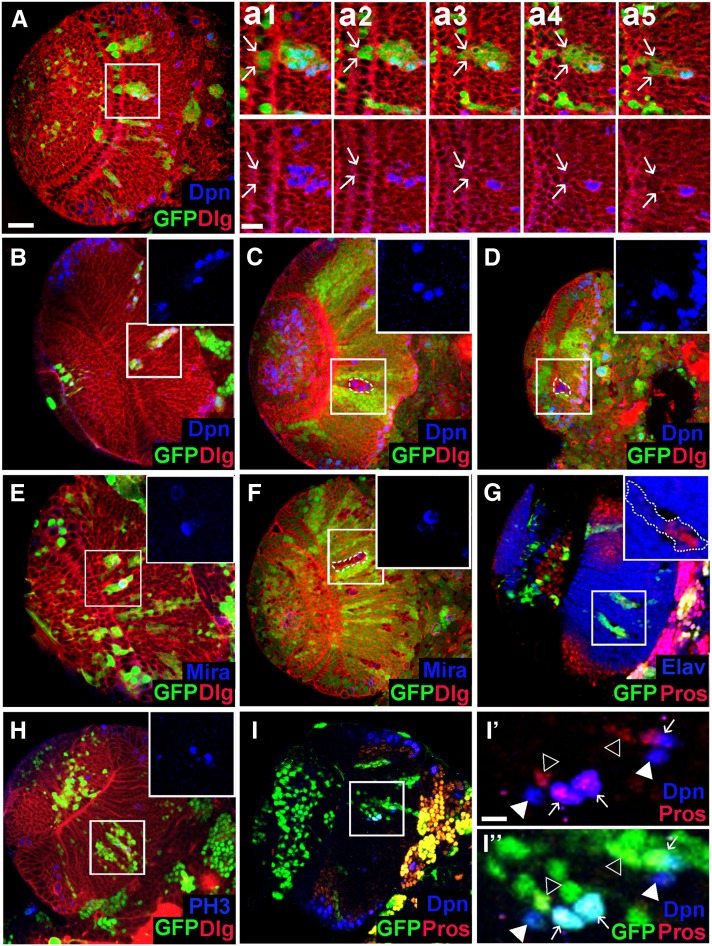
Figure 6.
Loss of Nop56 activity in cell clones leads to premature neuroepithelial differentiation into neuroblast. (A) A Nop56RNAi flip-out clone containing two to three NEs (indicated by arrows in a1 and a2) and a number of cells located in the medulla. a1–a5 show consecutive confocal sections of the mutant clone; arrows indicate the lateral edge of the clone. Several mutant cells in the medulla express Deadpan (Dpn). (B–D) Ectopic Dpn+ cells seen in Nop56RNAi clones (B) and Nop56G4900 clones (C and D) entirely localized in the medulla. (E and F) Mutant cells in a Nop56RNAi clone (E) or a Nop56G4900 clone (F) in the medulla undergo mitotic division with asymmetric polar localization of Miranda (Mira). (G) Mutant cells in a Nop56RNAi clone in the medulla express Prospero (Pros) or Elav. (H) Mutant cells in Nop56RNAi clones in the medulla undergo mitosis as detected by anti-phospho histone 3 (PH3) staining. (I, I′, I′′) Some Dpn+ cells in Nop56RNAi clones in the medulla express Prospero while other Dpn+ cells do not. Arrows in I′ and I′′ indicate coexpression of Dpn and Pros; arrowheads indicate expression of either Dpn or Pros. (A–I) Frontal view, lateral is to the left, medial to the right. Scale bar in A, 20 μm for A–I; scale bar in a1, 10 μm for a1–a5; scale bar in I′, 10 μm for I′ and I′′.