Abstract
Life extension by calorie restriction (CR) has been widely reported in a variety of species and remains on the forefront of anti-aging intervention studies. We report healthspan and survival effects of CR from a 23-year study in rhesus macaques conducted at the National Institute on Aging (NIA). CR initiated at older ages did not increase survival relative to Controls; however, CR monkeys demonstrated an improved metabolic profile and may have less oxidative stress as indicated by plasma isoprostane levels. When initiated in young monkeys, there was a trend (p=0.06) for a delay in age-associated disease onset in CR monkeys; but again, survival curves were not improved, in contrast to another study reported in the literature. This suggests that the effects of CR in a long-lived animal are complex and likely dependent on a variety of environmental, nutritional, and genetic factors.
Calorie restriction (CR) is often reported as the most robust non-genetic mechanism to extend lifespan and healthspan. Typically involving reductions of 10–40% in intake of a nutritious diet, the CR paradigm is frequently used as a tool to understand mechanisms that contribute to aging and age-associated diseases. In addition to lifespan, CR has also been reported to delay or prevent the occurrence of many chronic diseases in a variety of animals. Even without an extension in lifespan, any effect on improving function and delaying disease would be important. Beneficial effects of CR on outcomes such as immune function1, 2, motor coordination3, and resistance to sarcopenia4 in rhesus monkeys have recently been reported; however, the effect on survival remains an open question. An ongoing study at the Wisconsin National Primate Research Center (WNPRC) reported improved survival associated with 30% CR initiated in adult rhesus monkeys (7–14 years)5. We report here that a similar CR regimen implemented in young and older age rhesus monkeys at the National Institute on Aging (NIA) has not produced significant survival effects.
For over 20 years, the NIA study has documented the effects of CR in long-lived nonhuman primates, (Macaca mulatta, average lifespan in captivity is ~27 years and so-called maximal lifespan is ~40 years) to determine whether the results seen in lower organisms occur in monkeys and thus, might more plausibly translate to human aging6, 7. The NIA CR study began in 1987 at the NIH Animal Center in Poolesville, MD8. CR was initiated in monkeys of varying ages to evaluate the impact of age of onset of CR on its biological effects. Thus, monkeys of each sex were roughly divided into three age categories: Males were grouped as juvenile (1–2 years), adolescent (3–5 years), or old (16–23 years). Female monkeys were added to the study in 1992 as: juvenile (1–3 years), adult (6–14 years), and old (16–21 years)9. Data reported here for the NIA colony are grouped as either young-onset (includes juvenile, adolescent, and adult) or old-onset monkeys. See supplement Table 1 for census.
Monkeys were individually housed, and were matched within each sex for initial age, body size, and estimated food intake. Control (CON) monkeys were fed a meal twice a day based on their age and body weights. Food allotments for the CON monkeys were based on National Research Council guidelines and were considered to be approximately ad libitum (AL) since they often left a few uneaten biscuits at each meal that were subsequently removed; they did not have continual access to food. Allotments were increased for the young monkeys as they matured and grew in order to keep the CONs at approximately AL levels. CR monkeys were provided 30% less food than sex-, age- and initial body size-matched CONs. Food allotments were kept constant after all monkeys had reached adulthood (approximately 10 years old). A significant age-related decline in energy intake was already reported for all monkey groups (CON and CR, male and female) so that by age 26 years, CR males were eating only ~20% less than their matched CONs and CR females 12% less than matched CONs9. The age associated decline in food intake is not unusual, a similar decline was observed in the WNPRC study, and after 15 years, the difference between CON and CR males was only 17%10. Food intake estimates for age-matched monkeys at both NIA and WNPRC are reported in Table 1 and have been previously reported9, 11.
Table 1.
Body weight and food intake estimates
| Body Weight | Food Intake | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||
| Sex | Age (yrs) | Diet | NIA body wt (kg ± SEM) | % change in weight | WNPRCb body wt (kg ± SEM) | % change in weight | NIAa kcal/day | % restriction | WNPRCb kcal/day | % restriction |
| Male | 17 | CON | 13 ± 0.9 | 15 ± 0.5 | 720 | 840 | ||||
| CR | 9.7 ± 0.5 | −25.40% | 11 ± 0.4 | −26.70% | 533 | −25.9% | 640 | −23.8% | ||
| Male | 21 | CON | 12.6 ± 0.9 | 14 ± 0.3 | 664 | 720 | ||||
| CR | 9.9 ± 0.6 | −21.40% | 10 ± 0.2 | −28.60% | 507 | −23.6% | 548 | −21.9% | ||
| Female | 17 | CON | 7.3 ± 0.5 | 9 ± 0.2 | 520 | 621 | ||||
| CR | 6.5 ± 0.4 | −11% | 8 ± 0.2 | −11% | 404 | −22.3% | 474 | −23.7% | ||
extracted from mixed model data reported in Mattison et al. 2005 (9)
data reported in Raman et al. 2007 (11)
Any animal that died underwent a complete necropsy by a board-certified pathologist. A gross description of the pathology related to each organ was provided along with the probable cause of death and any contributing factors. An exact cause of death was not always evident and, in some cases, more than one contributing factor was noted. In these cases, the predominant factor listed on the gross pathology report was listed as the cause of death. Survival data were analyzed in two ways: all-cause mortality and age-related deaths. This distinction for cause of death was also reported by Colman et al.5. In both studies (NIA and WNPRC), age-related survival excluded deaths due to acute conditions that do not have an age-related increase in risk such as gastrointestinal bloat, anesthesia, injury, or endometriosis.
