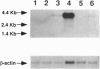
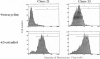
Abstract
We have previously shown that the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV-G) can be incorporated into the virions of retroviruses. Since expression of VSV-G is toxic to most mammalian cells, development of stable VSV-G packaging cell lines requires inducible VSV-G expression. We have modified the tetracycline-inducible system by fusing the ligand binding domain of the estrogen receptor to the carboxy terminus of a tetracycline-regulated transactivator. Using this system, we show that VSV-G expression is tetracycline-dependent and can be modulated by beta-estradiol. Stable packaging cell lines can readily be established and high-titer pseudotyped retroviral vectors can be generated upon induction of VSV-G expression.
Full text
PDF

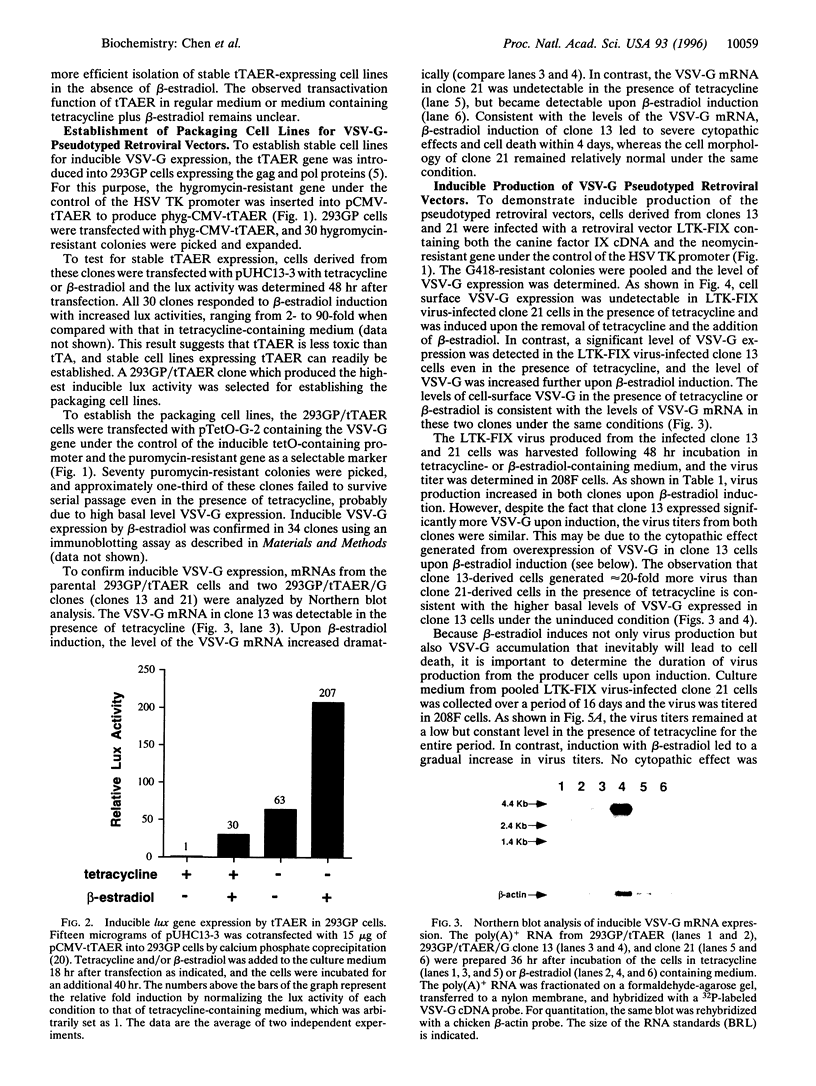
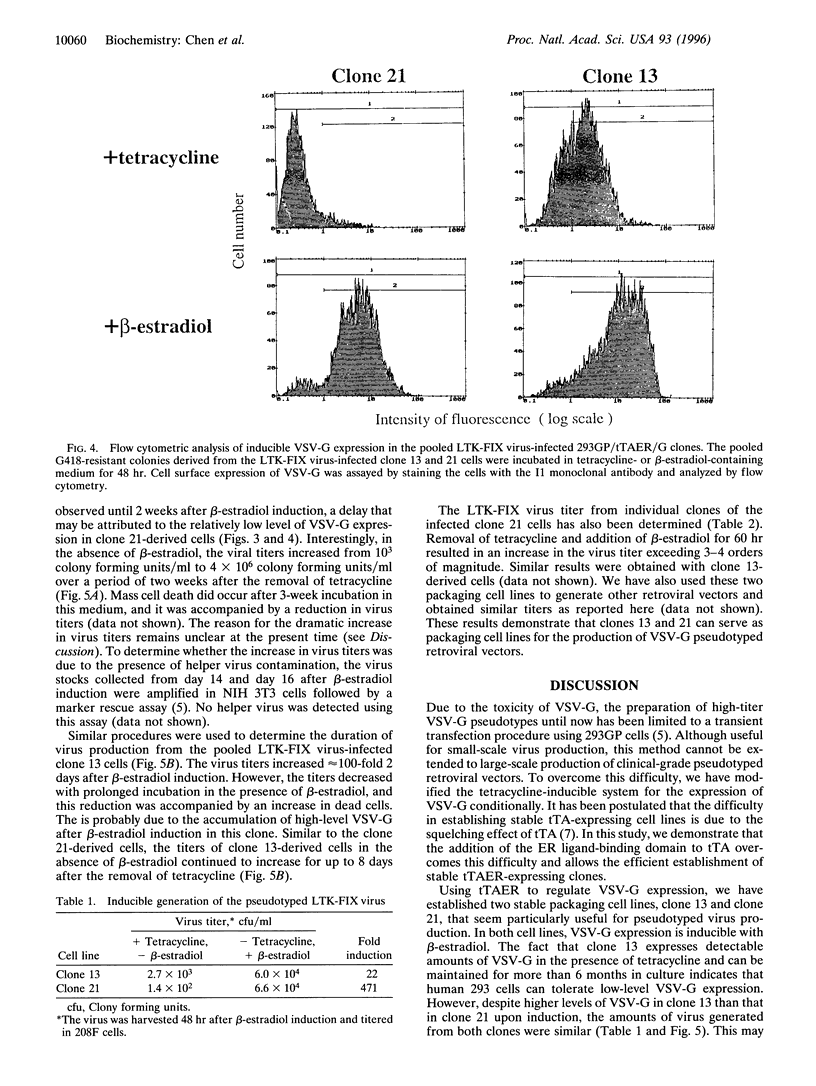

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boshart M., Weih F., Schmidt A., Fournier R. E., Schütz G. A cyclic AMP response element mediates repression of tyrosine aminotransferase gene transcription by the tissue-specific extinguisher locus Tse-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90201-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. C., Friedmann T., Driever W., Burrascano M., Yee J. K. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8033–8037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti C., Mastromarino P., Ciuffarella M. G., Orsi N. Characterization of rat brain cellular membrane components acting as receptors for vesicular stomatitis virus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1988;99(3-4):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01311075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi N., Friedmann T., Yee J. K. Pseudotype formation of murine leukemia virus with the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1202–1207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1202-1207.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth P. A., St Onge L., Böger H., Gruss P., Gossen M., Kistner A., Bujard H., Hennighausen L. Temporal control of gene expression in transgenic mice by a tetracycline-responsive promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9302–9306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Skryabin B. V., Belcher S. M., Zerillo C. A., Schmauss C. The responsiveness of a tetracycline-sensitive expression system differs in different cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14168–14174. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Gaiano N., Culp P., Burns J. C., Friedmann T., Yee J. K., Hopkins N. Integration and germ-line transmission of a pseudotyped retroviral vector in zebrafish. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.8036514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino P., Conti C., Goldoni P., Hauttecoeur B., Orsi N. Characterization of membrane components of the erythrocyte involved in vesicular stomatitis virus attachment and fusion at acidic pH. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2359–2369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioni T., Louvion J. F., Picard D. Regulation of protein activities by fusion to steroid binding domains. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43(Pt A):335–352. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60611-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Human gene therapy comes of age. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):455–460. doi: 10.1038/357455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C. The basic science of gene therapy. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):926–932. doi: 10.1126/science.8493530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H., Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1669–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman M., Axelrod J. H., Dai Y., Naviaux R. K., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Circulating human or canine factor IX from retrovirally transduced primary myoblasts and established myoblast cell lines grafted into murine skeletal muscle. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1992 May;18(3):247–258. doi: 10.1007/BF01233861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockett P., Difilippantonio M., Hellman N., Schatz D. G. A modified tetracycline-regulated system provides autoregulatory, inducible gene expression in cultured cells and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Vanin E. F., Whitt M. A., Fornerod M., Zwart R., Schneiderman R. D., Grosveld G., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible, high-level production of infectious murine leukemia retroviral vector particles pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus G envelope protein. Hum Gene Ther. 1995 Sep;6(9):1203–1213. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.9-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K., Miyanohara A., LaPorte P., Bouic K., Burns J. C., Friedmann T. A general method for the generation of high-titer, pantropic retroviral vectors: highly efficient infection of primary hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9564–9568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]