159–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00237760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopytova F. V., Mednikova YuS, Rusinova E. V. Analog of a conditioned reflex of sensomotor cortical units following microinjection of acetylcholine. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1981 May-Jun;11(3):213–220. doi: 10.1007/BF01184411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Nagy J. I., Atmadia S., Fibiger H. C. The nucleus basalis magnocellularis: the origin of a cholinergic projection to the neocortex of the rat. Neuroscience. 1980;5(7):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Levey A. I., Wainer B. H. Cholinergic innervation of cortex by the basal forebrain: cytochemistry and cortical connections of the septal area, diagonal band nuclei, nucleus basalis (substantia innominata), and hypothalamus in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 20;214(2):170–197. doi: 10.1002/cne.902140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metherate R., Cox C. L., Ashe J. H. Cellular bases of neocortical activation: modulation of neural oscillations by the nucleus basalis and endogenous acetylcholine. J Neurosci. 1992 Dec;12(12):4701–4711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-12-04701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metherate R., Tremblay N., Dykes R. W. Transient and prolonged effects of acetylcholine on responsiveness of cat somatosensory cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Apr;59(4):1253–1276. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.4.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metherate R., Weinberger N. M. Cholinergic modulation of responses to single tones produces tone-specific receptive field alterations in cat auditory cortex. Synapse. 1990;6(2):133–145. doi: 10.1002/syn.890060204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir J. L., Page K. J., Sirinathsinghji D. J., Robbins T. W., Everitt B. J. Excitotoxic lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: effects on learning, memory and attention. Behav Brain Res. 1993 Nov 30;57(2):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(93)90128-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Fibiger H. C. Learning and memory deficits after lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis: reversal by physostigmine. Neuroscience. 1985 Apr;14(4):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Ishihara T. Task-dependent memory loss and recovery following unilateral nucleus basalis lesion: behavioral and neurochemical correlation. Behav Brain Res. 1990 Jul 9;39(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P., Jr, Sirviö J., Hannila T., Miettinen R., Riekkinen P. Effects of quisqualic acid nucleus basalis lesioning on cortical EEG, passive avoidance and water maze performance. Brain Res Bull. 1990 Jun;24(6):839–842. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(90)90148-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigdon G. C., Pirch J. H. Nucleus basalis involvement in conditioned neuronal responses in the rat frontal cortex. J Neurosci. 1986 Sep;6(9):2535–2542. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-09-02535.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. W., Escobar M. L., Booth R. A., Bermúdez-Rattoni F. Accelerating behavioral recovery after cortical lesions. II. In vivo evidence for cholinergic involvement. Behav Neural Biol. 1994 Jan;61(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(05)80047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye D. B., Wainer B. H., Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Saper C. B. Cortical projections arising from the basal forebrain: a study of cholinergic and noncholinergic components employing combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase. Neuroscience. 1984 Nov;13(3):627–643. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper C. B. Organization of cerebral cortical afferent systems in the rat. II. Magnocellular basal nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jan 20;222(3):313–342. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M., Kemp J. A. Cholinergic modulation of the functional organization of the cat visual cortex. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger N. M., Javid R., Lepan B. Long-term retention of learning-induced receptive-field plasticity in the auditory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester K. Reinforcing effects of thalamic stimulation resistant to habituation. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 11;43(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woody C. D., Swartz B. E., Gruen E. Effects of acetylcholine and cyclic GMP on input resistance of cortical neurons in awake cats. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 15;158(2):373–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90682-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



