Abstract
The inherited deficiency of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase (PNPase; purine-nucleoside:orthophosphate ribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.1) in humans is associated with a severe deficiency of the T lymphocytes of the immune system. Because of the unsatisfactory nature of previously described model systems, we have selected, cloned, and characterized a mutant mouse T cell lymphoma (S49) completely deficient in PNPase. Of the four substrates of PNPase, only deoxyguanosine at low concentrations is toxic to the PNPase-deficient (NSU-1) cells.
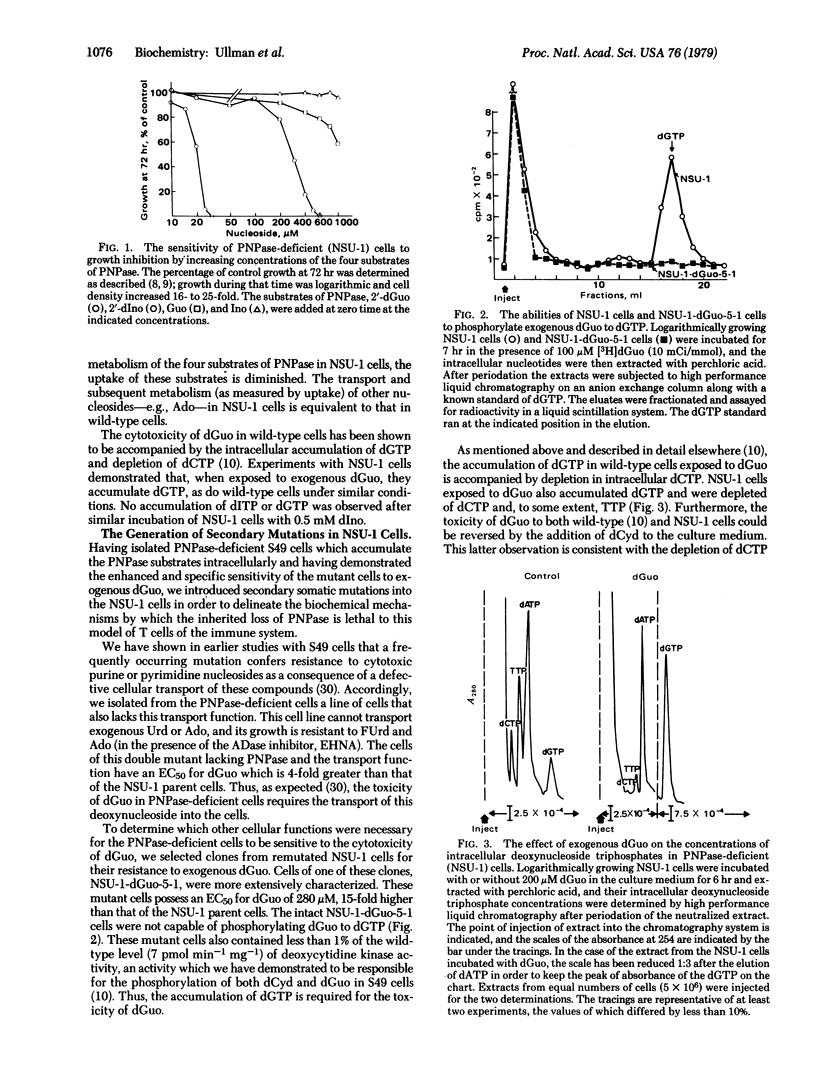
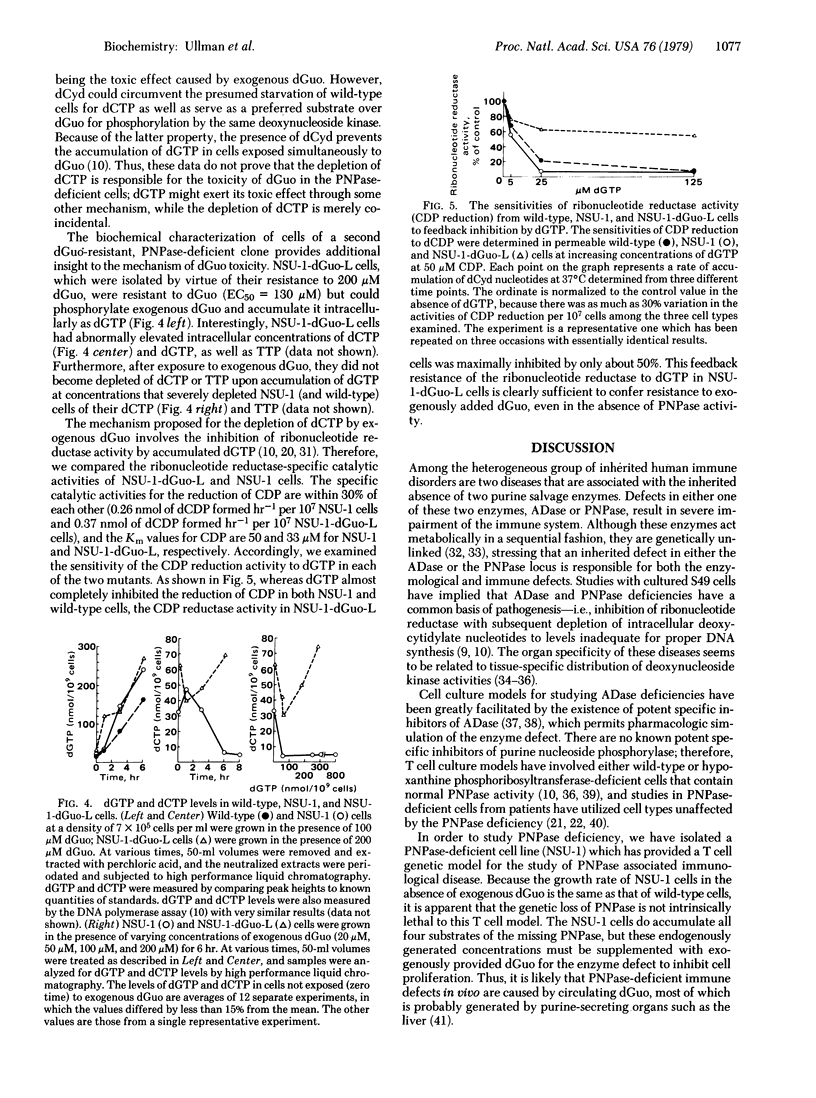
In order to delineate the biochemical processes necessary for the sensitivity of the NSU-1 cells to deoxyguanosine, we have isolated a series of secondary mutants resistant to deoxyguanosine from the PNPase-deficient line. One of these mutants is defective in its ability to transport deoxyguanosine into the cell. A second type of mutant cannot phosphorylate the deoxyguanosine and is totally deficient in deoxycytidine kinase activity. A third type of mutant (NSU-1-dGuo-L) can both transport and phosphorylate deoxyguanosine and accumulates dGTP. However, unlike its parent, NSU-1-dGuo-L does not become depleted of dCTP and TTP when exposed to exogenous deoxyguanosine. This observation is accounted for by the fact that the reduction of CDP to dCDP by the ribonucleotide reductase (ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase, 2′-deoxyribonucleoside-diphosphate:oxidized-thioredoxin 2′-oxidoreductase, EC 1.17.4.1) of NSU-1-dGuo-L cells is not normally sensitive to feedback inhibition by dGTP.
Thus, in order to exert its toxicity deoxyguanosine must be transported into the cell, be phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase, and be accumulated as dGTP. By inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase, dGTP depletes the cell of dCTP and to some extent TTP, thus preventing the synthesis of DNA, a process necessary for any proliferation-dependent function of T cells.
Keywords: ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase, dGTP, feedback resistance, deoxycytidine kinase, deoxyguanosine
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Lymphospecific toxicity in adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency: possible role of nucleoside kinase(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S. Deoxyguanosine toxicity on lymphoid cells as a cause for immunosuppression in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A. Mutations affecting adenine phosphoribosyl transferase activity in Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Baumal R., Laskov R., Scharff M. D. Cloning of mouse myeloma cells and detection of rare variants. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Jun;79(3):429–440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040790313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Doyle D., Martin D. W., Jr, Ammann A. J. Abnormal purine metabolism and purine overproduction in a patient deficient in purine nucleoside phosphorylase. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 23;295(26):1449–1454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612232952603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Gudas L. J., Ammann A. J., Staal G. E., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyguanosine triphosphate as a possible toxic metabolite in the immunodeficiency associated with purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1405–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI109058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Hirschhorn R., Horowitz S. D., Rubinstein A., Polmar S. H., Hong R., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyadenosine