Abstract
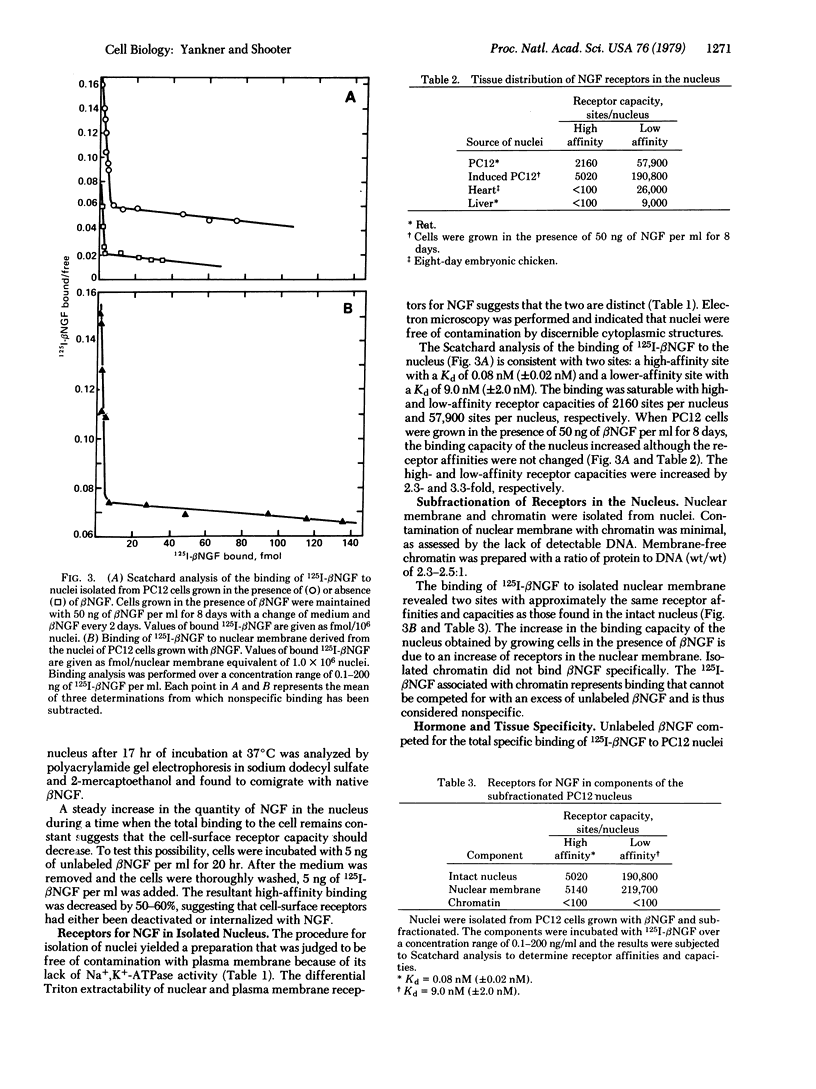
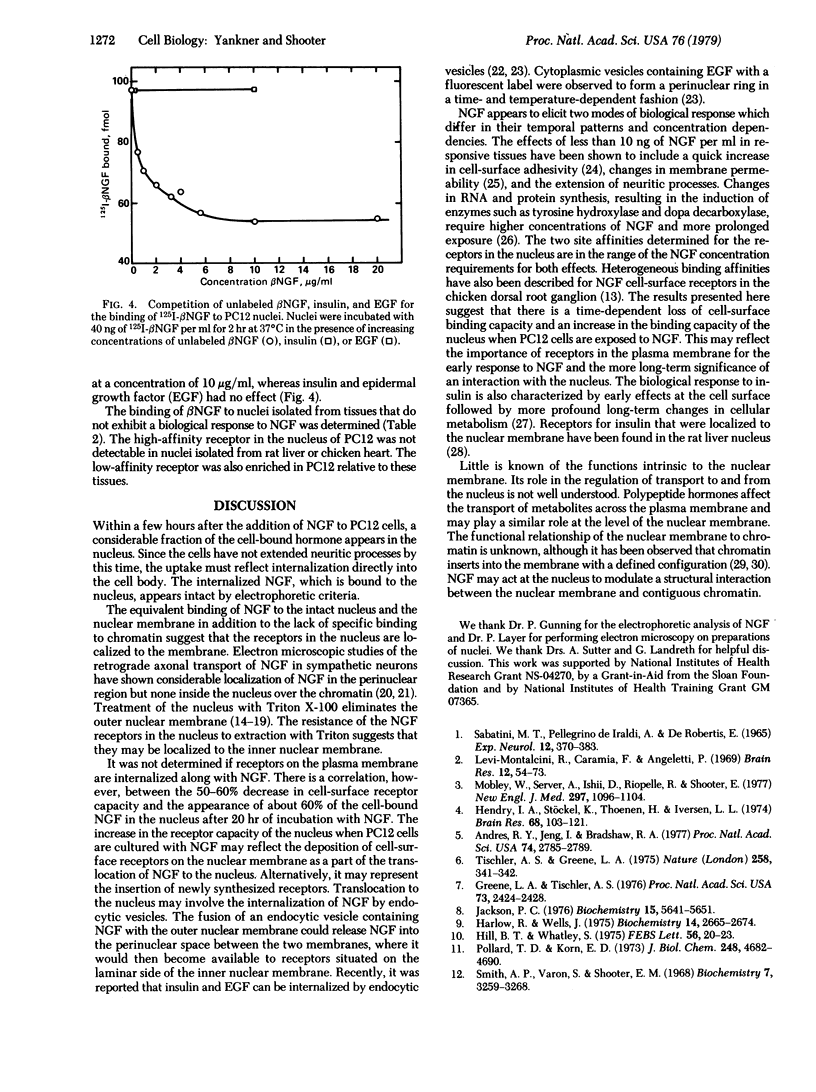
Cells of a continuous line of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) were incubated with 125I-labeled beta nerve growth factor (beta NGF), and at given time intervals the cell nuclei were isolated by a procedure that used the detergent Triton X-100. NGF was detectable in the nucleus after 20 min and continued to accumulate in a linear fashion for several hours after the total binding to the cell had reached steady state. After 17 hr at 37 degrees C, about 60% of the NGF bound to the cell was in the nucleus, NGF was not translocated to the nucleus at 4 degrees C. When nuclei were purified from PC12 cells and incubated with 125I-labeled beta NGF, specific binding sites were found. Binding was saturable and consistent with two sites: a high-affinity site with a Kd of 0.08 nM (+/- nM) and a lower-affinity site with a Kd of 9.0 nM (+/- 2.0 nM). The receptors in the nucleus were shown to be localized to the nuclear membrane. Membrane-free chromatin did not bind NGF specifically. The translocation of NGF to the nucleus was accompanied by a commensurate decrease in the cell-surface binding capacity. In the nucleus, however, the receptor capacities of both sites were increased when PC12 cells were grown in the presence of NGF.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Y., Jeng I., Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor receptors: identification of distinct classes in plasma membranes and nuclei of embryonic dorsal root neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Okada T. A. Association of chromatin fibers with the annuli of the nuclear membrane. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Oct;62(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Okada T. A. Condensation of chromosomes onto the nuclear membrane during prophase. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Dec;63(2):471–473. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYMER W. C., KUFF E. L. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI FROM MAMMALIAN TISSUES THROUGH THE USE OF TRITON X-100. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:359–363. doi: 10.1177/12.5.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Tencheva Z. S., Bojadjieva-Mikhailova A. G. Isolation and some characteristics of cell nuclei from brain cortex of adult cat. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):383–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J., Cohen S. Visualization by fluorescence of the binding and internalization of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow R., Wells J. R. Preparation of membrane-free chromatin bodies from avian erythroid cells and analysis of chromatin acidic proteins. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2665–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A., Stöckel K., Thoenen H., Iversen L. L. The retrograde axonal transport of nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 15;68(1):103–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. T., Whatley S. A simple, rapid microassay for DNA. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):20–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Z. I., Varon S. Nerve growth factor action on membrane permeation to exogenous substrates in dorsal root ganglionic dissociates from the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C. Polypeptides of the nuclear envelope. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 14;15(25):5641–5651. doi: 10.1021/bi00670a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Caramia F., Angeletti P. U. Alterations in the fine structure of nucleoli in sympathetic neurons following NGF-antiserum treatment. Brain Res. 1969 Jan;12(1):54–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Server A. C., Ishii D. N., Riopelle R. J., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1096–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba myosin. I. Isolation from Acanthamoeba castellanii of an enzyme similar to muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4682–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPOPORT D. A., FRITZ R. R., MORACZEWSKIA Biochemistry of the developing rat brain. I. Soluble enzymes in isolated neonatal brain nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 2;74:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI M. T., PELLEGRINODEIRALDI A., DEROBERTIS E. EARLY EFFECTS OF ANTISERUM AGAINST THE NERVE GROWTH FACTOR ON FINE STRUCTURE OF SYMPATHETIC NEURONS. Exp Neurol. 1965 Aug;12:370–383. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(65)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Whitlock C. Alteration of cellular adhesion by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4055–4058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M. E. Ultrastructural localization of a nerve growth factor-horseradish peroxidase (NGF-HRP) coupling product after retrograde axonal transport in adrenergic neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 8;130(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90857-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Thoenen H. Selective trans-synaptic migration of tetanus toxin after retrograde axonal transport in peripheral sympathetic nerves: a comparison with nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):459–474. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Varon S., Shooter E. M. Multiple forms of the nerve growth factor protein and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3259–3268. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Kettler R. Selective induction by nerve growth factor of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine- -hydroxylase in the rat superior cervical ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced process formation by cultured rat pheochromocytoma cells. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):341–342. doi: 10.1038/258341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D., Wong K. Y., Smith G. J., Pezzino V. The nuclear envelope. The major site of insulin binding in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2098–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



