Abstract
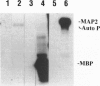
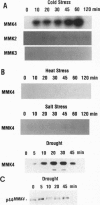
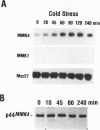
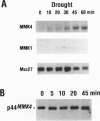
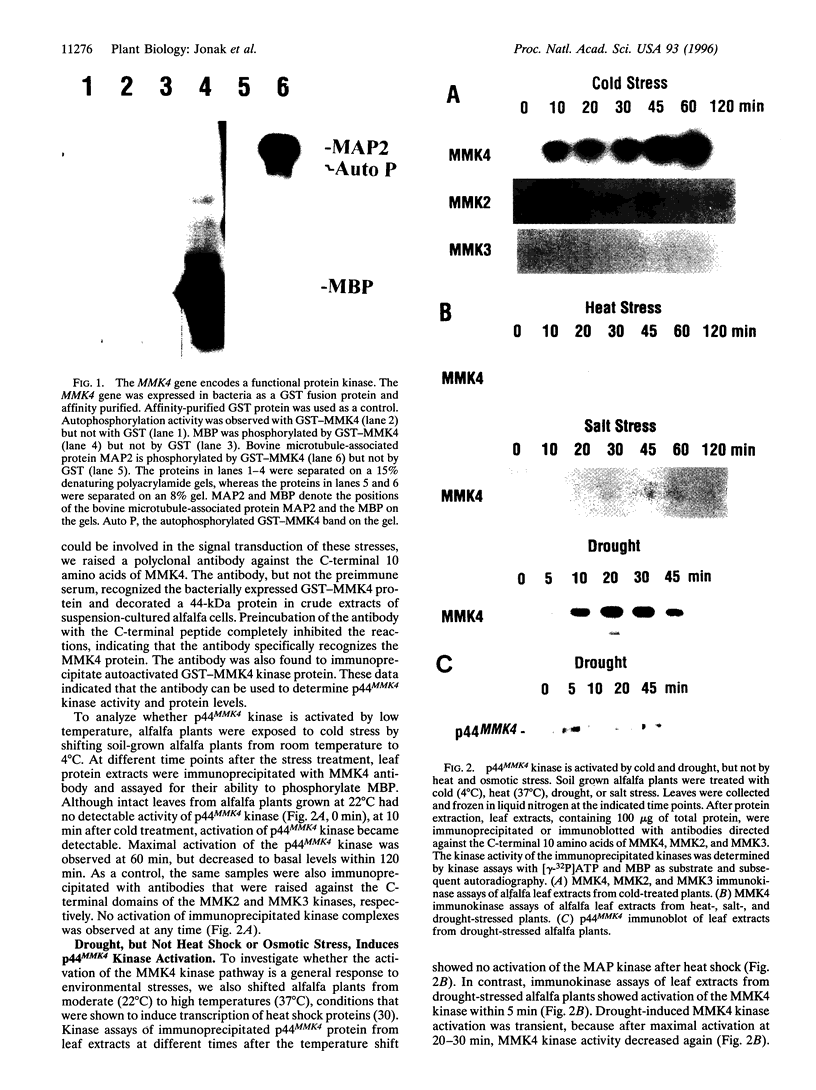
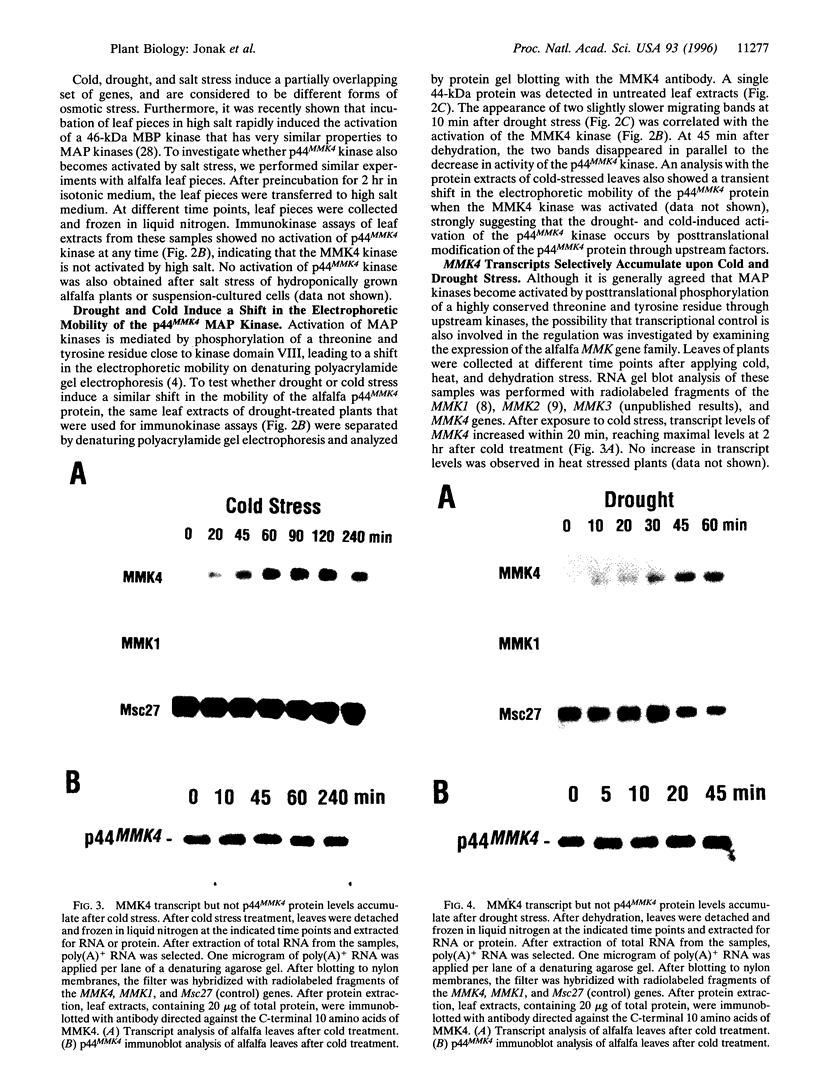
Yeast and animals use mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascades to mediate stress and extracellular signals. We have tested whether MAP kinases are involved in mediating environmental stress responses in plants. Using specific peptide antibodies that were raised against different alfalfa MAP kinases, we found exclusive activation of p44MMK4 kinase in drought- and cold-treated plants. p44MMK4 kinase was transiently activated by these treatments and was correlated with a shift in the electrophoretic mobility of the p44MMK4 protein. Although transcript levels of the MMK4 gene accumulated after drought and cold treatment, no changes in p44MMK4 steady state protein levels were observed, indicating a posttranslational activation mechanism. Extreme temperatures, drought, and salt stress are considered to be different forms of osmotic stress. However, high salt concentrations or heat shock did not induce activation of p44MMK4, indicating the existence of distinct mechanisms to mediate different stresses in alfalfa. Stress adaptation in plants is mediated by abscisic acid (ABA)-dependent and ABA-independent processes. Although ABA rapidly induced the transcription of an ABA-inducible marker gene, MMK4 transcript levels did not increase and p44MMK4 kinase was not activated. These data indicate that the MMK4 kinase pathway mediates drought and cold signaling independently of ABA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banno H., Hirano K., Nakamura T., Irie K., Nomoto S., Matsumoto K., Machida Y. NPK1, a tobacco gene that encodes a protein with a domain homologous to yeast BCK1, STE11, and Byr2 protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4745–4752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. H., Li P. H., Brenner M. L. Involvement of abscisic Acid in potato cold acclimation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):362–365. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. MAP kinase pathways. Straight and narrow or tortuous and intersecting? Curr Biol. 1994 Dec 1;4(12):1118–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decroocq-Ferrant V., Decroocq S., Van Went J., Schmidt E., Kreis M. A homologue of the MAP/ERK family of protein kinase genes is expressed in vegetative and in female reproductive organs of Petunia hybrida. Plant Mol Biol. 1995 Jan;27(2):339–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00020188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich A., Mayer J. E., Hahlbrock K. Fungal elicitor triggers rapid, transient, and specific protein phosphorylation in parsley cell suspension cultures. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6360–6368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr B., Gawienowski M., Ropp T., Jacobs T. MsERK1: a mitogen-activated protein kinase from a flowering plant. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):87–96. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G., Grosskopf D. G., Regenass M., Boller T. Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8831–8834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galcheva-Gargova Z., Dérijard B., Wu I. H., Davis R. J. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.8047888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosti F., Bertauche N., Vartanian N., Giraudat J. Abscisic acid-dependent and -independent regulation of gene expression by progressive drought in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Jan 6;246(1):10–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00290128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero F., Mullet J. E. Increased Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis during Plant Dehydration Requires Transcription. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):588–591. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györgyey J., Gartner A., Németh K., Magyar Z., Hirt H., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Alfalfa heat shock genes are differentially expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1007/BF00016072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez J., Sánchez-Martínez D., Stiefel V., Rigau J., Puigdomènech P., Pagès M. A gene induced by the plant hormone abscisic acid in response to water stress encodes a glycine-rich protein. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):262–264. doi: 10.1038/334262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. MAP kinase pathways in yeast: for mating and more. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak C., Kiegerl S., Lloyd C., Chan J., Hirt H. MMK2, a novel alfalfa MAP kinase, specifically complements the yeast MPK1 function. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Oct 25;248(6):686–694. doi: 10.1007/BF02191708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak C., Páy A., Bögre L., Hirt H., Heberle-Bors E. The plant homologue of MAP kinase is expressed in a cell cycle-dependent and organ-specific manner. Plant J. 1993 Apr;3(4):611–617. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.03040611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieber J. J., Rothenberg M., Roman G., Feldmann K. A., Ecker J. R. CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the raf family of protein kinases. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90119-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang V., Mantyla E., Welin B., Sundberg B., Palva E. T. Alterations in Water Status, Endogenous Abscisic Acid Content, and Expression of rab18 Gene during the Development of Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Hayashida N., Iwasaki T., Kamada H., Shinozaki K. Characterization of two cDNAs that encode MAP kinase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana and analysis of the possible role of auxin in activating such kinase activities in cultured cells. Plant J. 1994 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.5010111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T., Hayashida N., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Kamada H., Shinozaki K. ATMPKs: a gene family of plant MAP kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80852-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T., Irie K., Hirayama T., Hayashida N., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Matsumoto K., Shinozaki K. A gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is induced simultaneously with genes for a mitogen-activated protein kinase and an S6 ribosomal protein kinase by touch, cold, and water stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 23;93(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra S. S., Wolfraim L., Poole R. J., Dhindsa R. S. Molecular cloning and relationship to freezing tolerance of cold-acclimation-specific genes of alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):375–380. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy A. F., Sarhan F., Dhindsa R. S. Cold-Induced Changes in Freezing Tolerance, Protein Phosphorylation, and Gene Expression (Evidence for a Role of Calcium). Plant Physiol. 1993 Aug;102(4):1227–1235. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin K., Heino P., Palva E. T. Separate signal pathways regulate the expression of a low-temperature-induced gene in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):1061–1071. doi: 10.1007/BF00016077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pay A., Heberle-Bors E., Hirt H. An alfalfa cDNA encodes a protein with homology to translationally controlled human tumor protein. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jun;19(3):501–503. doi: 10.1007/BF00023399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz V., Fluhr R. Ethylene Signal Is Transduced via Protein Phosphorylation Events in Plants. Plant Cell. 1993 May;5(5):523–530. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.5.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Ferguson B., Sprague G. F., Jr Signal transduction and growth control in yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo S., Okamoto M., Seto H., Ishizuka K., Sano H., Ohashi Y. Tobacco MAP kinase: a possible mediator in wound signal transduction pathways. Science. 1995 Dec 22;270(5244):1988–1992. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5244.1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata W., Banno H., Ito Y., Hirano K., Irie K., Usami S., Machida C., Machida Y. A tobacco protein kinase, NPK2, has a domain homologous to a domain found in activators of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKKs). Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Feb 20;246(4):401–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00290443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafstrom J. P., Altschuler M., Anderson D. H. Molecular cloning and expression of a MAP kinase homologue from pea. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Apr;22(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00038997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Shinshi H. Transient Activation and Tyrosine Phosphorylation of a Protein Kinase in Tobacco Cells Treated with a Fungal Elicitor. Plant Cell. 1995 May;7(5):639–647. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.5.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usami S., Banno H., Ito Y., Nishihama R., Machida Y. Cutting activates a 46-kilodalton protein kinase in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8660–8664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Eller N., Gartner A., Vicente O., Heberle-Bors E. Isolation and characterization of a tobacco cDNA clone encoding a putative MAP kinase. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Nov;23(3):543–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00019302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K. A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell. 1994 Feb;6(2):251–264. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]