Abstract
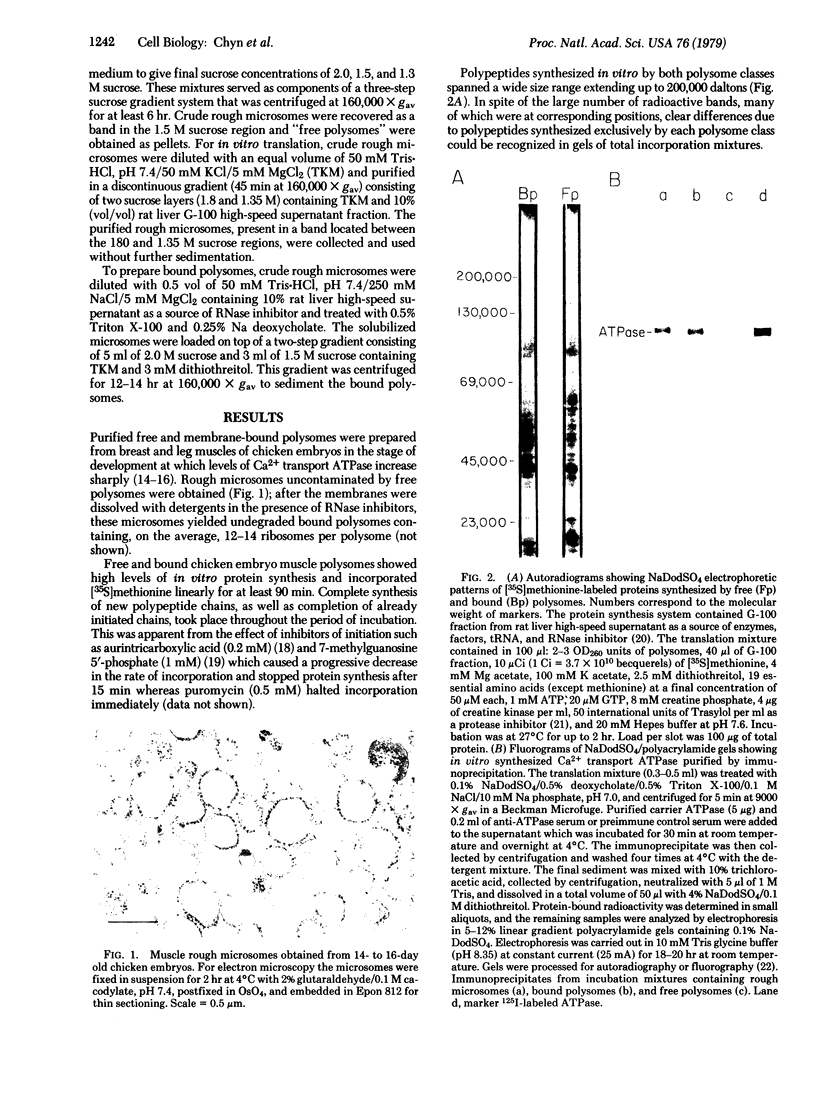
The calcium transport ATPase (Mr 100,000) from sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes was synthesized in a cell-free translation system containing rough microsomes or detergent-treated bound polysomes from 14- to 16-day old chicken embryo muscles. Immunoprecipitates obtained from total translation mixtures treated with anti-ATPase antiserum contained 1.5% of the total radioactivity incorporated in vitro. A polypeptide with the electrophoretic mobility, isoelectric point, and [35S]methionine-labeled tryptic peptide pattern of the mature ATPase was a major component of these immunoprecipitates. By contrast, free polysomes from the same source, which were capable of high levels of in vitro protein synthesis, did not yield immunoprecipitable ATPase. ATPase synthesized in rough microsomes was not released by treatment with 10 mM EDTA in a high-salt medium (0.5 M KCl) which removes ribosomes and peripheral membrane proteins. Furthermore, labeled ATPase remained associated with the microsomes after these were treated with low concentrations of deoxycholate (0.1 mg/mg of protein in 0.3 ml) which release the luminal content of the vesicles. Only with higher deoxycholate concentrations (0.5 mg/mg of protein in 0.3 ml), which cause membrane dissolution, was the labeled ATPase found on the detergent extracts. These observations indicate that newly synthesized ATPase discharged from bound ribosomes is transferred directly to the sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes where it is incorporated as an integral membrane protein.
