Abstract
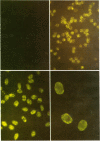
In vitro binding of a Herpesvirus ateles (HVA)-associated soluble antigen to amphibian erythrocyte nuclei was demonstrated by the acid-fixed nuclear binding technique in combination with anticomplement immunofluorescence. Incubation of concentrated salt-extracted soluble antigens derived from HVA-carrying marmoset lines with methanol/acetic acid-fixed erythrocytes of frogs and salamanders resulted in a brilliant nuclear fluorescence after exposure to a live virus-boostered, anti-HVS-positive squirrel monkey serum. Anti-HVS-negative sera did not stain. The activity of the positive serum could be abosrbed completely with extracts of HVA-carrying cells but not with Epstein-Barr virus-carrying or Herpesvirus papio-carrying cells. The HVA-associated antigen was also present in lytically HVA-infected marmoset kidney cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ErnbergI, Masucci G., Klein G. Persistence of Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen (EBNA) in cells entering the EB viral cycle. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):197–203. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L. A., Henle G., Henle W., Deinhardt F., Schudel A. Transformation of lymphocytes by Herpesvirus papio. Int J Cancer. 1977 Aug 15;20(2):219–226. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L. A., Nigida S. M., Deinhardt F., Wolfe L. G., Cooper R. W., Hernandez-Camacho J. I. Herpesvirus ateles: properties of an oncogenic herpesvirus isolated from circulating lymphocytes of spider monkeys (Ateles sp.). Int J Cancer. 1974 Oct 15;14(4):473–482. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L., Deinhardt F., Nonoyama M., Wolfe L. G., Bergholz C. Properties of a baboon lymphotropic herpesvirus related to Epstein-Barr virus. Int J Cancer. 1976 Dec 15;18(6):798–807. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L., Johnson D., Deinhardt F. Transformation of marmoset lymphocytes in vitro with Herpesvirus ateles. Int J Cancer. 1978 May 15;21(5):652–657. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L., Wolfe L., Deinhardt F., Paciga J., Dombos L., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation of non-human primate lymphocytes in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1974 Mar 15;13(3):363–376. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L., Wright J., Wolfe L., Deinhardt F. Herpesvirus ateles: transformation in vitro of marmoset splenic lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1974 Aug 15;14(2):244–251. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROWE W. P., BLACK P. H., HUEBNER R. J. PRODUCTION OF "TUMOR-SPECIFIC" ANTIGENS BY ONCOGENIC VIRUSES DURING ACUTE CYTOLYTIC INFECTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:12–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I., Suchánková A., Závadová H., Vonka V. Study of Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) by chromatography on fixed cell nuclei. Int J Cancer. 1978 Nov 15;22(5):535–541. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Dulbecco R. Characterization of polyoma virus T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L. Relationship between the sensitivity of EBV-carrying lymphoblastoid lines to superinfection and the inducibility of the resident viral genome. Int J Cancer. 1973 Mar 15;11(2):327–337. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Pearson G., Rabson A., Ablashi D. V., Falk L., Wolfe L., Dienhardt F., Rabin H. Antibody reactions to herpesvirus saimiri (HVS)-induced early and late antigens (EA and LA) in HVS-infected squirrel, marmoset and owl monkeys. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jul 15;12(1):270–289. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Siegert W., Klein G. Solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen and its characterization as a DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.1-8.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Luka J., Falk L. A., Klein G. Serological reactivities of human and baboon sera against EBNA and Herpesvirus papio-determined nuclear antigen (HUPNA). Eur J Cancer. 1978 Sep;14(9):955–960. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(78)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Luka J., Falk L., Klein G. Detection of a nuclear, EBNA-type antigen in apparently EBNA-negative Herpesvirus papio (HVP)-transformed lymphoid lines by the acid-fixed nuclear binding technique. Int J Cancer. 1977 Dec 15;20(6):941–946. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Identification of a purified complement-fixing antigen as the Epstein-Barr-virus determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) by its binding to metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallen W. C., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H., Cicmanec J. L. Nonimmune rosette formation by lymphoma and leukemia cells from Herpesvirus saimiri-infected owl monkeys. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):967–975. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W., Herberman R. B. A human lymphoid cell line with receptors for both sheep red blood cells and complement. Cell Immunol. 1974 Oct;14(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Green M. Adenovirus DNA replication. I. Requirement for protein synthesis and isolation of nuclear membrane fractions containing newly synthesized viral DNA and proteins. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):412–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.412-420.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]