Abstract
Nevus comedonicus (NC) is a very rare, benign hamartoma characterised by the occurrence of dilated, comedo-like openings, typically on the face, neck, upper arms, chest or abdomen. In uncertain cases, histopathological examination confirms the diagnosis. The authors suggest dermoscopy as a rapid and useful method of initial diagnosis of nevus comedonicus based upon its distinctive dermoscopic features. The dermoscopy reveals numerous light- and dark-brown, circular or barrel-shaped, homogenous areas with prominent keratin plugs.
Keywords: dermoscopy, dermatoscopy, nevus comedonicus, epidermal nevus, acne vulgaris
Introduction
Nevus comedonicus (NC) is a benign hamartoma characterised by the occurrence of dilated comedo-like openings, with black or brown keratin plugs, typically localised on the face, neck, upper arms, chest or abdomen. The diagnosis of nevus comedonicus is relatively easy. In uncertain cases, a typical histopathological picture confirms the diagnosis. Dermoscopy is a safe, non-invasive, easy-to-repeat diagnostic method mainly used in melanocytic lesion [1–3] but it also may prove helpful in the diagnosis of nevus comedonicus.
The aim of the study was to present a case of nevus comedonicus with regard to its clinical and dermoscopic picture and the use of dermoscopy in the diagnosis of this rare condition.
Case report
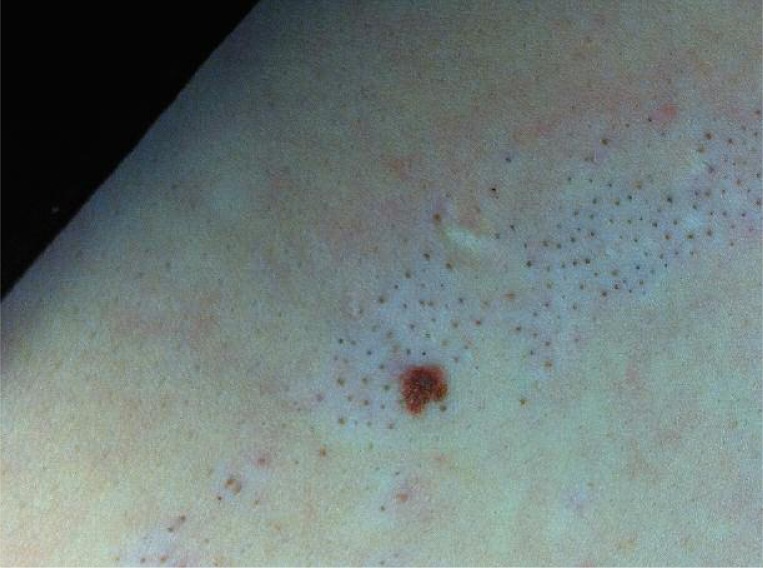
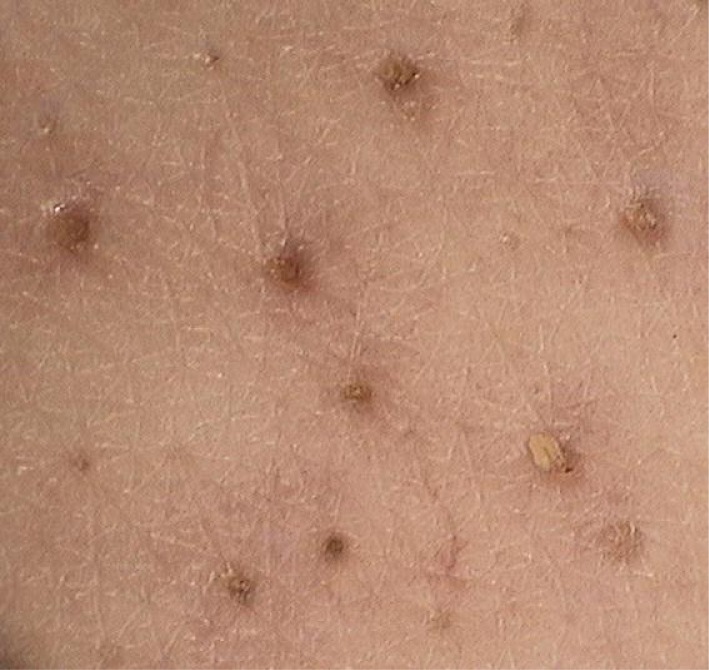
We report a case of nevus comedonicus in a 21-year-old female patient. The solitary lesion appeared on the right breast when the patient was 15 years old and since then it has slightly enlarged in parallel to the body growth. The patient denied any association with previous trauma or irritation. Clinically, the lesion consisted of multiple, comedo-like openings with dark keratin plugs dispersed over a hypopigmented, slightly hypotrophic, linear spot of 2 cm × 8 cm (Figure 1). The plugs could not be extracted mechanically. The dermoscopic examination revealed the distinctive pattern consisting of dark, sharply demarcated keratin plugs of 1–3 mm diameter, numerous structureless, circular- and barrel-shaped, homogenous areas with hyperkeratotic plugs of various shades of brown (Figure 2). The patient's health status was otherwise normal, with no congenital abnormalities or internal organ involvement. Treatment options were discussed with the patient who consented to topical retinoid therapy. After application of 0.05% tazarotene gel twice daily, clinical improvement was achieved with total evacuation of keratin plugs from dilated openings within 10 weeks.