Old-onset CR
Old-onset CR monkeys (16–23 years) did not live longer than CONs in either the all-cause (Fig. 1) or age-related survival analysis (there were 3 cases of non-age related deaths in the CR group and 2 in the CON group, graph not shown). In this group, males had significantly longer survival compared to females (p = 0.0003) and neither sex benefitted from CR. To date, four CR monkeys and one CON from the old-onset group have lived beyond 40 years. Although CR has not increased mean or maximum lifespan relative to CON, 50% survival for the females is 27.8 years and 35.4 years for the males, exceeding the ~27 year median lifespan previously reported for monkeys in captivity12. These monkeys may have benefitted from improved husbandry conditions and thus CR started at older ages provided no additional increase in survival. Furthermore, there were no apparent differences in causes of death between the two diet groups. Neoplasia, cardiovascular disease, amyloidosis, and general organism deterioration in the oldest animals were equally represented in both diet groups. In the old-onset CR group there were also two deaths due to pneumonia and 2 CONs that died from complications of diabetes. Additional pathology details are in the supplemental documents.
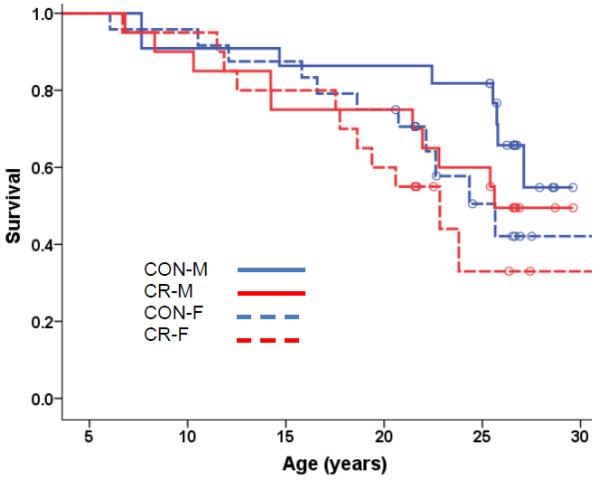
Fig 1.
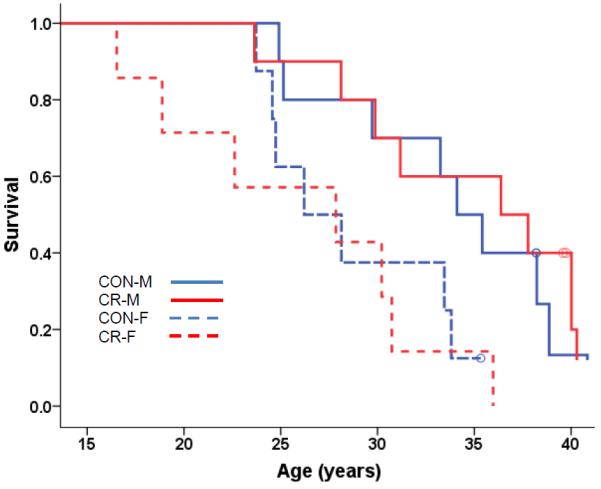
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for All-Cause Mortality for Old-Onset Monkeys. All-cause mortality in the old-onset monkeys was analyzed using Cox regression with age of onset, sex, and diet as predictors. The effect of Diet was not significant (p = 0.934) and Sex was the only significant predictor (p =0.003), therefore Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the four (diet-by-sex) groups were plotted to display the results. Open circles represent monkeys that are still alive.
Old-onset CR was beneficial on several measures of metabolic health and overall function. Both male and female CR monkeys weighed less than the CON counterparts, although the diet effect was greater in the males (Fig. 2a). In longitudinal measures from serum of fasted monkeys, triglycerides, cholesterol, and glucose levels increased with age for both male and female CONs. However, CR significantly lowered triglycerides [F(1,21) = 5.76, p = 0.026] (Fig. 2b); cholesterol remained significantly lower in the CR males (Fig. 2c) [F(40,774) = 1.53, p = 0.02]. At the oldest ages, fasting glucose was numerically lower in the CR monkeys (Fig. 2d) and significantly lower in CR males compared to CONs (p = 0.04). On a single measure of plasma free isoprostane, an indicator of oxidative stress, CON males had significantly higher levels than the CR monkeys (23.24 ±1.25 vs 15.93 ±1.97 pg/ml; p= 0.009). In contrast, we previously reported that old-onset CR may negatively affect immune function as evident in a decreased T-cell proliferative capacity and trends toward a worsening immune phenotype and function13. Despite many improvements in health and function, we did not observe any changes in survival.
Fig 2A.
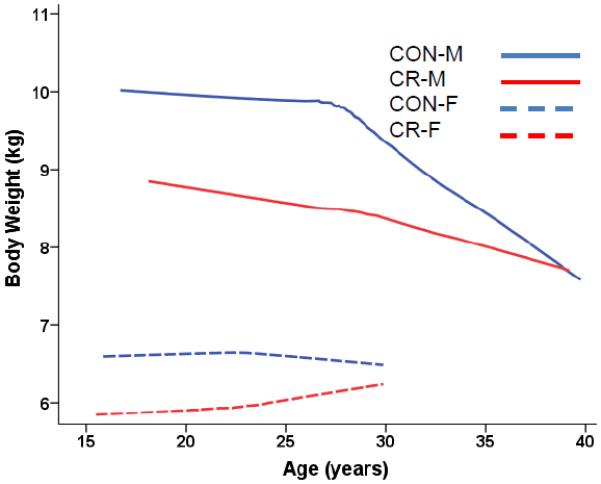
Body weight (kg) predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for CR and CON monkeys (Old-onset). There were significant changes in body weight over time [F(20,311) = 2.52, p = 0.0004]. There was a significant main effect for Sex [F(1,29) = 21.11, p < 0.0001] with males being substantially heavier. Also there were significant Sex-by-Year [F(18,311) = 2.96, p < 0.0001] and Diet-Sex-Year interactions [F(17,311) = 2.37, p = 0.0019] with reductions in body weight due to CR being more prevalent for the male animals. Solid lines represent males; dashed lines represent females. Overall body weight trajectories were based 420 observations for 34 monkeys (84 observations for 8 CON-F; 145 for 10 CON-M; 57 for 7 CR-F; 134 for 9 CR-M). For ages 15–20 years, there were: 12 observations for 5 CON-F; 17 for 7 CON-M; 9 for 5 CR-F; 7 for 4 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 38 observations for 8 CON-F; 42 for 10 CON-M; 21 for 5 CR-F; 34 for 8 CR-M. For ages 25–30 years, there were: 21 observations for 5 CON-F; 40 for 8 CON-M; 20 for 4 CR-F; and 41 for 8 CR-M. For ages > 30 years, there were: 46 observations for 8 CON-M; 52 for 6 CR-M and too few to plot for the females. One CR Male that weighed over 14 kg at the start of the experiment had undue influence on the average trend lines for CR Males and therefore the first 5 observations of his data were not used to construct the plot; however, the omission of these observations had virtually no influence on the results of the statistical analyses.
