Full text
PDF

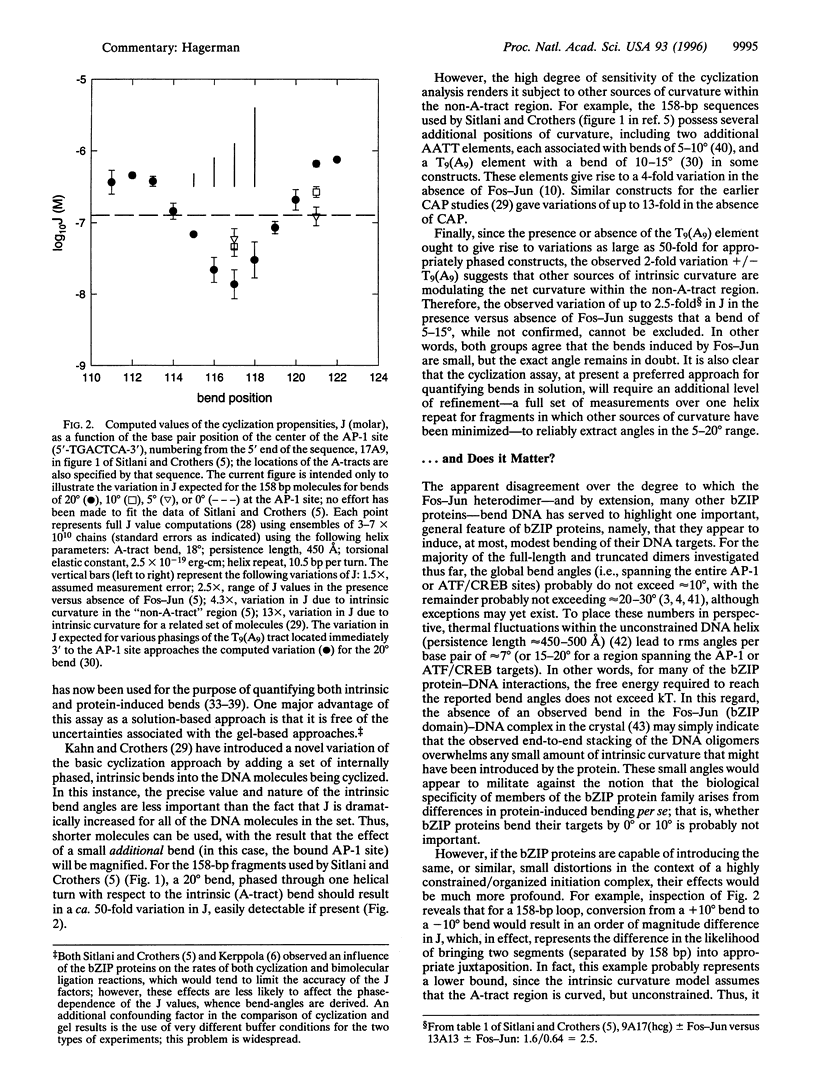

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cann J. R. Phenomenological theory of gel electrophoresis of protein-nucleic acid complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17032–17040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. O., Cann J. R. Extended theory of the electrophoretic mobility-shift analysis of nonspecific protein-DNA complexes, featuring cooperativity. Electrophoresis. 1996 Jan;17(1):12–19. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSantis P., Palleschi A., Savino M., Scipioni A. Theoretical prediction of the gel electrophoretic retardation changes due to point mutations in a tract of SV40 DNA. Biophys Chem. 1992 Feb;42(2):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(92)85004-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., McLaughlin L. W. DNA curvature in native and modified EcoRI recognition sites and possible influence upon the endonuclease cleavage reaction. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):823–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dripps D., Wartell R. M. DNA bending induced by the catabolite activator protein allows ring formation of a 144 bp DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Aug;5(1):1–13. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. N., Harrison S. C. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):257–261. doi: 10.1038/373257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Flexibility of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J., Ramadevi V. A. Application of the method of phage T4 DNA ligase-catalyzed ring-closure to the study of DNA structure. I. Computational analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90130-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Protein carpentry. Curr Biol. 1991 Apr;1(2):71–73. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90280-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges-Garcia Y., Hagerman P. J., Pettijohn D. E. DNA ring closure mediated by protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14621–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Protein-induced bending and DNA cyclization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Selective DNA bending by a variety of bZIP proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5479–5489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K. Fos and Jun bend the AP-1 site: effects of probe geometry on the detection of protein-induced DNA bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Sep 17;93(19):10117–10122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.19.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Burley S. K. 1.9 A resolution refined structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of TATAAAAG. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Sep;1(9):638–653. doi: 10.1038/nsb0994-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlarz D., Fritsch A., Buc H. Variations of intramolecular ligation rates allow the detection of protein-induced bends in DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):799–803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine B., Culard F., Maurizot J. C., Sautière P. The chromosomal protein MC1 from the archaebacterium Methanosarcina sp. CHTI 55 induces DNA bending and supercoiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3041–3045. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Frisch H. L. Why does the electrophoretic mobility of DNA in gels vary with the length of the molecule? Biopolymers. 1982 May;21(5):995–997. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. Ring closure probabilities for DNA fragments by Monte Carlo simulation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90381-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Understanding the anomalous electrophoresis of bent DNA molecules: a reptation model. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):396–399. doi: 10.1126/science.2756426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin O. J. Mobility of DNA in gel electrophoresis. Biopolymers. 1982 Nov;21(11):2315–2316. doi: 10.1002/bip.360211116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y., Shlyakhtenko L., Chernov B., Harrington R. E. DNA bending induced by Cro protein binding as demonstrated by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5331–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella D. N., Palmer C. R., Schepartz A. DNA targets for certain bZIP proteins distinguished by an intrinsic bend. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1130–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.8178171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Chow C. S., Lippard S. J. High-mobility-group 1 protein mediates DNA bending as determined by ring closures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitlani A., Crothers D. M. Fos and Jun do not bend the AP-1 recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. H., Hagerman P. J. Application of the method of phage T4 DNA ligase-catalyzed ring-closure to the study of DNA structure. II. NaCl-dependence of DNA flexibility and helical repeat. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Ellenberger T., Wobbe C. R., Lee J. P., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Folding transition in the DNA-binding domain of GCN4 on specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):575–578. doi: 10.1038/347575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