triphosphate as a potentially toxic metabolite in adenosine deaminase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Ullman B., Martin D. W., Jr Characterization of a mutant mouse lymphoma cell with deficient transport of purine and pyrimidine nucleosides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. S., Donofrio J., Hutton J. J., Hahn L., Daoud A., Lampkin B., Dyminski J. Identification and quantitation of adenine deoxynucleotides in erythrocytes of a patient with adenosine deaminase deficiency and severe combined immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1619–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Litwack G., Tomkins G. M. Induction of cytolysis of cultured lymphoma cells by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and the isolation of resistant variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):76–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham J. P., Ives D. H. Deoxycytidine kinase. I. Distribution in normal and neoplastic tissues and interrelationships of deoxycytidine and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):358–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards N. L., Magilavy D. B., Cassidy J. T., Fox I. H. Lymphocyte ecto-5'-nucleotidase deficiency in agammaglobulinemia. Science. 1978 Aug 18;201(4356):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.27864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Francke U. Gene dose effect: regional mapping of human nuceloside phosphorylase on chromosome 14. Science. 1976 Nov 19;194(4267):851–852. doi: 10.1126/science.824731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. D., Martin D. W., Jr Characterization of a feedback-resistant phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase from cultured, mutagenized hepatoma cells that overproduce purines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Cohen A., Ullman B., Martin D. W., Jr Analysis of adenosine-mediated pyrimidine starvation using cultured wild-type and mutant mouse T-lymphoma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Mar;4(2):201–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01538985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Ullman B., Cohen A., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyguanosine toxicity in a mouse T lymphoma: relationship to purine nucleoside phosphorylase-associated immune dysfunction. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzig W. H., Dohmann U., Pluss H. J., Vischer D. Hereditary transcobalamin II deficiency: clinical findings in a new family. J Pediatr. 1974 Nov;85(5):622–628. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., North M. E., Asherson G. L., Allsop J., Watts R. W., Webster A. D. Lymphocyte purine 5'-nucleotidase edficiency in primary hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):168–170. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91765-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLENOW H. Further studies on the effect of deoxyadenosine on the accumulation of deoxyadenosine triphosphate and inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:885–896. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Martin D. V., Jr Role of S-adenosylhomocysteine in adenosinemediated toxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Tuttle J. V., Koszalka G. W., Chen I. S., Beacham L. M., 3rd, Rideout J. L., Elion G. B. Deoxycytidine kinase from calf thymus. Substrate and inhibitor specificity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4055–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAJTHA L. G., VANE J. R. Dependence of bone marrow cells on the liver for purine supply. Nature. 