Fig 2B.
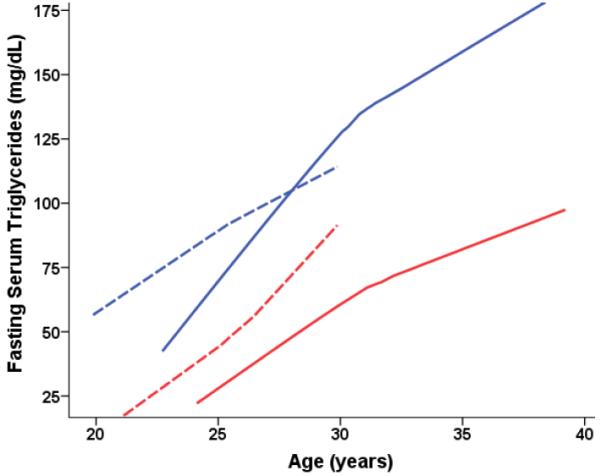
Fasting serum triglycerides (mg/dL) predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for Old-onset CR and CON monkeys. Triglyceride levels increased with age [F(16,162) = 2.12, p = 0.0096] and CR monkeys had significantly lower levels than CON [F(1,21) = 5.76, p = 0.026]. Overall triglyceride trajectories were based 249 observations for 34 monkeys (50 observations for 6 CON-F; 87 for 8 CON-M; 32 for 4 CR-F; 80 for 8 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 16 observations for 5 CON-F; 10 for 6 CON-M; 5 for 3 CR-F; 3 for 3 CR-M. For ages 25–30 years, there were: 21 observations for 5 CON-F; 32 for 7 CON-M; 20 for 4 CR-F; 27 for 7 CR-M. For ages > 30 years, there were: 45 observations for 7 CON-M; 50 for 6 CR-M and too few to plot for the females.
Fig 2C.
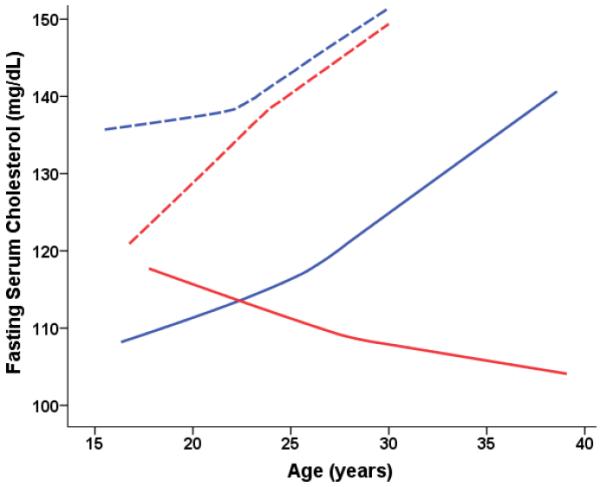
Cholesterol predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for Old-onset CR and CON monkeys. Cholesterol levels increased with age [F(53,774) = 1.54, p = 0.009], and male monkeys had significantly lower levels than females [F(1,24) = 23.60, p < 0.0001]. A significant 3-way Diet-Sex-Age interaction [F(40,774) = 1.53, p = 0.02] indicated that cholesterol levels increased with age for CON males while CR males tended to have a slight reduction in cholesterol. Thus, at older ages (> 30 years), CR male monkeys have significantly lower cholesterol levels as compared to CONs. Overall cholesterol trajectories were based on 994 observations for 28 animals (204 observations for 7 CON-F; 301 for 7 CON-M; 134 observations for 5 CR-F; and 355 observations for 9 CR-Male). For ages 15–20 years, there were: 48 observations for 6 CON-F; 65 observations for 6 CON-M; 21 observations for 4 CR-F; and 32 observations for 4 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 91 observations for 5 CON-F; 102 observations for 7 CON-M; 62 observations for 5 CR-F; and 118 observations for 8 CR-M. For ages 25–30 years, there were: 41 observations for 5 CON-F; 70 observations for 6 CON-M; 39 observations for 4 CR-F; and 101 observations for 8 CR-M. For ages > 30 years, there were: 64 observations for 6 CON-M; and 104 observations for 7 CRM; and too few to plot for the females.
Fig 2D.
