Abstract
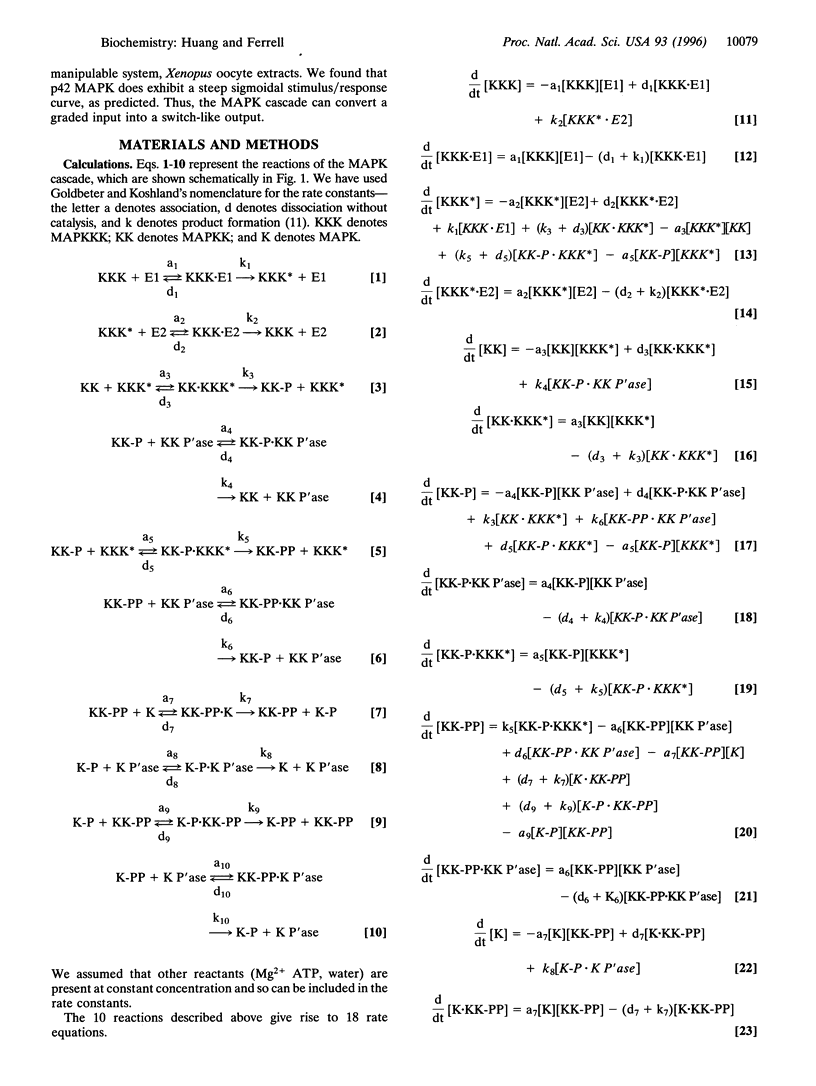
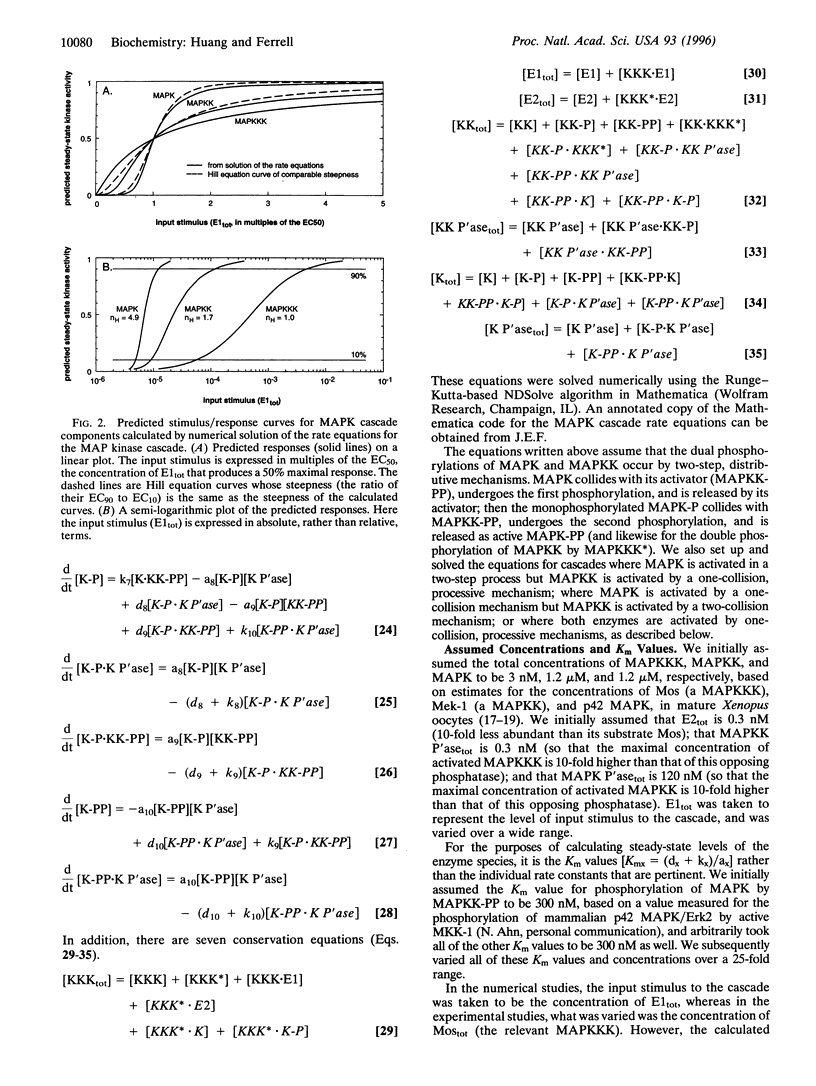
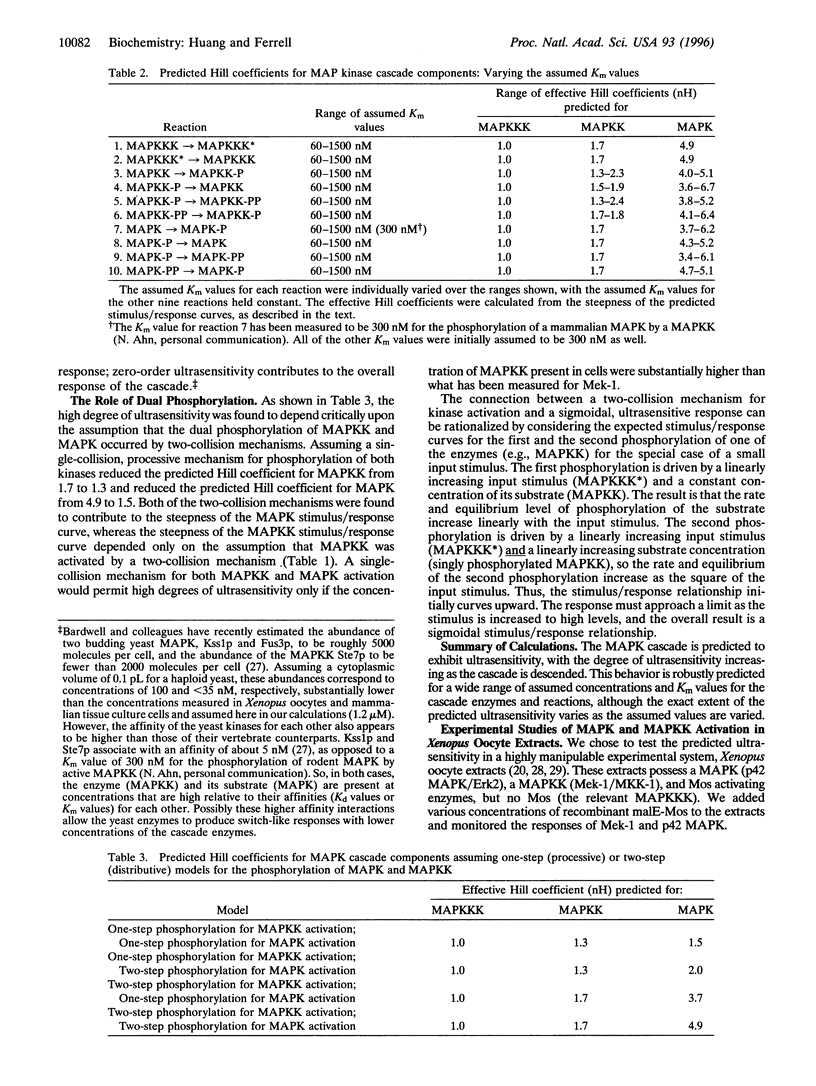
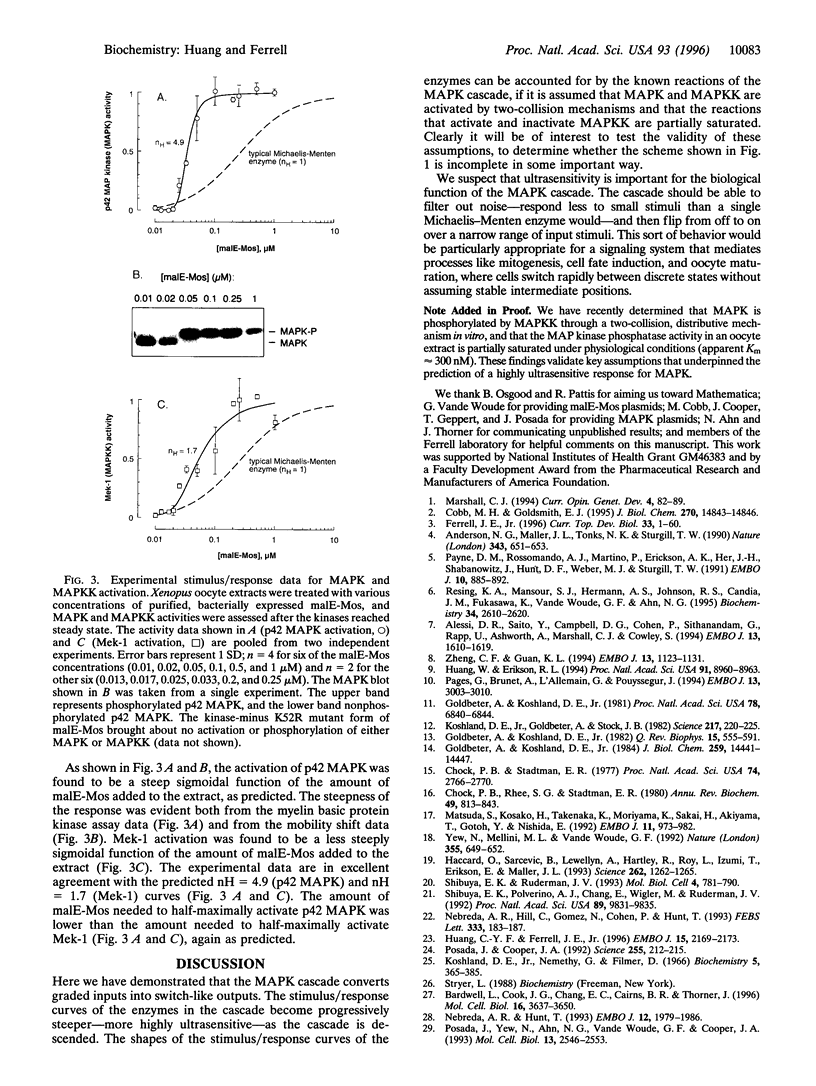
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade is a highly conserved series of three protein kinases implicated in diverse biological processes. Here we demonstrate that the cascade arrangement has unexpected consequences for the dynamics of MAPK signaling. We solved the rate equations for the cascade numerically and found that MAPK is predicted to behave like a highly cooperative enzyme, even though it was not assumed that any of the enzymes in the cascade were regulated cooperatively. Measurements of MAPK activation in Xenopus oocyte extracts confirmed this prediction. The stimulus/response curve of the MAPK was found to be as steep as that of a cooperative enzyme with a Hill coefficient of 4-5, well in excess of that of the classical allosteric protein hemoglobin. The shape of the MAPK stimulus/ response curve may make the cascade particularly appropriate for mediating processes like mitogenesis, cell fate induction, and oocyte maturation, where a cell switches from one discrete state to another.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D. R., Saito Y., Campbell D. G., Cohen P., Sithanandam G., Rapp U., Ashworth A., Marshall C. J., Cowley S. Identification of the sites in MAP kinase kinase-1 phosphorylated by p74raf-1. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1610–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell L., Cook J. G., Chang E. C., Cairns B. R., Thorner J. Signaling in the yeast pheromone response pathway: specific and high-affinity interaction of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases Kss1 and Fus3 with the upstream MAP kinase kinase Ste7. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jul;16(7):3637–3650. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.7.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. Interconvertible enzyme cascades in cellular regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:813–843. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Stadtman E. R. Superiority of interconvertible enzyme cascades in metabolite regulation: analysis of multicyclic systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):14843–14846. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.14843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr MAP kinases in mitogenesis and development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1996;33:1–60. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Koshland D. E., Jr An amplified sensitivity arising from covalent modification in biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Koshland D. E., Jr Sensitivity amplification in biochemical systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1982 Aug;15(3):555–591. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Koshland D. E., Jr Ultrasensitivity in biochemical systems controlled by covalent modification. Interplay between zero-order and multistep effects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14441–14447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haccard O., Sarcevic B., Lewellyn A., Hartley R., Roy L., Izumi T., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Induction of metaphase arrest in cleaving Xenopus embryos by MAP kinase. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1262–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.8235656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Y., Ferrell J. E., Jr Dependence of Mos-induced Cdc2 activation on MAP kinase function in a cell-free system. EMBO J. 1996 May 1;15(9):2169–2173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W., Erikson R. L. Constitutive activation of Mek1 by mutation of serine phosphorylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8960–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Goldbeter A., Stock J. B. Amplification and adaptation in regulatory and sensory systems. Science. 1982 Jul 16;217(4556):220–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7089556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. MAP kinase kinase kinase, MAP kinase kinase and MAP kinase. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hill C., Gomez N., Cohen P., Hunt T. The protein kinase mos activates MAP kinase kinase in vitro and stimulates the MAP kinase pathway in mammalian somatic cells in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 25;333(1-2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80401-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hunt T. The c-mos proto-oncogene protein kinase turns on and maintains the activity of MAP kinase, but not MPF, in cell-free extracts of Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1979–1986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Brunet A., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. Constitutive mutant and putative regulatory serine phosphorylation site of mammalian MAP kinase kinase (MEK1). EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3003–3010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06599.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resing K. A., Mansour S. J., Hermann A. S., Johnson R. S., Candia J. M., Fukasawa K., Vande Woude G. F., Ahn N. G. Determination of v-Mos-catalyzed phosphorylation sites and autophosphorylation sites on MAP kinase kinase by ESI/MS. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 28;34(8):2610–2620. doi: 10.1021/bi00008a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Polverino A. J., Chang E., Wigler M., Ruderman J. V. Oncogenic ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescent Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Ruderman J. V. Mos induces the in vitro activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in lysates of frog oocytes and mammalian somatic cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Aug;4(8):781–790. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.8.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Mellini M. L., Vande Woude G. F. Meiotic initiation by the mos protein in Xenopus. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):649–652. doi: 10.1038/355649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Activation of MEK family kinases requires phosphorylation of two conserved Ser/Thr residues. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1123–1131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




