Sir,
Swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) uses a wavelength swept laser as the light source, and it has less roll-off in sensitivity with increasing depth than spectral-domain OCT.1 In addition, SS-OCT instruments use a longer centre wavelength, which improved their ability to penetrate deeper into ocular tissues. Thus, evaluations of the deeper structures of the eye are possible. Herein, we report a case of optic disc pit (ODP) in whom a connection between the vitreous cavity and the retrobulbar subarachnoid space (SAS) was clearly demonstrated using SS-OCT.
Case report
A 66-year-old man diagnosed with ODP was examined with an SS-OCT instrument (DRI OCT-1, Topcon, Tokyo, Japan). The patient had visual disturbances in his left eye, and his best-corrected visual acuity was 1.2 OD and 0.7 OS. The intraocular pressure was 14 mm Hg OU. Slit-lamp examination of both eyes and fundus examination of the right eye were unremarkable. Fundus examination of the left eye showed an ODP with macular retinoschisis (Figure 1). SS-OCT clearly delineated the SAS and its direct communication with the vitreous cavity (Figure 2). The opening in the optic disc became clearly visible by a three-dimensional OCT reconstruction. Perimetry showed no glaucomatous visual field defects. Brain and orbital magnetic resonance imagings were normal.
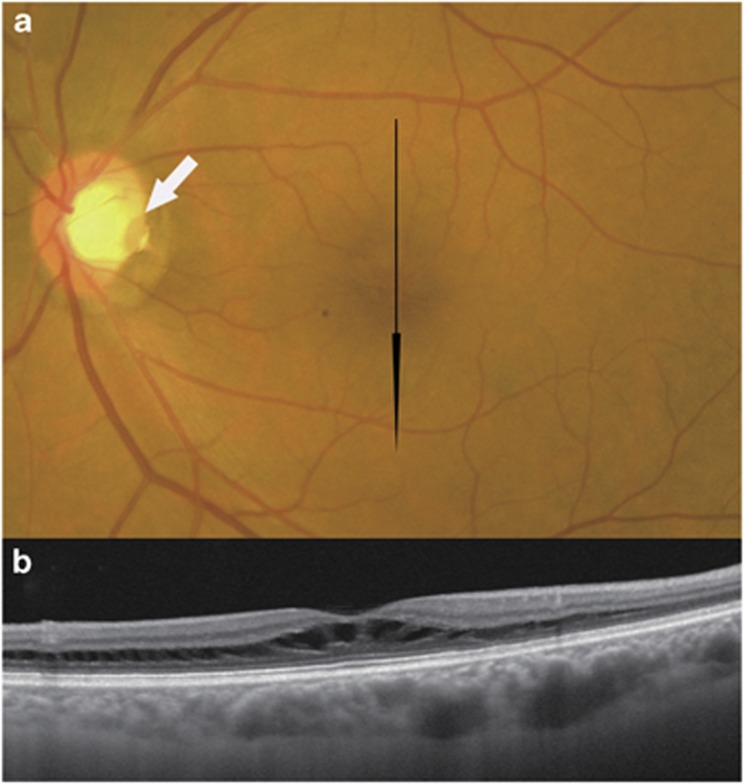
Figure 1.
Fundus photograph and swept-source optical coherence tomographic (SS-OCT) image of the left eye of a 66-year-old man with an optic disc pit. The light source of this SS-OCT system is a wavelength tunable laser centred at 1050 nm. (a) Colour fundus photograph. A grey, oval-shaped optic disc pit (white arrow) at the temporal margin of the disc and peripapillary pigmentary changes are observed. The optic disc tissue other than the pit seems normal. Glaucomatous cupping is not seen. Black arrow indicates the direction of the OCT scan. (b) Vertical SS-OCT image through the fovea showing retinoschisis. Tissue columns connecting the schisis cavities can be seen.