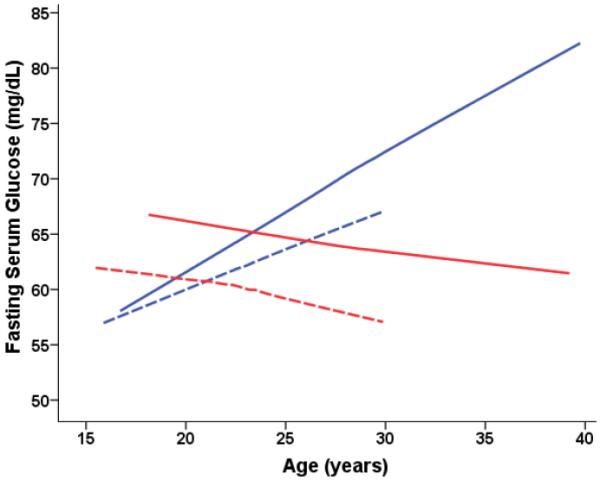
Fasting serum glucose (mg/dL) levels predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for Old-onset CR and CON monkeys. Five glucose measurements above 100mg/dL for one diabetic CON-M were omitted to remove the influence of these outliers on the analyses and graphs. There were significant changes in glucose over time [F(20,285) = 10.48, p < 0.0001] and males and females were significantly different in the trends over time [F(18,285) = 3.58, p < 0.0001] with males having increases in glucose levels over time whereas the glucose levels of the females slightly decreased. The overall CR difference was not significant, F(1,22) = 1.18, p = 0.288, and the CR differences in trend over time were not significant, F(20,285) = 1.23, = 0.2259. Additional analyses stratified by sex conditions showed that CON males had significantly higher glucose levels compared to CR males, F(1, 14) = 5.27, p = 0.04. Overall glucose trajectories were based 387 observations for 34 monkeys (79 observations for 7 CON-F; 131 for 8 CON-M; 48 for 4 CR-F; 129 for 8 CR-Male). For ages 15–20 years, there were: 12 observations for 5 CON-F; 17 for 7 CON-M; 2 for 2 CR-F; 6 for 3 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 33 observations for 7 CON-F; 39 for 8 CON-M; 19 for 4 CR-F; 30 for 7 CR-M. For ages 25–30 years, there were: 21 observations for 5 CON-F; 35 for 7 CON-M; 20 for 4 CR-F; 41 for 8 CR-M. For ages > 30 years, there were: 45 observations for 7 CON-M; 52 for 6 CR-M; and too few to plot for the females.
Young-onset CR
Current survival curves for the young-onset male and females are shown in Fig. 3a (all-cause mortality) and Fig. 3b (age-related mortality). No significant diet effects are noted in survival between these groups of CON and CR monkeys for either analysis. Statistical control in the analysis was made for sex and source of the monkey (See supplemental documents for details). Of the original 86 monkeys in the young-onset cohorts, 24% (11/46) of the CON animals and 20% (8/40) of the CR group died of age-related causes. The NIA findings contrast with the adult-onset study at WNPRC that demonstrated a beneficial CR effect in which 37% (14/38) of the CON monkeys had died from age-related causes compared to only 13% (5/38) in the CR group. When accounting for all deaths in the young-onset NIA colony, the trend persisted with 9 CON and 13 CR animals dying of non-age related causes. Survival probabilities for all NIA age groups combined are shown in Supplement Fig. 1a, b.
Fig 3A.
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for All-Cause Mortality for Young-Onset Monkeys. All-cause mortality in the young-onset monkeys was analyzed using Cox regression with age of onset, origin, sex, and diet (p = 0.255) as predictors with none of these factors being statistically significant. Therefore Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the two diet groups were plotted to display the results. Open circles represent monkeys that are still alive.
Fig 3B.
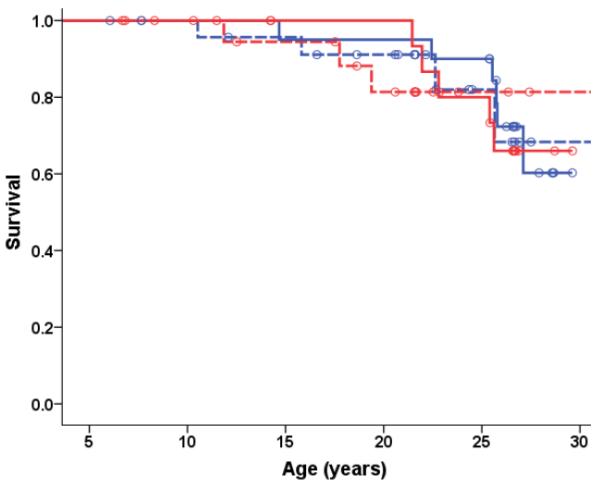
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for Age-Related Mortality for Young-Onset Monkeys. Age-related mortality in the young-onset monkeys was analyzed using Cox regression with age of onset, origin, sex, and diet (p = 0.975) as predictors with none of these factors being statistically significant. Therefore Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the two diet groups were plotted to display the results. Open circles represent monkeys that were censored as non-age related deaths or are still alive.
Considering that just less than 50% of young monkeys are still alive, these data do not represent final lifespan curves in this study. Based on lifespan projections using the hazard function14, most animals are projected to be dead 10 years from now and the estimated probability statistics indicates a likelihood of less than 0.1% chance that the overall survival outcome would favor the CR group. The probability that a significantly different effect on mean survival will emerge in the next 5–10 years of the study is very low; however, a potential effect on maximum lifespan has not been ruled out.
As there is a clear difference in CR effect on mortality between the colonies at NIA and WNPRC, further comparisons of these two longitudinal studies are warranted and planned. In an estimate of NIA's current data (as of 12/1/2011) to the published WNPRC data summarized as of 2/22/08 and reported in Colman et al.5, NIA monkeys, both CON and CR, may have a lifespan advantage comparable to the WNPRC CR monkeys.
