Abstract
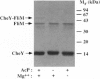
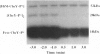
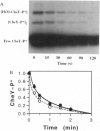
Chemotaxis in bacteria is controlled by regulating the direction of flagellar rotation. The regulation is carried out by the chemotaxis protein CheY. When phosphorylated, CheY binds to FliM, which is one of the proteins that constitute the "gear box" (or "switch") of the flagellar motor. Consequently, the motor shifts from the default direction of rotation, counterclockwise, to clockwise rotation. This biased rotation is terminated when CheY is dephosphorylated either spontaneously or, faster, by a specific phosphatase, CheZ. Logically, one might expect CheZ to act directly on FliM-bound CheY. However, here we provide direct biochemical evidence that, in contrast to this expectation, phosphorylated CheY (CheY approximately P), bound to FliM, is protected from dephosphorylation by CheZ. The complex between CheY approximately P and FliM was trapped by cross-linking with dimethylsuberimidate, and its susceptibility to CheZ was measured. CheY approximately P complexed with FliM, unlike free CheY approximately P, was not dephosphorylated by CheZ. However, it did undergo spontaneous dephosphorylation. Nonspecific cross-linked CheY dimers, measured as a control, were dephosphorylated by CheZ. No significant binding between CheZ and any of the switch proteins was detected. It is concluded that, in the termination mechanism of signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis, CheZ acts only on free CheY approximately P. We suggest that CheZ affects switch-bound CheY approximately P by shifting the equilibrium between bound and free CheY approximately P.
Full text
PDF

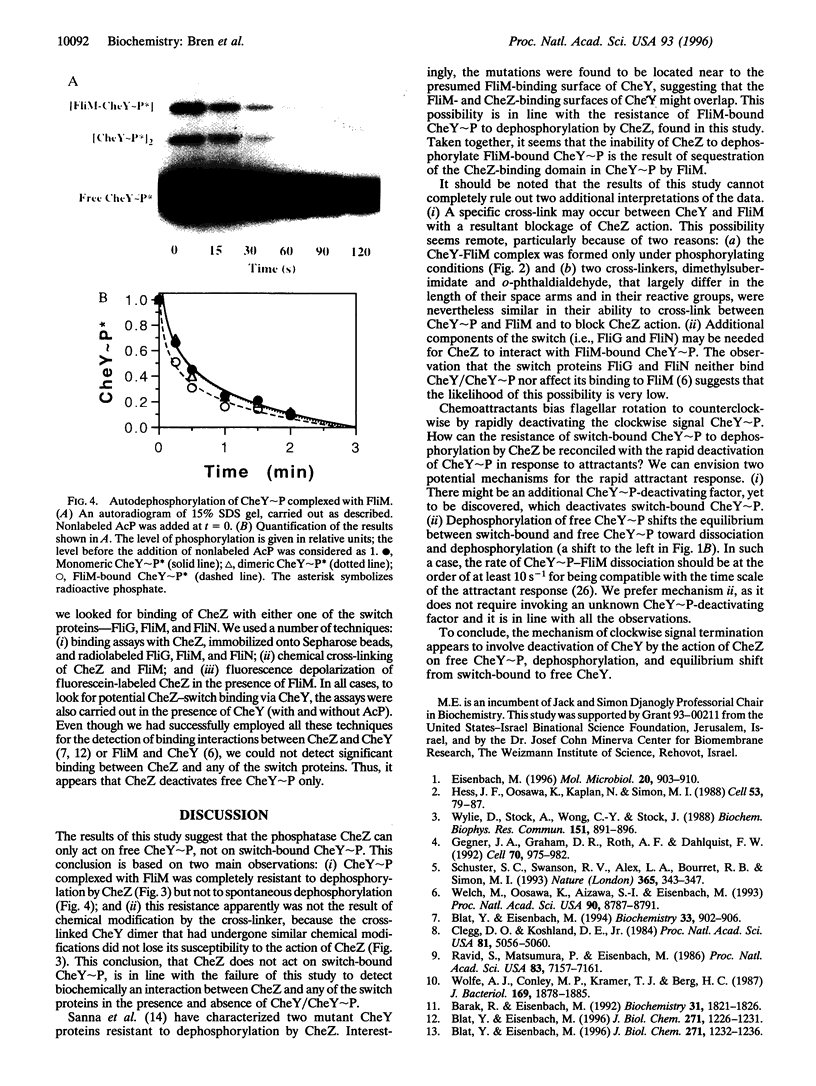

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barak R., Eisenbach M. Correlation between phosphorylation of the chemotaxis protein CheY and its activity at the flagellar motor. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1821–1826. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blat Y., Eisenbach M. Mutants with defective phosphatase activity show no phosphorylation-dependent oligomerization of CheZ. The phosphatase of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):1232–1236. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blat Y., Eisenbach M. Oligomerization of the phosphatase CheZ upon interaction with the phosphorylated form of CheY. The signal protein of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):1226–1231. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blat Y., Eisenbach M. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of the chemotaxis signal molecule CheY to its phosphatase, CheZ. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 1;33(4):902–906. doi: 10.1021/bi00170a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of a signaling protein in bacterial sensing: behavioral effects of increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M. Control of bacterial chemotaxis. Mol Microbiol. 1996 Jun;20(5):903–910. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegner J. A., Graham D. R., Roth A. F., Dahlquist F. W. Assembly of an MCP receptor, CheW, and kinase CheA complex in the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):975–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90247-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irikura V. M., Kihara M., Yamaguchi S., Sockett H., Macnab R. M. Salmonella typhimurium fliG and fliN mutations causing defects in assembly, rotation, and switching of the flagellar motor. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):802–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.802-810.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Castellano F., Spudich J. L., McCray J. A., Goody R. S., Reid G. P., Trentham D. R. Excitatory signaling in bacterial probed by caged chemoeffectors. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2368–2382. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81317-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., McCleary W. R., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Phosphorylation of bacterial response regulator proteins by low molecular weight phospho-donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Ueno T., Aizawa S. Overproduction of the bacterial flagellar switch proteins and their interactions with the MS ring complex in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3683–3691. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3683-3691.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R. Interaction of the cheC and cheZ gene products is required for chemotactic behavior in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2390–2394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanna M. G., Swanson R. V., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Mutations in the chemotactic response regulator, CheY, that confer resistance to the phosphatase activity of CheZ. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Mar;15(6):1069–1079. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. C., Swanson R. V., Alex L. A., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Assembly and function of a quaternary signal transduction complex monitored by surface plasmon resonance. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):343–347. doi: 10.1038/365343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Parkinson J. S. Overlapping genes at the cheA locus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5370–5374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sockett H., Yamaguchi S., Kihara M., Irikura V. M., Macnab R. M. Molecular analysis of the flagellar switch protein FliM of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):793–806. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.793-806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M., Oosawa K., Aizawa S. I., Eisenbach M. Effects of phosphorylation, Mg2+, and conformation of the chemotaxis protein CheY on its binding to the flagellar switch protein FliM. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10470–10476. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M., Oosawa K., Aizawa S., Eisenbach M. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a signal molecule to the flagellar switch of bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8787–8791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Kramer T. J., Berg H. C. Reconstitution of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1878-1885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylie D., Stock A., Wong C. Y., Stock J. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves phosphotransfer between Che proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):891–896. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]