Abstract
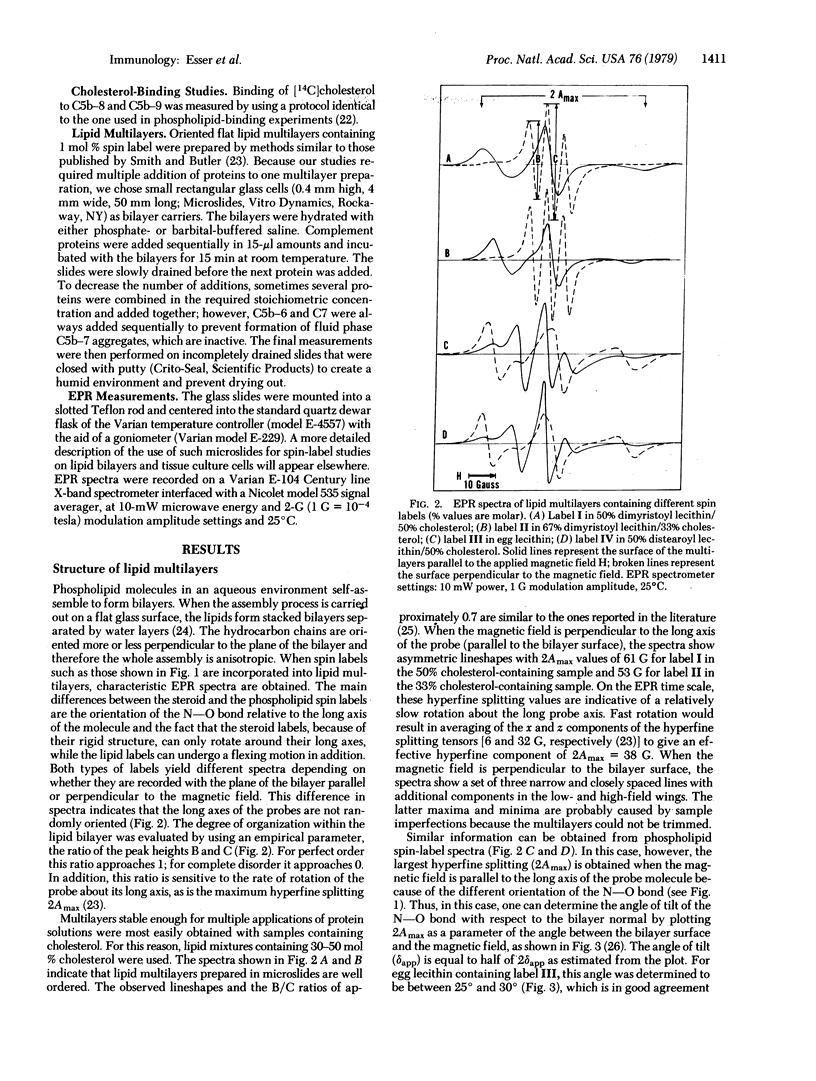
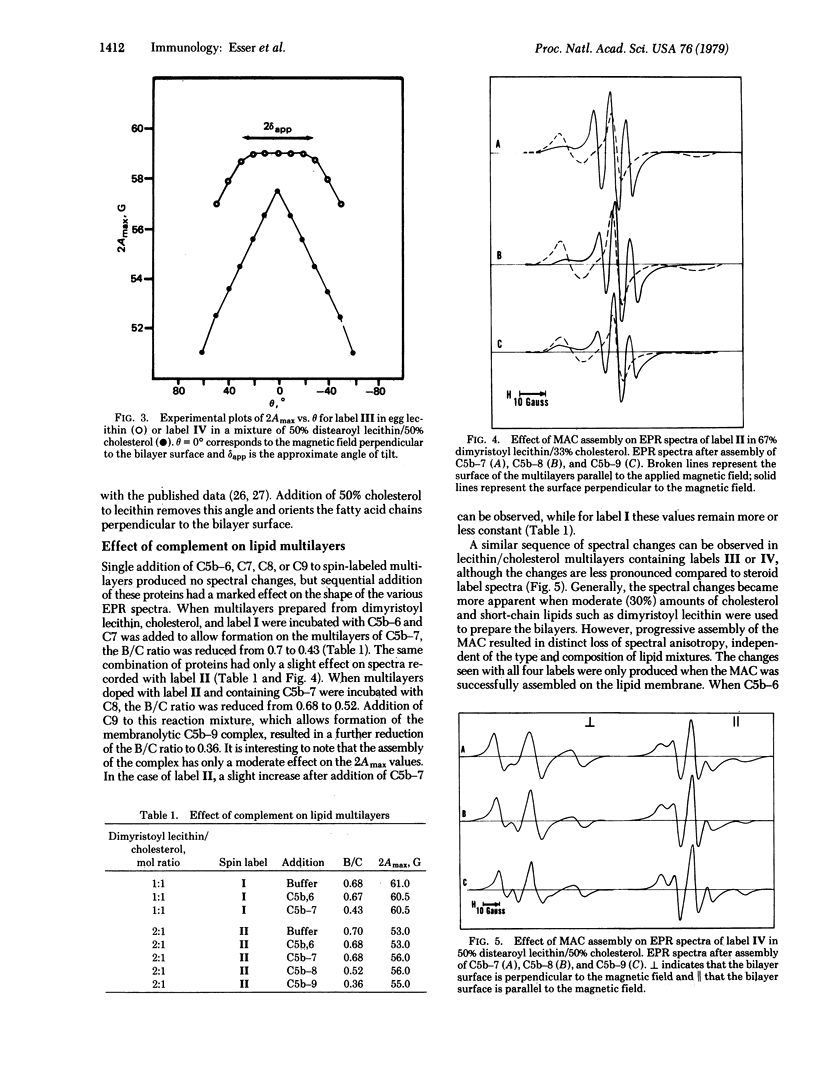
The interaction between the membrane attack complex (MAC) of complement and flat lipid bilayers was investigated. Using spin-labeled derivatives of phospholipids and cholesterol and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, we measured the penetration of the MAC into bilayers and its influence on the order of bilayers. The MAC precursor components C5b--6, C7, C8, and C9 did not exert any measurable influence on lipid membranes. Functional C5b--7 was shown to interact strongly with the bilayer surface without deep penetration into the bilayer. Formation of C5b--8 and especially C5b--9 caused a marked change in the anisotropy of spectra from probes located within the hydrocarbon phase. The spectral changes are not caused by changes in probe rotation and, in the case of the cholesterol probes, are not due to direct probe--protein interactions. For these reasons we interpret the spectral changes to be the result of reorientation of ordered bilayer lipids effected by strong binding of phospholipids to MAC proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birrell G. B., Griffith O. H. Angle of tilt and domain structure in dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine multilayers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok M. C., van der Neut-Kok E. C., van Deenen L. L., de Gier J. The effect of chain length and lipid phase transitions on the selective permeability properties of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Cornell B. A., Ellasz A. W., Perry A. Interactions of helical polypepetide segments which span the hydrocarbon region of lipid bilayers. Studies of the gramicidin A lipid-water system. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):517–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Levine R. P. Electron spin resonance studies on interaction of complement proteins with erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4930–4934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. A., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Kinsky S. C. Release of trapped marker from liposomes by the action of purified complement components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):290–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., McGill K. A., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. Annular lipids determine the ATPase activity of a calcium transport protein complexed with dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4145–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Bowyer D. E., Nicol P., Dawson R. M., Munn E. A. Studies on the terminal stages of complement lysis. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):135–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Bailey A. I., Wilkins M. H. Multilayers of phospholipid bimolecular leaflets. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):577–578. doi: 10.1038/220577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Knowles P. F. Evidence for phase boundary lipid. Permeability of Tempo-choline into dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles at the phase transition. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3570–3578. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. P., Giavedoni E. B., Dalmasso A. P. Complement-induced decrease in membrane mobility: introducing a more sensitive index of spin-label motion. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1196–1201. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland B. G., McConnell H. M. Bent fatty acid chains in lecithin bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Ohnishi S., Kitamura H., Inai S. Membrane fluidity change in erythrocytes induced by complement system. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4838–4843. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Jacobson K., Nir S., Isac T. Phase transitions in phospholipid vesicles. Fluorescence polarization and permeability measurements concerning the effect of temperature and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):330–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: reaction with C7, C8, C9. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):484–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: generation of high-affinity phospholipid binding sites by fusion of five hydrophilic plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Purification of the sixth and seventh component of human complement without loss of hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: formation, isolation, and inhibition of its activity by lipoprotein and the S-protein of human serum. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier-Muccillo S., Butler K. W., Smith I. C. Structural requirements for the formation of ordered lipid multibilayers--a spin probe study. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90456-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Conformation of protein in biological membranes and a model transmembrane channel. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:108–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Okamoto H., Sone N., Hirata H., Kagawa Y. Reconstitution of thermostable ATPase capable of energy coupling from its purified subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