Although they eat less (Table 1) and weigh less9, young-onset CR monkeys lack many of the expected CR benefits. Fasting serum glucose levels were not significantly lower in the CR monkeys compared to CON (Fig. 4a), and only the CR males had somewhat lower triglycerides compared to respective CONs (p = 0.051) (Fig. 4b). We have shown in two reports an improved immune response in young-onset CR monkeys. In the first, Messaoudi et al. showed that adolescent-onset CR monkeys had a better maintenance of naïve T cells and T cell receptor repertoire diversity, as well as a reduced production of inflammatory cytokines2. However, as with old-onset CR, beneficial effects were not apparent in the juvenile-onset cohort. We previously reported the protective effect of CR in all young-onset monkeys in a ligature-induced model of inflammation in the oral cavity1. At baseline, scores for standard dental clinical measures were similar between CON and CR monkeys; both diet groups were healthy. However, when challenged by induction of periodontitis, CR monkeys had significantly less deterioration, inflammation, bleeding, and attachment loss than the CONs1. In contrast, CR rodents challenged by an influenza15, bacterial16, and parasitic17 infection experienced detrimental effects despite reports of overall improvement on many immune parameters18.
Fig. 4A.
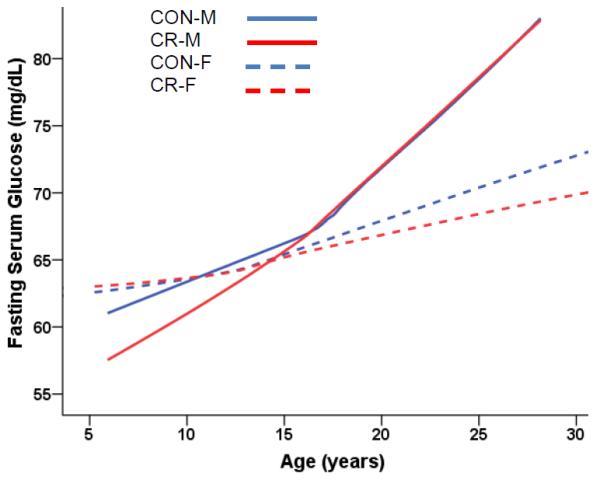
Fasting serum glucose (mg/dL) levels predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for young-onset CR and CON monkeys. 14 glucose measurements above 100mg/dL in diabetic monkeys (7 observations for 3 CON-M; 5 for 2 CR-M; 2 for 1 CON-F) were omitted to remove the influence of these outliers on the analyses and graphs. There were significant changes in glucose over time [F(18,1112) = 11.24, p < 0.0001], and males and females were significantly different in the trends over time [F(18,1112) = 1.98, p = 0.0088] with males having a larger increase in glucose levels over time. There was no significant difference due to diet group. Solid lines represent males; dashed lines represent females. Overall glucose trajectories were based 1260 observations for 81 monkeys (346 observations for 23 CON-F; 350 for 20 CON-M; 281 for 20 CR-F; 283 for 19 CR-M). For ages < 5 years, there were: 23 observations for 8 CON-F and 22 observations for 9 CR-F; data for males < 5 years was not available. For ages 5–10 years, there were: 71 observations for 18 CON-F; 55 for 19 CON-M; 65 for 16 CR-F; 48 for 15 CR-M. For ages 10–15 years, there were: 93 observations for 20 CON-F; 100 for 20 CON-M; 79 for 17 CR-F; 85 for 18 CR-M. For ages 15–20 years, there were: 95 observations for 20 CON-F; 95 for 19 CON-M; 75 for 16 CR-F; 75 for15 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 53 observations for 17 CON-F; 85 for 18 CON-M; 30 for 12 CR-F; 64 for 15 CR-M. For ages > 25 years, there were: 13 observations for 6 CON-F; 22 for 12 CON-M; 10 for 2 CR-F; 16 for 11 CR-M.
Fig 4B.
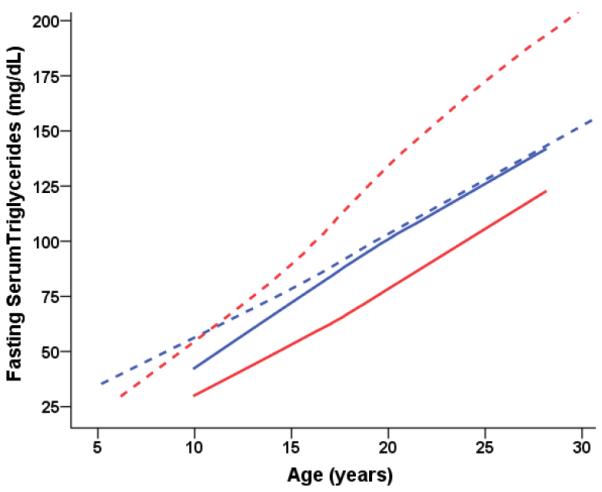
Fasting serum triglycerides (mg/dL) predicted from age-dependent individual-specific trajectories for young-onset CR and CON monkeys. There were significant changes in triglycerides over time [F(14,843) = 17.59, p < 0.0001] and males and females were significantly different in the trends over time [F(14,843) = 5.36, p < 0.0001]. Furthermore, there was a Diet-by-Sex interaction indicating that the overall effect of CR on triglycerides was significantly different for male and female monkeys [F(1,68) = 5.07, p = 0.0276]. Specifically, CR males had lower triglycerides than CON males. By contrast, CR females had higher triglyceride levels than CON females. Overall triglyceride trajectories were based 973 observations for 81 monkeys (266 observations for 23 CON-F; 280 for 20 CON-M; 213 for 20 CR-F; 14 for 19 CR-M). For ages < 10 years, there were: 32 observations for 9 CON-F; 30 for 8 CR-F; data for males < 10 years was not available. For ages 10–15 years, there were: 76 observations for 18 CON-F; 77 for 20 CON-M; 71 for 16 CRF; 58 for 16 CR-M. For ages 15–20 years, there were: 91 observations for 20 CON-F; 95 for 19 CON-M; 72 for 16 CR-F; 75 observations for 15 CR-M. For ages 20–25 years, there were: 55 observations for 17 CON-F; 86 for 18 CON-M; 30 for 12 CR-F; 65 for 15 CR-M. For ages > 25 years, there were: 12 observations for 5 CON-F; 22 for 12 CON-M; 10 for 2 CR-F; 16 for 11 CR-M.
