Abstract
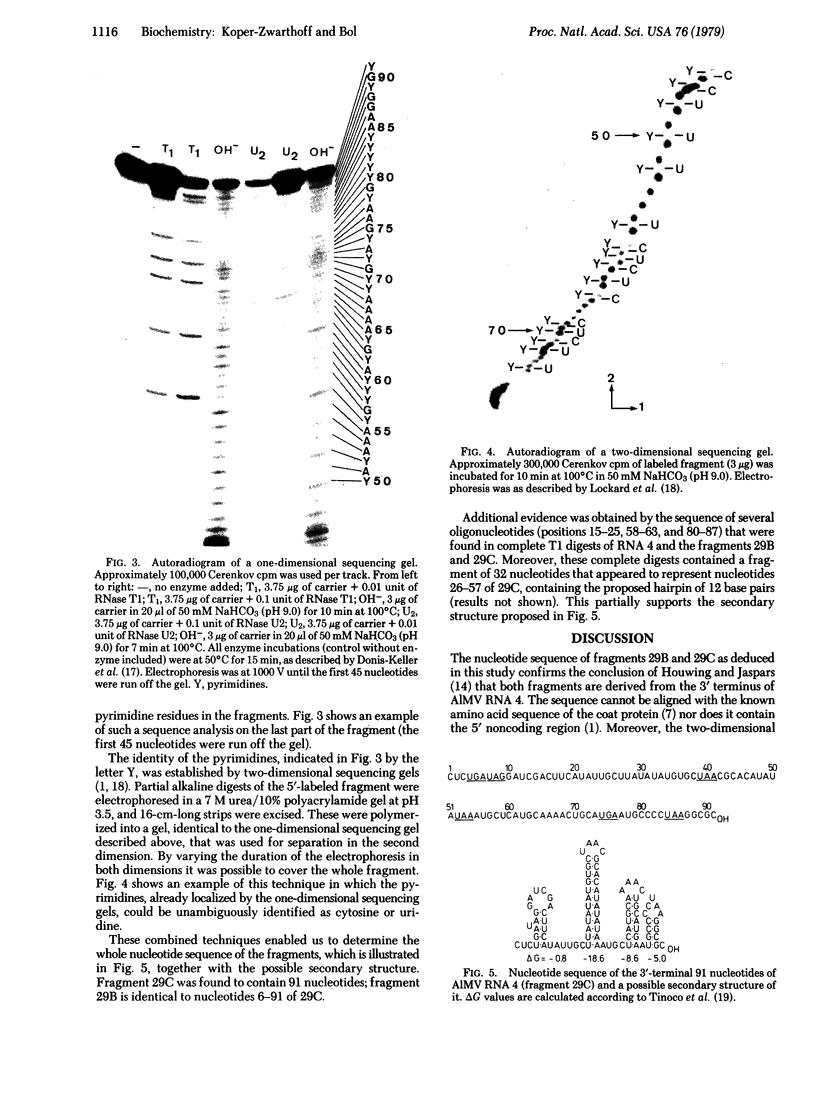
The sequence of the 3'-terminal 91 nucleotides of alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4, the messenger for the viral coat protein, has been elucidated. A fragment containing the 3' terminus of the RNA was obtained by mild digestion with RNase T1. The primary structure of the fragment was deduced by labeling it in vitro at its 5' terminus and application of RNA sequencing techniques. The sequence is completely extracistronic and is believed to contain the binding sites for the viral coat protein and replicase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bol J. F., Bakhuizen C. E., Rutgers T. Composition and biosynthetic activity of polyribosomes associated with alfalfa mosaic virus infections. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bol J. F., van Vloten-Doting L. Function of top component a RNA in the initiation of infection by alfalfa mosaic virus. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bol J. F., van Vloten-Doting L., Jaspars E. M. A functional equivalence of top component a RNA and coat protein in the initiation of infection by alfalfa mosaic virus. Virology. 1971 Oct;46(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Jonard G., Guilley H., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence (n=159) of the amino-acid-accepting 3'-OH extremity of turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus RNA and the last portion of its coat-protein cistron. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):453–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Richards K. E., Bouley J. P., Witz J., Hirth L. Stucture of the amino-acid accepting 3'-end of high-molecular-weight eggplant mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Sequence of an oligonucleotide derived from the 3' end of each of the four brome mosaic viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4900–4904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Jonard G., Hirth L. Sequence of 71 nucleotides at the 3'-end of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijtink R. A., Houwing C. J., Jaspars E. M. Molecular weights of particles and RNAs of alfalfa mosaic virus. Number of subunits in protein capsids. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4684–4693. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwing C. J., Jaspars E. M. Coat protein binds to the 3'-terminal part of RNA 4 of alfalfa mosaic virus. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2927–2933. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspars E. M. Plant viruses with a multipartite genome. Adv Virus Res. 1974;19:37–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60659-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koper-Zwarthoff E. C., Lockard R. E., Alzner-deWeerd B., RajBhandary U. L., Bol J. F. Nucleotide sequence of 5' terminus of alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4 leading into coat protein cistron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Alzner-Deweerd B., Heckman J. E., MacGee J., Tabor M. W., RajBhandary U. L. Sequence analysis of 5'[32P] labeled mRNA and tRNA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):37–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Prochiantz A., Haenni A. L., Rajbhandary U. L. Studies on the sequence of the 3'-terminal region of turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):465–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vloten-Doting L., Jaspars E. M. The uncoating of alfalfa mosaic virus by its own RNA. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):699–708. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wachter R., Fiers W. Preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 32 P-labeled RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Sep;49(1):184–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Manna M. M., Bruening G. Polyadenylate sequences in the ribonucleic acids of cowpea mosaic virus. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):198–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beynum G. M., de Graaf J. M., Castel A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Structural studies on the coat protein of alfalfa mosaic virus. The complete primary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan 3;72(1):63–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]