Abstract
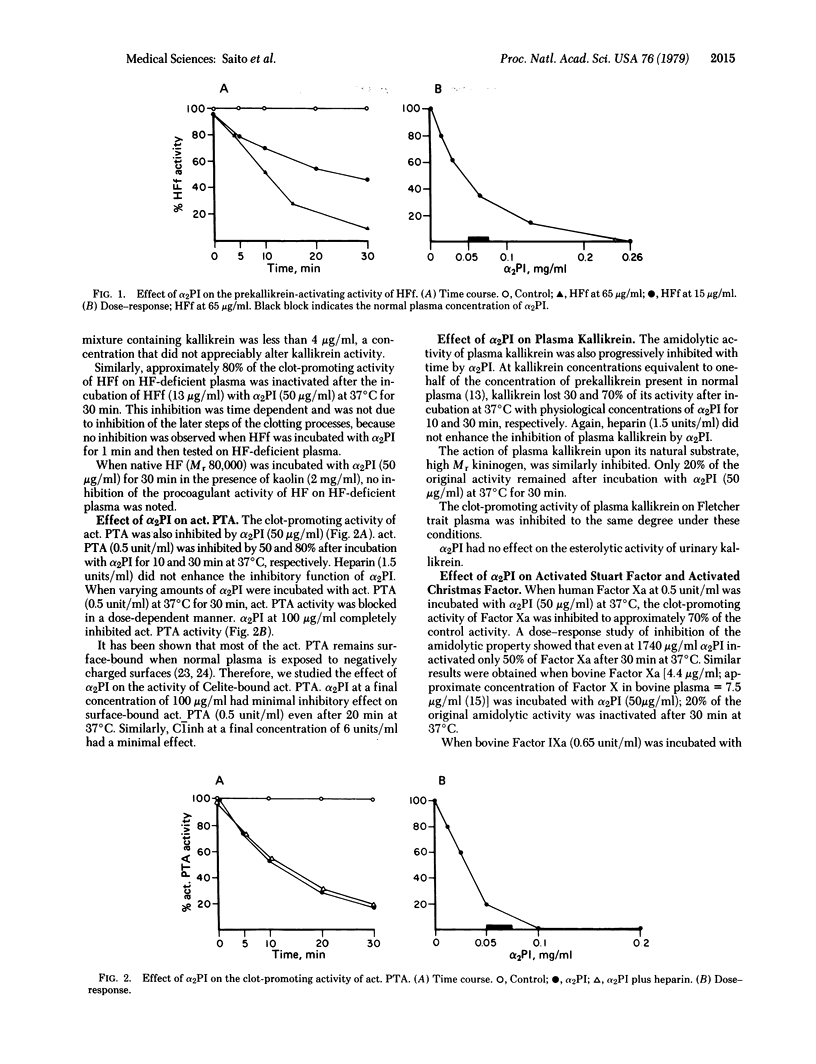
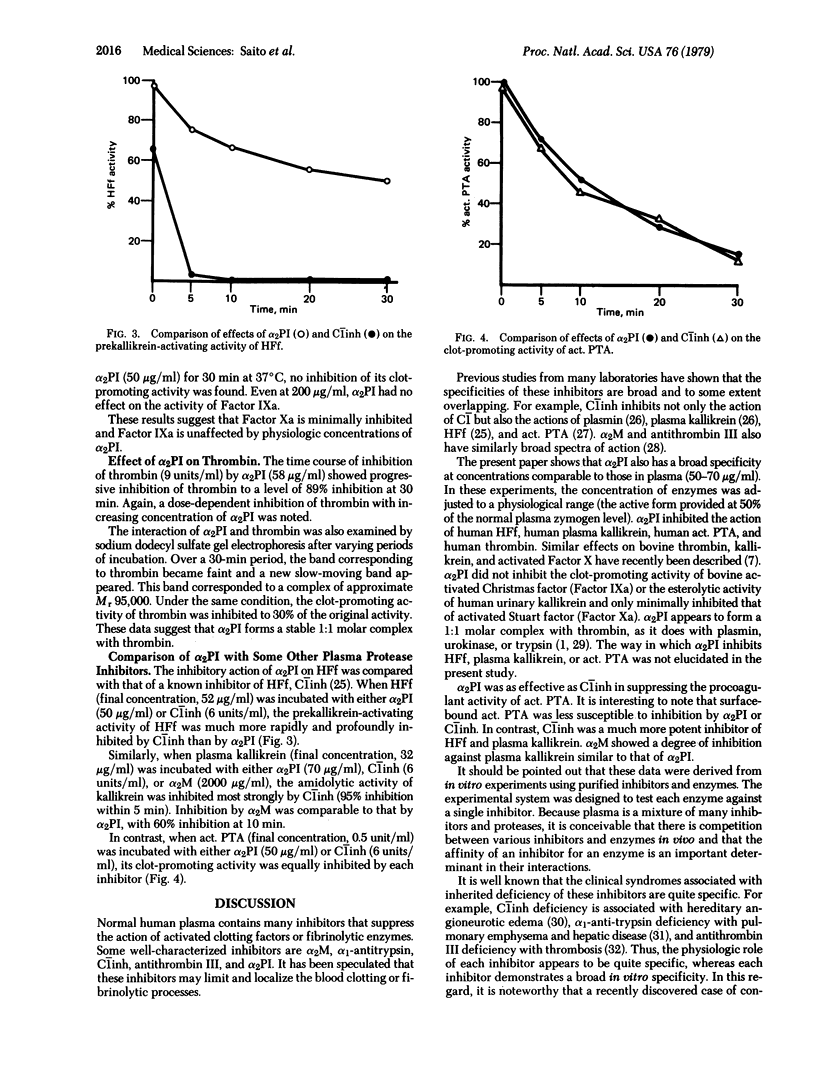
alpha 2-Plasmin inhibitor (alpha 2PI) has been recently characterized as a fast-reacting inhibitor of plasmin in human plasma and appears to play an important role in the regulation of fibrinolysis in vivo. We have studied the effect of purified alpha 2PI upon various proteases participating in human blood coagulation and kinin generation. At physiological concentration (50 microgram/ml), alpha 2PI inhibited the clot-promoting and prekallikrein-activating activity of Hageman factor fragments, the amidolytic, kininogenase, and clot-promoting activities of plasma kallikrein, and the clot-promoting properties of activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA, Factor XIa) and thrombin. alpha 2PI had minimal inhibitory effect on surface-bound activated PTA and activated Stuart factor (Factor Xa). alpha 2PI did not inhibit the activity of activated Christmas factor (Factor IXa) or urinary kallikrein. Heparin (1.5-2.0 units/ml) did not enhance the inhibitory function of alpha 2PI. These results suggest that, like other plasma protease inhibitors, alpha 2PI possesses a broad in vitro spectrum of inhibitory properties.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Matsuda M., Tachiya K. The behavior of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in fibrinolytic states. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Tachiya K. Effects of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor on fibrin clot lysis. Its comparison with alpha2-macroglobulin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Feb 28;39(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. Identification and some properties of a new fast-reacting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H., EVANS R. R. A BIOCHEMICAL ABNORMALITY IN HEREDIATRY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA: ABSENCE OF SERUM INHIBITOR OF C' 1-ESTERASE. Am J Med. 1963 Jul;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. INHERITED ANTITHROMBIN DEFICIENCY CAUSING THROMBOPHILIA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Jun 15;13:516–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human alpha2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:639–652. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Plasmin inhibitor interactions. The effectiveness of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in the presence of alpha2-macroglobulin. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist P. A., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent) and a protease from Russell's viper venom. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Inhibition of proteases in coagulation, kinin-forming and complement systems by alpha2-plasmin inhibitor. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):969–972. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. On the interaction of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor and proteases. Evidence for the formation of a covalent crosslinkage and non-covalent weak bondings between the inhibitor and proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 10;482(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllertz S., Clemmensen I. The primary inhibitor of plasmin in human plasma. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):545–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1590545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Poon M. C., Vicic W., Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Menitove J. E. Human plasma prekallikrein (Fletcher factor) clotting activity and antigen in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jul;92(1):84–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H. Purification of high molecular weight kininogen and the role of this agent in blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):584–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI108810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D. Alteration of factor VII activity by activated Fletcher factor (a plasma kallikrein): a potential link between the intrinsic and extrinsic blood-clotting systems. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Mar;85(3):405–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Ratnoff O. D., Marshall J. S., Pensky J. Partial purification of plasma thromboplastin antecedent (factor XI) and its activation by trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):850–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI107249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Bouma B. N., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. Role of high-molecular-weight kininogen in surface-binding and activation of coagulation Factor XI and prekallikrein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