The incidence of cancer was dramatically improved in young-onset CR monkeys, in fact, neoplasia has not been identified in any monkey from this group (Fig. 5a). In contrast, 5 of the 6 cases in young-onset CON monkeys were considered the cause of death with a mean age at diagnosis of 22.8 ±1.7 years. The incidence was similar between the CON and old-onset CR groups indicating that early intervention may be necessary to have an impact on cancer. Colonic carcinomas were the most common in all the monkeys. Other cancers included: hepatocellular and thyroid carcinomas, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, fibrosarcoma, lymphoplasmacytic leukemia, basal squamous cell carcinoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, esophogeal squamous cell carcinoma, renal and adrenal adenoma.
Fig 5A.
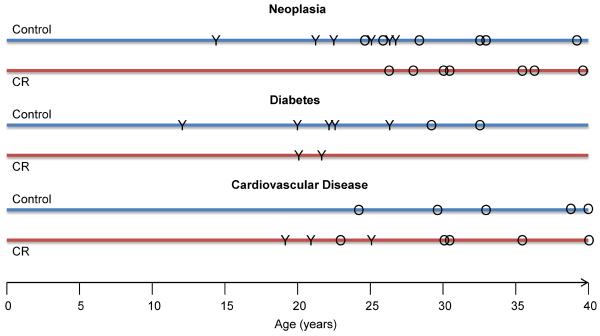
Incidence of three major age-related conditions. “Y” represents an occurrence in a young-onset monkey and “O” indicates an old-onset monkey at the age of diagnosis. Animals may be represented more than once if multiple conditions existed. All cardiac conditions were diagnosed at necropsy and were either the cause of death or a significant pathological finding in addition to the immediate cause of death.
Glucoregulatory function is also improved in CR monkeys (Fig. 5a). However, 2 cases of diabetes have been diagnosed in CR monkeys; thus, the prevention of obesity did not prevent the occurrence of insulin-dependent diabetes and further investigation of the etiology of such cases is of interest. Interestingly, CR did not reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease as was reported in the WNPRC colony; however, our findings were based on tissue pathology since these diagnoses were identified after death.
An analysis of first occurrence of age-related disease was done on the NIA monkeys using the same disease criteria as defined by the WNPRC study. These conditions included: cancer, diabetes, arthritis, diverticulosis, and cardiovascular disease. Although age-related diseases were detected in CON monkeys at an earlier age than in CR monkeys, the incident curves were not significantly different at this time (p=0.06) (Fig. 5b).
Fig 5B.
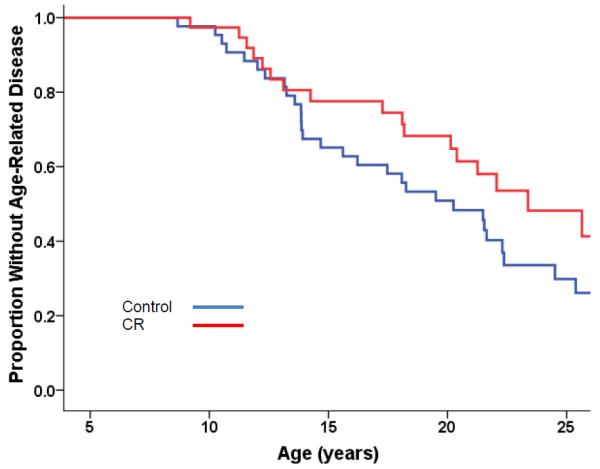
Estimated proportions for the first occurrence of any age-related disease in each monkey from the young-onset age group (males and females combined) statistically controlling for sex of the animal and sex-by-CR interaction. These conditions included: cancer, diabetes, arthritis, diverticulosis, and cardiovascular disease. The difference between CON and CR is not statistically significant, p=0.06. Old-onset monkeys are not represented.
In many reports emerging over years, both NIA and WNPRC have extensively documented beneficial health effects of CR in these two apparently parallel studies. Additionally, Bodkin et al. reported in a preliminary study with a small number of CR monkeys that survival was improved compared to AL-fed controls19. In 2009, Colman et al. reported that the positive effects of CR implemented in adulthood decreased mortality due to age-related deaths5. The implications of this finding were important as it extended CR findings beyond the laboratory rodent and to a long-lived primate. By contrast, CR appears to have had no significant effect on survival in the NIA colony. Considering that these two projects maintain high quality veterinary support in comparable experimental settings, study the same species of primates, and test the same intervention, what could account for the differences in survival outcome?
A notable difference between the two studies is the composition of the monkey diets. The NIA-1-87 formulation (Labdiet, PMI Nutrition International, LLC, Brentwood, MO) has a natural ingredient base while WNPRC's diet is purified (Harlan Teklad, Madison, WI). Although natural ingredient diets risk having some variation between batches, they contain components that may impact health such as phytochemicals, ultra trace minerals, and other unidentified elements; yet some consider them to be more complete and possibly better for long-term studies 20. In purified diets, each ingredient supplies a specific nutrient and each required mineral and vitamin is added as a separate component.
Additional differences between the two diets include the source of nutrients. Protein sources for the NIA study include wheat, corn, soybean, fish, and alfalfa meal, whereas the WNPRC diet protein source was lactalbumin. The NIA study diet also contains flavonoids, known for their antioxidant activity and specifically, isoflavones with estrogenic activity, which may contribute to decreased arterial stiffness21, 22. Fat content of the NIA study diet was derived from soy oil and the oils from the other natural ingredients (i.e. corn, wheat, and fish). Fish meal contains approximately 8–12% fat and is rich in omega-3 fatty acids. The WNPRC study dietary fat was derived from corn oil. Carbohydrate content was also strikingly different; although both diets have 57–61% carbohydrate by weight, the NIA study diet was comprised primarily of ground wheat and corn, while the WNPRC study diet contained corn starch and sucrose. Indeed, the WNPRC diet was 28.5% sucrose, while the NIA study diet was only 3.9% sucrose. This latter point may be particularly important as a diet high in sucrose can contribute to the incidence of type II diabetes23, 24.