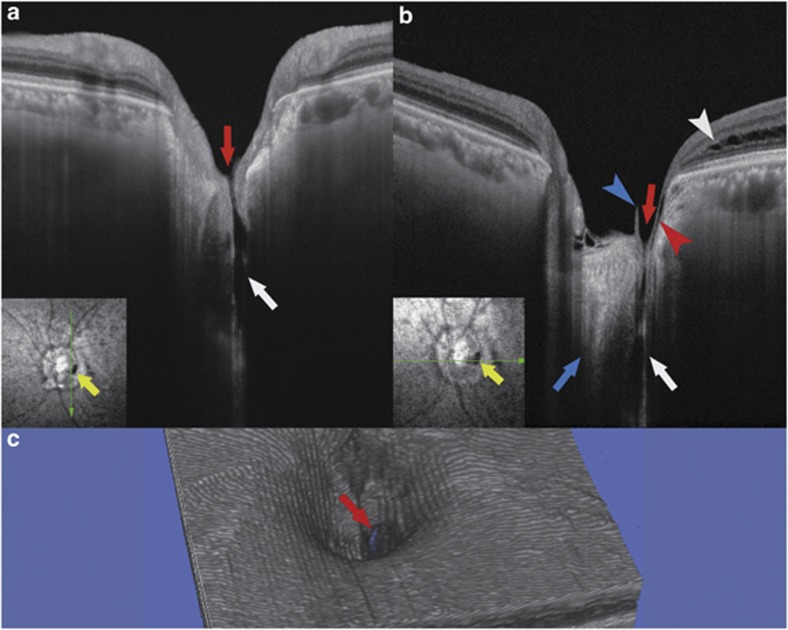
Figure 2.
Swept-source optical coherence tomographic (SS-OCT) image of the left eye with an optic disc pit. The imaging depth of this SS-OCT system is 2.6 mm in tissue. (a, b) Vertical (a) and horizontal (b) B-scan cross-sectional images near the optic disc pit are shown. Retrobulbar subarachnoid space (white arrows) is clearly seen around the optic nerve. There is a direct communication between the retrobulbar subarachnoid space and the vitreous cavity (red arrows). Blue arrow indicates the optic nerve. Red arrowhead indicates a thin line of fluid that is presumably connecting with the retrobulbar subarachnoid space, but communication with this line and the schisis cavity (white arrowhead) is unclear. Blue arrowhead points to a part of a vitreous strand. Yellow arrows indicate the optic disc pit, and green arrows indicate the direction of the OCT scan. (c) Three-dimensional OCT reconstruction shows a break in the cup of the optic disc (red arrow).
Comment
In our case, the macular retinoschisis was most likely the cause of the visual impairment. The schisis formation is the initial step in the evolution of serous retinal detachments associated with ODPs.2, 3 Krivoy et al2 suggested that the ODP acts as a conduit for fluid flow between the SAS and the schisis cavity or subretinal space. In our case, SS-OCT delineated a thin line of fluid in the disc that was presumably connected to the SAS.
Ohno-Matsui et al1 reported that SAS could be seen by SS-OCT in 93.2% of highly myopic eyes. They described that an SAS was seen as a hyporeflective space around the optic nerve. In one myopic patient, there was a direct communication between the SAS and the vitreous cavity.1
In ODP, previous reports only inferred that there were direct communications among the SAS, vitreous cavity, and subretinal space.3, 4, 5 Kuhn et al5 reported a case of ODP in whom intravitreally injected silicone oil was detected intracranially indicating a communication between the SAS and the vitreous cavity. Our findings demonstrated a direct communication between the SAS and the vitreous cavity in an eye with an ODP.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ohno-Matsui K, Akiba M, Moriyama M, Ishibashi T, Tokoro T, Spaide RF. Imaging retrobulbar subarachnoid space around optic nerve by swept-source optical coherence tomography in eyes with pathologic myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:9644–9650. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivoy D, Gentile R, Liebmann JM, Stegman Z, Rosen R, Walsh JB, et al. Imaging congenital optic disc pits and associated maculopathy using optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114:165–170. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1996.01100130159008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besada E, Barr R, Schatz S, Brewer C. Vitreal pathogenic role in optic pit foveolar retinoschisis and central serous retinopathy. Clin Exp Optom. 2003;86:390–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2003.tb03084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine AR, Crawford JB, Sullivan JH. The pathogenesis of retinal detachment with morning glory disc and optic pit. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1986;84:280–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn F, Kover F, Szabo I, Mester V. Intracranial migration of silicone oil from an eye with optic pit. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;244:1360–1362. doi: 10.1007/s00417-006-0267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]