1958 Jul 19;182(4629):191–192. doi: 10.1038/182191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E., Nuki G., Seegmiller J. E. Expression of purine overproduction in a series of 8-azaguanine-resistant diploid human lymphoblast lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Kuzik B. A., Wright J. A. Assay of ribonucleotide reduction in nucleotide-permeable hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Mar;94(3):287–298. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040940306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Wright J. A. Altered ribonucleotide reductase activity in mammalian tissue culture cells resistant to hydroxyurea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):926–933. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Wright J. A. Genetic characterization of hydroxyurea-resistance in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Oct;97(1):73–85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M., Green H. Alterations leading to increased ribonucleotide reductase in cells selected for resistance to deoxynucleosides. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. C., Hurlbert R. B. Regulation of mammalian deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis by nucleotides as activators and inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4802–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHARD P., CANELLAKIS Z. N., CANELLAKIS E. S. Studies on a possible regulatory mechanism for the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2514–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H. Linkage analysis in man by somatic cell genetics. Nature. 1973 Mar 16;242(5394):165–169. doi: 10.1038/242165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Slesinski R. S., Littlefield J. W. Chemical mutagenesis at the phosphoribosyltransferase locus in cultured human lymphoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1244–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Schwender C. F. Enzyme inhibitors. 26. Bridging hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions on adenosine deaminase with some 9-(2-hydroxy-3-alkyl)adenines. J Med Chem. 1974 Jan;17(1):6–8. doi: 10.1021/jm00247a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector E. B., Hershfield M. S., Seegmiller J. E. Purine reutilization and synthesis de novo in long-term human lymphocyte cell lines deficient in adenine phosphoribosyltransferase activity. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 May;4(3):253–264. doi: 10.1007/BF01542842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeper J. R., Steuart C. D. A rapid assay for CDP reductase activity in mammalian cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:123–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. F., Willis R. C., Stoop J. W., Seegmiller J. E. Purine metabolism in cultured human fibroblasts derived from patients deficient in hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase, purine nucleoside phosphorylase, or adenosine deaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3722–3726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Cohen A., Martin D. W. Characterization of a cell culture model for the study of adenosine deaminase- and purine nucleoside phosphorylase-deficient immunologic disease. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Cohen A., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyadenosine metabolism and cytotoxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells: a model for immunodeficiency disease. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V., Doyle D., Martin D. W., Jr Purification and characterization of human erythrocyte purine nucleoside phosphorylase and its subunits. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):504–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