Fig. 1 .
A macroscopic image of the nevus comedonicus on the breast
Fig. 2 .
Dermoscopy of nevus comedonicus – there are numerous circular and barrel-shaped, homogenous areas in lightand dark-brown shades, with remarkable keratin plugs (videodermoscope, 20×)
Discussion
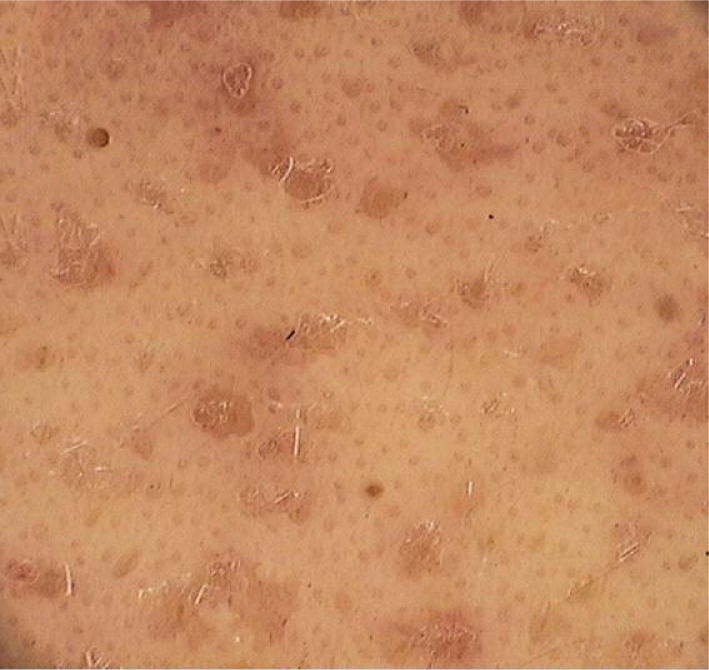
Nevus comedonicus belongs to the spectrum of the epidermal nevi syndrome. It is an extremely rare dermatological entity. According to Inoue et al. [4], until 2000, only 200 cases were described [4]. Almost a half of the cases are present at birth, the rest occurs before the age of 10 [5, 6]. The late onset is typically related to irritation or trauma [5]. Patients with nevus comedonicus are divided into two groups, reflecting the severity of the condition: the first group is characterised by the presence of slightly pronounced skin lesions or comedo-like changes, which represent merely a cosmetic defect. The second group present with severe cutaneous symptoms including large cysts with scarring, often with a tendency to recurrences with formation of fistulas and abscesses [6]. In extreme cases, nevus comedonicus may appear as an extensive inflammatory lesion involving large areas of the body, with suppuration and residual scarring [7]. The diagnosis of nevus comedonicus is based upon the clinical picture, presenting as a group of open comedo-like plugs distributed segmentally or linearly, in some cases following Blaschko's lines [5]. These lesions are most commonly located on the face, neck, upper arms, chest or abdomen [6], occurring elevated, as follicular openings with plugs resembling black comedones. In contrast to this, the dermoscopic image of acne vulgaris – is characterised by the presence of numerous homogenous, light- or dark-brown (or sometimes black) areas depending on the acne type (open or closed comedones), usually circular in shape and located superficially in the epidermis (Figure 3).
Fig. 3 .