Keywords: chicken embryonic muscle cells, integral membrane proteins, tryptic peptide map, membrane biogenesis
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Ribosome-membrane interaction. Nondestructive disassembly of rat liver rough microsomes into ribosomal and membranous components. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):206–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland R., Martonosi A., Tillack T. W. Developmental changes in the composition and function of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):612–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Membrane structure: some general principles. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):622–629. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Raff M. C. Mammalian plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):43–49. doi: 10.1038/258043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Ingram V. M. Structural studies on chick embryonic hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3960–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Blobel G., Model P. Detection of prokaryotic signal peptidase in an Escherichia coli membrane fraction: endoproteolytic cleavage of nascent f1 pre-coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. I. Structural and chemical differentiation in developing rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):73–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. II. Synthesis of constitutive microsomal enzymes in developing rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):97–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Baskin R. J. Ultrastructure of sarcoplasmic reticulum preparations. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):296–307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Kindt T., Scheele G., Blobel G. Homology in amino-terminal sequence of precursors to pancreatic secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan P. F., Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. IX. The permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):147–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisentraut A. M., Whissen N., Unger R. H. Incubation damage in the radioimmunoassay for human plasma glucagon and its prevention with "Trasylol". Am J Med Sci. 1968 Feb;255:137–142. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196802000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezerman E. B., Ishikawa H. Differentiation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and T system in developing chick skeletal muscle in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov 1;35(2):405–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen D. A., Armes L. G., Yasunobu K. T., Coon M. J. Amino-terminal sequence of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 from rabbit liver microsomes: similarity to hydrophobic amino-terminal segments of preproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):967–973. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., Marquardt J., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. A direct analysis of lamellar x-ray diffraction from hydrated oriented multilayers of fully functional sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):245–272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85547-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E. D., Weber L. A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis by 7-methylguanosine-5'-monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):19–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. A., Toneguzzo F., Rhee S. H., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and assembly of membrane glycoproteins: presence of leader peptide in nonglycosylated precursor of membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Harano T., Omura T. Biogenesis of the mitochondrial matrix enzyme, glutamate dehydrogenase, in rat liver cells. I. Subcellular localization, biosynthesis, and intracellular translocation of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1403–1416. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Mulligan R. C., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Pre-proparathyroid hormone: a direct translation product of parathyroid messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3731–3735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Debey P., Sabatini D. D. Selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. I. Permeability changes induced by low detergent concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):436–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. II. Electrophoretic and immunological characterization of microsomal subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):789–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Lingappa J. R., Prasad R., Ebner K. E., Blobel G. Coupled cell-free synthesis, segregation, and core glycosylation of a secretory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2338–2342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Seeman P., Iles G. H., Yip C. C. Membrane formation by the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2702–2710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Donley J., Halpin R. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. 3. The role of phospholipids in the adenosine triphosphatase activity and Ca++ transport. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Halpin R. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. X. The protein composition of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90455-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Membrane transport during development in animals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):311–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Roufa D., Boland R., Reyes E., Tillack T. W. Development of sarcoplasmic reticulum in cultured chicken muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):318–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. The protein composition of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 10;36(6):1039–1044. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Sawamura T., Morimoto T., Tashiro Y. Localization of nascent NADPH-cytochrome c reductase in rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 13;381(1):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Kuriyama Y. Role of rough and smooth microsomes in the biosynthesis of microsomal membranes. J Biochem. 1971 Apr;69(4):651–658. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PALADE G. E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. III. Its form and distribution in striated muscle cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Mar 25;3(2):269–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Walsh K. A. Ovalbumin: a secreted protein without a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):94–98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lodish H. F. Synchronised transmembrane insertion and glycosylation of a nascent membrane protein. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):775–780. doi: 10.1038/269775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Biologically and chemically pure mRNA coding for a mouse immunoglobulin L-chain prepared with the aid of antibodies and immobilized oligothymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Grollman A. P., Huang M. T. Aurintricarboxylic acid: inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan D., Aviv H., Leder P. Purification and properties of biologically active messenger RNA for a myeloma light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Yamamoto T., Tonomura Y. Molecular mechanism of active calcium transport by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jan;58(1):1–79. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Ghosh H. P. In vitro synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus membrane glycoprotein and insertion into membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):715–719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






