Abstract
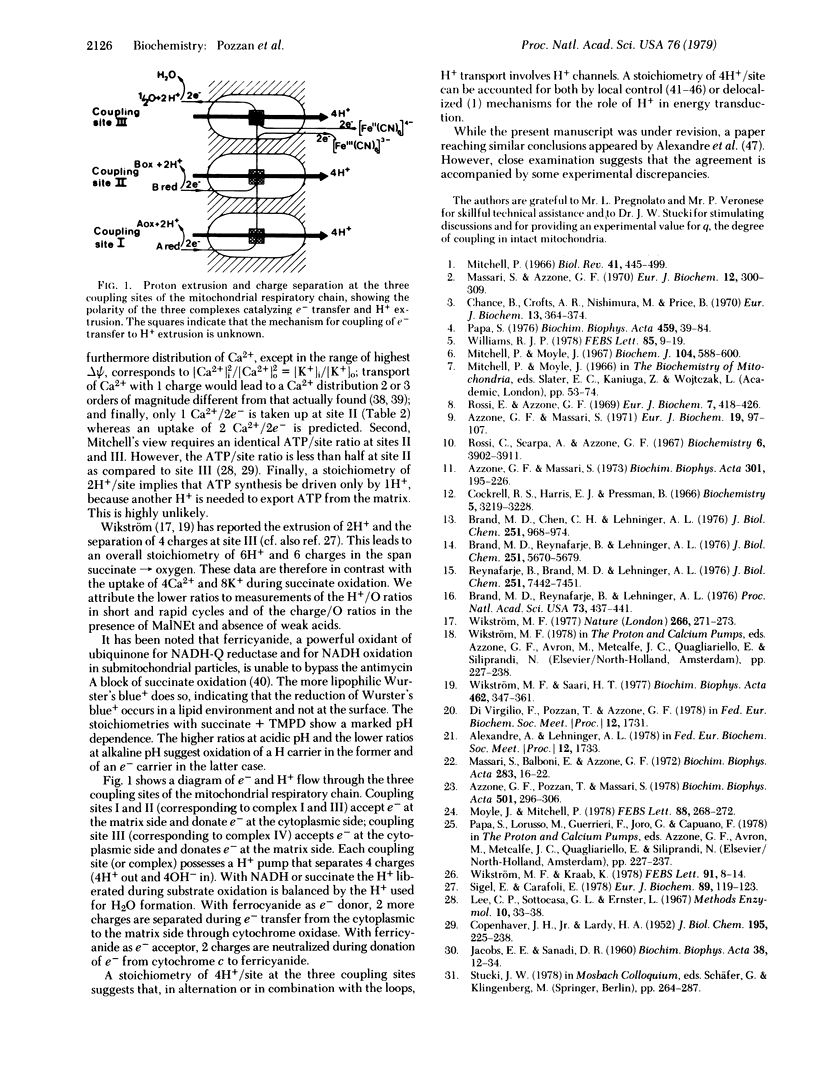
H+/site, charge/site, and ATP/site ratios have been determined at coupling sites I, II, and III. Three e- donors have been used for coupling site III: ferrocyanide, ascorbate + tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPD), and succinate + TMPD. The H+/site ratios are 4.0 with ferrocyanide and 6.0 with succinate + TMPD (at pH <7.0); the charge/site ratios are 6.0 with ferrocyanide and with succinate + TMPD (at pH <7.0) and 4.0 with ascorbate + TMPD; the ATP/site ratio is 1.34 with ascorbate + ferrocyanide. These ratios have been obtained in the presence of amounts of antimycin A that provide full inhibition of site II. For coupling sites I and II, ferricyanide has been used as e- acceptor and succinate or NAD-linked substrates as e- donors. The H+/site ratios are 4.0 at sites I and II; the charge/site ratios are 4.0 at site I and 2.0 at site II; the ATP/site ratios are 1.0 at site I and 0.5 at site II. Two major factors affect the stoichiometries: (i) dimension of [unk]H and (ii) supply of H+ from the matrix. There is a correlation between collapse of [unk]H and increase of H+/site and charge/site ratios. This indicates that approximation of the phenomenologic stoichiometry of the H+ pump is obtained when flow ratios are measured at level flow. That charge/site and ATP/site ratios increase when ferrocyanide is e- donor and decrease when ferricyanide is e- acceptor is attributed to the localization of the redox couple. This leads to separation of 1 charge/e- when ferrocyanide is e- donor and to consumption of 1 charge/e- when ferricyanide is e- acceptor. To account for an extrusion of H+ in excess of that predicted by the loop model, it is proposed that each coupling site contains a channel acting as a H+ pump.