Dermoscopy of typical comedones in acne vulgaris – numerous, homogenous areas, light- and dark-brown (at times black) in colour, depending on the type of acne (open or closed comedones), predominantly circular and situated superficially (videodermoscope, 20×)
To the authors’ best knowledge, supported by meticulous literature search (Medline), only one report of the use of dermoscopy in nevus comedonicus has been published. This was a 3-month-old boy who was clinically diagnosed with dispersed, multiple comedones nevi, in whom dermoscopy revealed that the “comedones” consisted of keratin plugs, however without dermoscopic images published in this report [8]. Dermoscopy was also used in differential diagnosis of another rare epidermal nevi, such as sebaceous nevus [9, 10] and hair follicle nevus [11]. Typical dermoscopic features of sebaceous nevus are bright, yellow dots that are not associated with hair follicles [9]. Aggregated yellow globules with crown vessels may also be seen in sebaceous nevus [10]. The very rare hair follicle nevus is characterised by the presence of many follicular openings and interfollicular “pseudo-pigment network” on dermoscopy [11].
The diagnosis of nevus comedonicus is based upon clinical picture. In the majority of cases, dermoscopy or video-dermoscopy may prove helpful. In each case of nevus comedonicus, it is obligatory to rule out the comedonicus syndrome, which may include ocular lesions (cataract, corneal erosion), skeletal abnormalities (syndactyly, clinodactyly, the absence of hand bones on X-ray, scoliosis, vertebral defects) and neurologic disturbances (microcephaly, mental deficiency, the dysgenesis of the corpus callosum) [12]. The treatment of nevus comedonicus is administered mainly for cosmetics reasons, or to alleviate inflammation in severe cases. In the past, treatment of limited, small areas involved the use of ammonium lactate lotion to evacuate the keratin plugs. It is also advisable to mechanically remove the keratin-sebaceous plugs through the application of cosmetic strips which produces excellent results [4]. Further therapeutic options range from topical retinoid application (tretinoin, adapalene, tazarotene) [5] to combined therapies: tazarotene and calcipotriene or tretinoin and corticosteroids e.g. mometasone furoate) [13, 14]. In resistant cases, more invasive techniques may be employed in order to eliminate the undesirable structures, for example laser therapy (diode laser 1450-nm, ultrapulse CO2 or Erbium: YAG) [5, 15, 16] or finally total surgical excision [17].
In our opinion, dermoscopy is a helpful method of confirmatory and differential diagnosis of nevus comedonicus.
References
- 1.Kamińska-Winciorek G, Śpiewak R. Basic dermoscopy of melanocytic lesions for beginners. Postępy Hig Med Dośw (Online) 2011;65:501–8. doi: 10.5604/17322693.955121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kamińska-Winciorek G. Dermatologia cyfrowa. Wrocław: Cornetis; 2008. pp. 11–84. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kamińska-Winciorek G, Śpiewak R. Tips and tricks in the dermoscopy of pigment lesions. BMC Dermatol. 2012;12:14. doi: 10.1186/1471-5945-12-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Inoue Y, Miyamoto Y, Ono T. Two cases of nevus comedonicus: successful treatment of keratin plugs with a pore strip. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:927–9. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2000.103992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Givan J, Hurley MY, Glaser DA. Nevus comedonicus: a novel approach to treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:721–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Guldbakke KK, Khachemoune A, Deng A, et al. Naevus comedonicus: a spectrum of body involvement. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:488–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2007.02459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kirtak N, Inaloz HS, Karakok M, et al. Extensive inflammatory nevus comedonicus involving half of the body. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:434–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vano-Galvan S, Hernández-Martín A, Colmenero I, et al. Disseminated congenital comedones. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:58–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Neri I, Savoia F, Giacomini F, et al. Usefulness of dermatoscopy for the early diagnosis of sebaceous naevus and differentiation from aplasia cutis congenita. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e50–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.03189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim NH, Zell DS, Kolm I, et al. The dermoscopic differential diagnosis of yellow lobularlike structures. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:962. doi: 10.1001/archderm.144.7.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Okada J, Moroi Y, Tsujita J, et al. Hair follicle nevus – a dermoscopic approach. Eur J Dermatol. 2008;18:185–7. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2008.0358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Happle R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes. Part I. Well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:1–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Deliduka SB, Kwong PC. Treatment of Nevus comedonicus with topical tazarotene and calcipotriene. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:674–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Manola I, Ljubojević S, Lipozencić J, et al. N. Nevus comedonicus – case report and review of therapeutical approach. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2003;11:221–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sardana K, Garg VK. Successful treatment of nevus comedonicus with ultrapulse CO2 laser. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:534–5. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.55419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Caers SJ, Van der Geer S, Beverdam EG, et al. Successful treatment of nevus comedonicus with the use of the Erbium Yag laser. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:375–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Milburn S, Whallett E, Hancock K, et al. The treatment of naevus comedonicus. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:805–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2004.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]