The NIA and WNPRC studies also had different approaches to vitamin and mineral supplementation to ensure that the CR monkeys received 100% of the recommended daily allowance. The NIA study used one diet for both CR and CON monkeys, which was supplemented with an additional 40% of the daily-recommended allowance. Thus, the NIA diet formulation super-supplemented the CON monkeys. The WNPRC study fed two different diets and only the CR monkeys were supplemented. Despite numerous attempts, it has not been established whether vitamin, mineral, and thus antioxidant intake beyond those naturally found in a healthy diet or the recommended levels has any additional protective effects. In fact, data suggest that supplementation has benefited specific pathologies25, 26 but also increased mortality26.
Another important difference in study design is that the NIA study CON monkeys were not truly fed AL, unlike the WNPRC study. The regulated portioning of food for the NIA CON monkeys may be a slight restriction and thus, largely prevented obesity. Rodents can benefit from even a moderate 10% CR; rats lived significantly longer than those fed AL as reported by Duffy et al.27. Survival was increased at all levels of CR (10, 25, and 40%) compared to AL. The NIA CON monkeys may experience survival benefits similar to the 10% restriction reported in the rodent data.
Calorie restriction effectively lowered body weight in the NIA and WNPRC monkeys (Table 1)9, 11. Female monkeys were more resistant to weight loss despite a comparable level of restriction9; this effect was evident in both studies. The effect of CR on body weight was slightly greater in WNPRC males compared to age-matched NIA males despite a comparable restriction level. However, overall WNPRC monkeys ate more and weighed more than matched NIA monkeys. At 17 years of age, WNPRC males weighed approximately 12% more than corresponding NIA males and the difference was approximately 18% for the females.
It has been suggested that lifespan extension by CR might be a laboratory phenomenon and thus might not extend lifespan in nonhuman primates simply because“control” animals are overfed28; CR merely optimizes survival to what might be expected under non-laboratory conditions29, 30. In a study of Wistar rats, Wang et al. reported that the effect of CR on mortality was dependent on more than body weight31. They calculated that only 11% of the CR effect was due to changes in weight; other variables, some likely correlated to weight, contributed to the majority of the CR effect on mortality. Additionally, CR in genetically obese ob/ob mice extended their lifespan beyond both normal and CR wild type mice despite a high level of body fat32. Moreover, short-term CR in adult (>18 years) rhesus monkeys improved glucoregulatory markers prior to changes in body composition33. Certainly more research is needed to understand the connection between body weight loss and the mechanisms of CR.
NIA monkeys originated from both China and India, and have greater genetic diversity compared to the strictly Indian colony at WNPRC. In comparison, a study of 41 recombinant inbred mouse strains demonstrated that CR had different effects on lifespan, CR induced shortening of lifespan in approximately a third of them34; thus, genetic components influenced the outcome. Similarly, in genetically heterogeneous wild-caught mice, although hormonal effects common in laboratory rodents were reported and the loss in body mass was approximately 50%, there was no overall mean survival effect of CR30. Although the basis for the strikingly different lifespan response in rhesus monkeys is unclear, it is apparent that the effect of CR is not straightforward, and genetic differences may play a larger role than has been considered to date. A final analysis which includes all monkeys and controls for genetic origin can address this confounding variable.
Lastly, as in rodent studies35, the age of onset of the CR regimen for the two studies could certainly impact survival outcome as it has other measures. CR initiated in the youngest male monkeys delayed maturation36 and slowed skeletal growth37. Additionally, the immune response of only the adolescent males was improved by CR13.
Data from human CR studies clearly document the benefits of a reduction in caloric intake and healthy life styles; yet, it remains unclear whether these benefits will translate to increases in lifespan. Six months of CR improved several biomarkers of aging and improved cardiovascular health in a controlled study in humans38. Even a self-imposed CR regimen in lean individuals improved several metabolic, inflammatory, and cardiovascular measures39. Current findings show that in nonhuman and human primates, CR evokes very similar metabolic, hormonal, and physiological changes that are linked to longevity in CR rodents39.
Conclusion
Our data indicate that under our laboratory conditions, CR does not improve mean survival in rhesus compared to CON monkeys despite clear improvements in overall health and function. Our finding contrasts with previous reports5, 19 and suggests that study design, husbandry, and diet composition are important factors for the life-prolonging effect of CR in a long-lived NHP, similar to what has been shown in rodent studies40–42. It will be valuable to continue to compare findings from on-going monkey CR studies to dissect mechanisms behind the improvement in health that occurred with and without significant effects on survival.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the excellent animal care staff and technicians, both past and present, especially Joe Travis; Kelli Vaughan for her editorial help; and the many collaborators that have contributed to this project. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute on Aging.
