Abstract
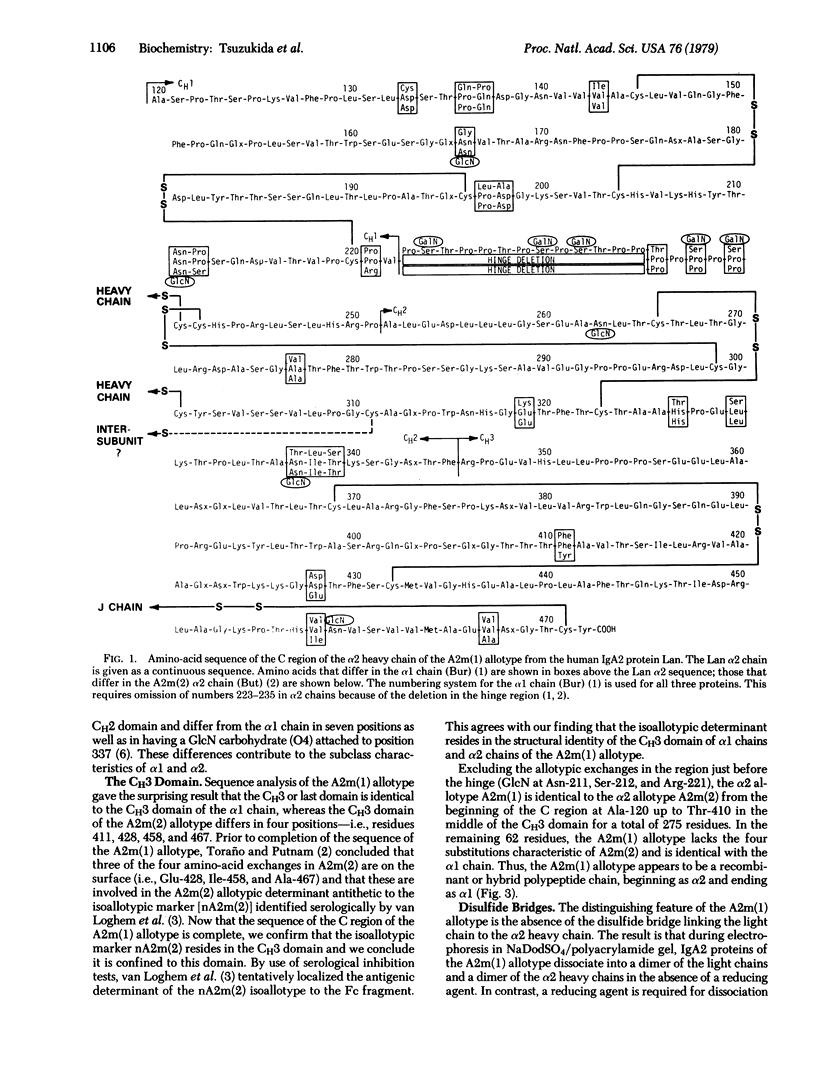
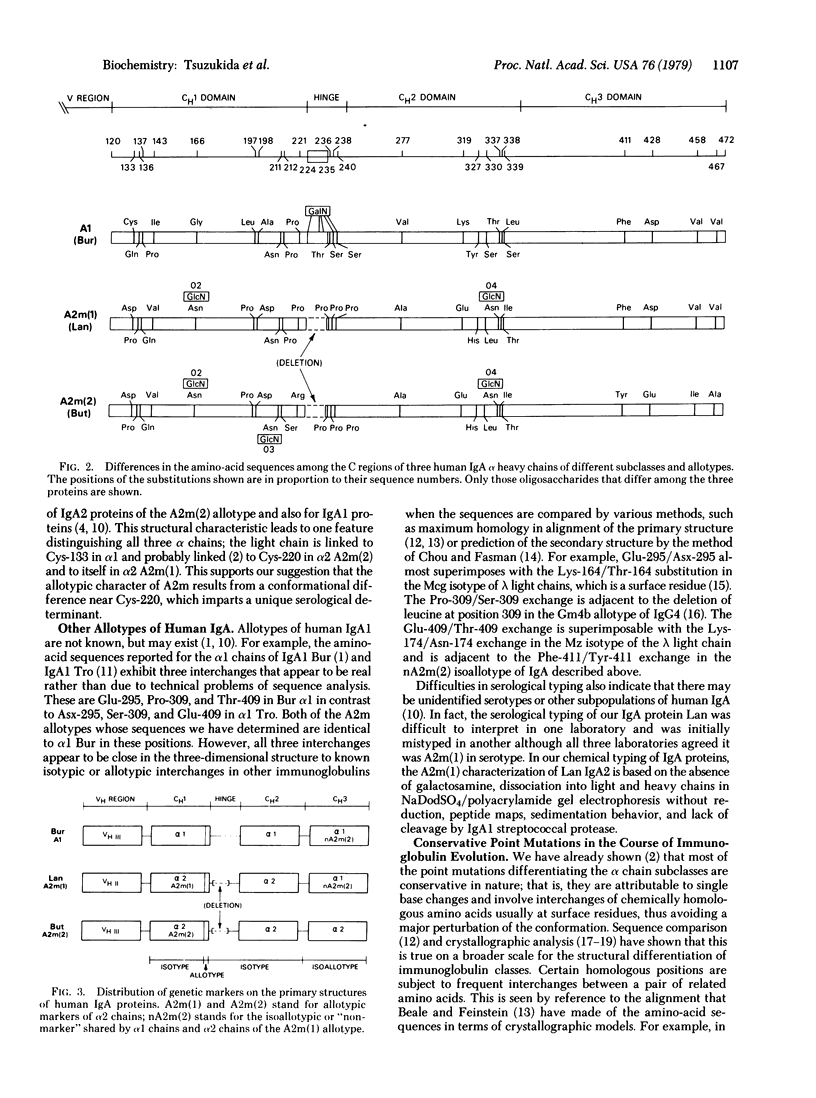
The complete amino-acid sequence of the constant (C) region of the α2 heavy chain of a human IgA2 protein of the A2m(1) allotype has been determined. Excluding the hinge region and the carbohydrate content, this α2 allotype differs from the α1 chain in only 14 amino-acid positions; all of these are identical to the A2m(2) allotype of the α2 chain and confer subclass (or isotypic) character on the α2 chains. However, the A2m(2) allotype differs in six positions where A2m(1) and α1 are identical; the first two are just before the hinge and the other four are in the last (CH3) domain. The A2m allotypic character of α2 chains is attributed to several conformational factors in the sequence at positions 211-221, just before the hinge. The isoallotypic determinant shared by α1 chains and the A2m(1) allotype of α2 resides in the identity of their CH3 domains. Thus, the A2m(1) allotype appears to be a hybrid chain that is identical with α1 in the CH3 domain and identical with the A2m(2) α2 chain in the CH1 and CH2 domains and in the hinge, except for the allotypic determinants arising from four structural differences from residues 211-221. The genetic origin of isotypes, allotypes, and isoallotypes of the α chain has involved several events of homologous crossing over and neutral point mutations accumulated late in the evolutionary development of IgA immunoglobulins. Since the crossing over appears to occur between CH2 and CH3, heavy chain domains may be coded for by independent units in embryonic DNA that are analogous to the variable (V) and C segments of light-chain genes.
Keywords: protein structure, amino-acid sequence, genetic markers, isoallotype, immunoglobulins
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J., Kornfeld S. Structure of the carbohydrate units of IgA1 immunoglobulin. II. Structure of the O-glycosidically linked oligosaccharide units. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7270–7281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale D., Feinstein A. Structure and function of the constant regions of immunoglobulins. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 May;9(2):135–180. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Padlan E. A., Segal D. M. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:639–667. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Colman P. M., Epp O., Huber R. Crystallographic structural studies of a human Fc fragment. II. A complete model based on a Fourier map at 3.5 A resolution. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Dec;357(10):1421–1434. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.2.