Keywords: energy transduction, H+ channel, stoichiometry of H+ pump
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandre A., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometry of vectorial H+ movements coupled to electron transport and to ATP synthesis in mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5296–5300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzone G. F., Massari S. Active transport and binding in mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 31;301(3):195–226. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzone G. F., Massari S., Pozzan T. The generation of the proton electrochemical potential and its role in energy transduction. Mol Cell Biochem. 1977 Sep 9;17(2):101–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01743433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzone G. F., Massari S. Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the interconversion of chemical and osmotic energies in mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):97–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzone G. F., Pozzan T., Massari S., Bragadin M. Proton electrochemical gradient and rate of controlled respiration in mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 9;501(2):296–306. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Chen C. H., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometry of H+ ejection during respiration-dependent accumulation of Ca2+ by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):968–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Re-evaluation of the H+/site ratio of mitochondrial electron transport with the oxygen pulse technique. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5670–5679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometric relationship between energy-dependent proton ejection and electron transport in mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):437–441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPENHAVER J. H., Jr, LARDY H. A. Oxidative phosphorylations; pathways and yield in mitochondrial preparations. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Crofts A. R., Nishimura M., Price B. Fast membrane H+ binding in the light-activated state of Chromatium chromatophores. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Apr;13(2):364–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupling mechanisms in capture, transmission, and use of energy. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:957–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Ernster L. Enzyme topology of intracellular membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:201–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernster L. Chemical and chemiosmotic aspects of electron transport-linked phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:981–995. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ion transport in liver mitochondria. Energy barrier and stoicheometry of aerobic K+ translocation. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):418–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS E. E., SANADI D. R. Phosphorylation coupled to electron transport mediated by high potential electron carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 12;38:12–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari S., Azzone G. F. The mechanism of ion translocation in mitochondria. 1. Coupling of K+ and H+ fluxes. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):301–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari S., Azzone G. F. The mechanism of ion translocation in mitochondria. 2. Active transport and proton pump. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):310–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari S., Balboni E., Azzone G. F. Distribution of permeant cations in rat liver mitochondria under steady-state conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972;283(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Possible molecular mechanisms of the protonmotive function of cytochrome systems. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):327–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell P. Cytochrome c oxidase is not a proton pump. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell P. Measurements of mitochondrial comes from H+/O quotients: effects of phosphate and N-ethylmaleimide. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The regulation of extramitochondrial free calcium ion concentration by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):463–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1760463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S. Proton translocation reactions in the respiratory chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;456(1):39–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Bragadin M., Azzone G. F. Disequilibrium between steady-state Ca2+ accumulation ratio and membrane potential in mitochondria. Pathway and role of Ca2+ efflux. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5618–5625. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. S., LEHNINGER A. L. STOICHIOMETRY OF RESPIRATORY STIMULATION, ACCUMULATION OF CA++ AND PHOSPHATE, AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN RAT LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3971–3980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynafarje B., Brand M. D., Lehninger A. L. Evaluation of the H+/site ratio of mitochondrial electron transport from rate measurements. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7442–7451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Electric charge stoichiometry of calcium translocation in mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1273–1279. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C., Azzi A., Azzone G. F. Ion transport in liver mitochondria. I. Metabolism-independent Ca++ binding and H+ release. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):951–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C., Scarpa A., Azzone G. F. Ion transport in liver mitochondria. V. The effect of anions on the mechanism of aerobic K+ uptake. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3902–3910. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Carafoli E. The proton pump of cytochrome c oxidase and its stoichiometry. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C. Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:1015–1026. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. J. Possible functions of chains of catalysts. J Theor Biol. 1961 Jan;1:1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(61)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom M. K. Proton pump coupled to cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):271–273. doi: 10.1038/266271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. K., Saari H. T. The mechanism of energy conservation and transduction by mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 17;462(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Krab K. Cytochrome c oxidase is a proton pump: a rejoinder to recent criticism. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 1;91(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J. The history and the hypotheses concerning ATP-formation by energised protons. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 1;85(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