References
- 1.Branch-Mays GL, et al. The effects of a calorie-reduced diet on periodontal inflammation and disease in a non-human primate model. J Periodontol. 2008;79:1184–91. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Messaoudi I, et al. Delay of T cell senescence by caloric restriction in aged long-lived nonhuman primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:19448–53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606661103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kastman EK, et al. A calorie-restricted diet decreases brain iron accumulation and preserves motor performance in old rhesus monkeys. J Neurosci. 30:7940–7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0835-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Colman RJ, Beasley TM, Allison DB, Weindruch R. Attenuation of sarcopenia by dietary restriction in rhesus monkeys. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63:556–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/63.6.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Colman RJ, et al. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science. 2009;325:201–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1173635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Messaoudi I, Young JE, Colman RJ, Handy AM, Roth GS, Ingram DK, Mattison JA. In: Calorie Restriction, Aging, and Longevity. Everitt AV, Rattan S, Le Couteur D, de Cabo R, editors. Springer; Dordrecht: 2010. pp. 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Roth GS, et al. Aging in rhesus monkeys: relevance to human health interventions. Science. 2004;305:1423–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1102541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ingram DK, et al. Dietary restriction and aging: the initiation of a primate study. J Gerontol. 1990;45:B148–63. doi: 10.1093/geronj/45.5.b148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mattison JA, et al. Age-related decline in caloric intake and motivation for food in rhesus monkeys. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:1117–27. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rezzi S, et al. Metabolic shifts due to long-term caloric restriction revealed in nonhuman primates. Exp Gerontol. 2009;44:356–62. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2009.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Raman A, et al. Influences of calorie restriction and age on energy expenditure in the rhesus monkey. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292:E101–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00127.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Colman RJ, Kemnitz JW. In: Methods in Aging Research. Yu BP, editor. CRC; Boca Raton, FL: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Messaoudi I, et al. Optimal window of caloric restriction onset limits its beneficial impact on T-cell senescence in primates. Aging Cell. 2008;7:908–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Allison PD. Survival Analysis Using SAS: A Practical Guide. SAS Institute; Cary, NC: 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gardner EM, Beli E, Clinthorne JF, Duriancik DM. Energy intake and response to infection with influenza. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011;31:353–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-081810-160812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sun D, Muthukumar AR, Lawrence RA, Fernandes G. Effects of calorie restriction on polymicrobial peritonitis induced by cecum ligation and puncture in young C57BL/6 mice. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001;8:1003–11. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.8.5.1003-1011.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kristan DM. Chronic calorie restriction increases susceptibility of laboratory mice (Mus musculus) to a primary intestinal parasite infection. Aging Cell. 2007;6:817–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nikolich-Zugich J, Messaoudi I. Mice and flies and monkeys too: caloric restriction rejuvenates the aging immune system of non-human primates. Exp Gerontol. 2005;40:884–93. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bodkin NL, Alexander TM, Ortmeyer HK, Johnson E, Hansen BC. Mortality and morbidity in laboratory-maintained Rhesus monkeys and effects of long-term dietary restriction. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58:212–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/58.3.b212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nadon NL. Exploiting the rodent model for studies on the pharmacology of lifespan extension. Aging Cell. 2006;5:9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nestel P, Fujii A, Zhang L. An isoflavone metabolite reduces arterial stiffness and blood pressure in overweight men and postmenopausal women. Atherosclerosis. 2007;192:184–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang S, et al. Fish oil supplementation improves large arterial elasticity in overweight hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008;62:1426–31. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lomba A, et al. A high-sucrose isocaloric pair-fed model induces obesity and impairs NDUFB6 gene function in rat adipose tissue. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2009;2:267–72. doi: 10.1159/000308465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roncal-Jimenez CA, et al. Sucrose induces fatty liver and pancreatic inflammation in male breeder rats independent of excess energy intake. Metabolism. 60:1259–70. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Berger MM. Can oxidative damage be treated nutritionally? Clin Nutr. 2005;24:172–83. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama. 2007;297:842–57. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.8.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Duffy PH, et al. The effects of different levels of dietary restriction on aging and survival in the Sprague-Dawley rat: implications for chronic studies. Aging (Milano) 2001;13:263–72. doi: 10.1007/BF03353422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Martin B, Ji S, Maudsley S, Mattson MP. “Control” laboratory rodents are metabolically morbid: why it matters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107:6127–33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912955107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Austad SN, Kristan DM. Are mice calorically restricted in nature? Aging Cell. 2003;2:201–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-9728.2003.00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Harper JM, Leathers CW, Austad SN. Does caloric restriction extend life in wild mice? Aging Cell. 2006;5:441–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang C, et al. Caloric restriction and body weight independently affect longevity in Wistar rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:357–62. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Harrison DE, Archer JR, Astle CM. Effects of food restriction on aging: separation of food intake and adiposity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:1835–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lane MA, et al. Short-term calorie restriction improves disease-related markers in older male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) Mech Ageing Dev. 2000;112:185–96. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(99)00087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liao CY, Rikke BA, Johnson TE, Diaz V, Nelson JF. Genetic variation in the murine lifespan response to dietary restriction: from life extension to life shortening. Aging Cell. 9:92–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Speakman JR, Hambly C. Starving for life: what animal studies can and cannot tell us about the use of caloric restriction to prolong human lifespan. J Nutr. 2007;137:1078–86. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.4.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Roth GS, et al. Age-related changes in androgen levels of rhesus monkeys subjected to diet restriction. Endocrine J. 1993:227–234. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lane MA, et al. Aging and food restriction alter some indices of bone metabolism in male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) J Nutr. 1995;125:1600–10. doi: 10.1093/jn/125.6.1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Redman LM, Ravussin E. Caloric restriction in humans: impact on physiological, psychological, and behavioral outcomes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:275–87. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Omodei D, Fontana L. Calorie restriction and prevention of age-associated chronic disease. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:1537–42. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.03.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Forster MJ, Morris P, Sohal RS. Genotype and age influence the effect of caloric intake on mortality in mice. FASEB J. 2003;17:690–2. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0533fje. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Murtagh-Mark CM, Reiser KM, Harris R, Jr., McDonald RB. Source of dietary carbohydrate affects life span of Fischer 344 rats independent of caloric restriction. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995;50:B148–54. doi: 10.1093/gerona/50a.3.b148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Swindell WR. Dietary restriction in rats and mice: a meta-analysis and review of the evidence for genotype-dependent effects on lifespan. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11:254–70. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2011.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ward WF, et al. Effects of age and caloric restriction on lipid peroxidation: measurement of oxidative stress by F2-isoprostane levels. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2005;60:847–51. doi: 10.1093/gerona/60.7.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