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Structural variants of human and murine immunoglobulins. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1975;4:89–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8930-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Altevogt P., Ruban E., Kortt A., Staroscik K., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur eines monoklonalen IgA-Immunoglobulins (IgA Tro.), II. Die Aminosäuresequenz der H-Kette, alpha-Typ, Subgruppe III. Struktur des gesamten IgA-Moleküls. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Aug;356(8):1337–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Low T. L., Infante A., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1017–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.821146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Liu Y. S., Putnam F. W. Structure, function, and evolutionary relationships of Fc domains of human immunoglobulins A, G, M, and E. Science. 1976 Jan 30;191(4225):390–392. doi: 10.1126/science.1246619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J. X-ray diffraction studies of immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Low T., Liu V., Huser H., Raff E., Wong F. C., Clamp J. R. Isolation, properties, and structure of human IgA myeloma globulins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):177–189. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toraño A., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 2 heavy chain of a human IgA2 immunoglobulin of the A2m (2) allotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):966–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toraño A., Tsuzukida Y., Liu Y. S., Putnam F. W. Location and structural significance of the oligosaccharides in human Ig-A1 and IgA2 immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2301–2305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Loghem E., De Lange G., Koistinen J. The first isoallotype of human IgA proteins. An antigenic determinant occurring as allotype in the IgA2 subclass and as isotype in the IgA1 subclass. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(1-2):161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virella G., Koistinen J., Cardenas R., Patrick C. C., Higerd T. B., Fett J. W., Fudenberg H. H. Differential sensitivity of IgA proteins of different subclasses and allotypes to reduction of disulfide bonds and digestion by streptococcal protease. Immunochemistry. 1978 Mar;15(3):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Partial amino acid sequence of an IgA2 human immunoglobulin heavy chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


