Abstract
We have determined the packing efficiency at the protein-water interface by calculating the volumes of atoms on the protein surface and nearby water molecules in 22 crystal structures. We find that an atom on the protein surface occupies, on average, a volume approximately 7% larger than an atom of equivalent chemical type in the protein core. In these calculations, larger volumes result from voids between atoms and thus imply a looser or less efficient packing. We further find that the volumes of individual atoms are not related to their chemical type but rather to their structural location. More exposed atoms have larger volumes. Moreover, the packing around atoms in locally concave, grooved regions of protein surfaces is looser than that around atoms in locally convex, ridge regions. This as a direct manifestation of surface curvature-dependent hydration. The net volume increase for atoms on the protein surface is compensated by volume decreases in water molecules near the surface. These waters occupy volumes smaller than those in the bulk solvent by up to 20%; the precise amount of this decrease is directly related to the extent of contact with the protein.
Full text
PDF
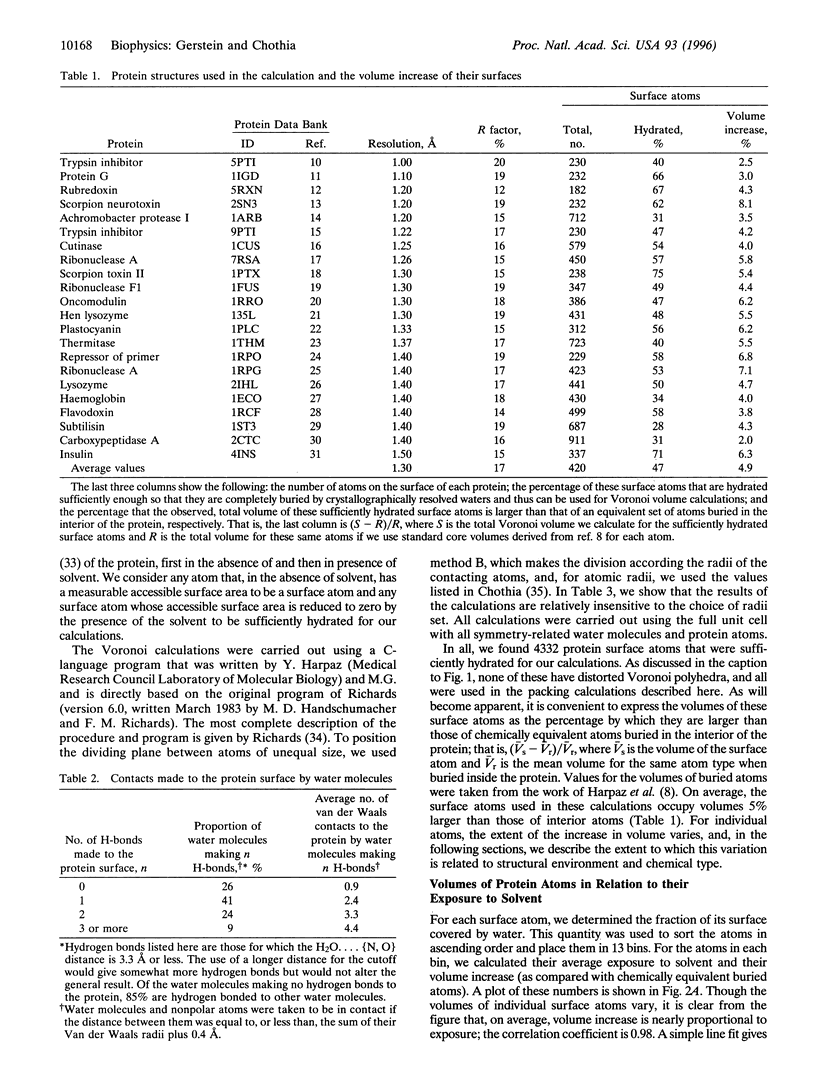

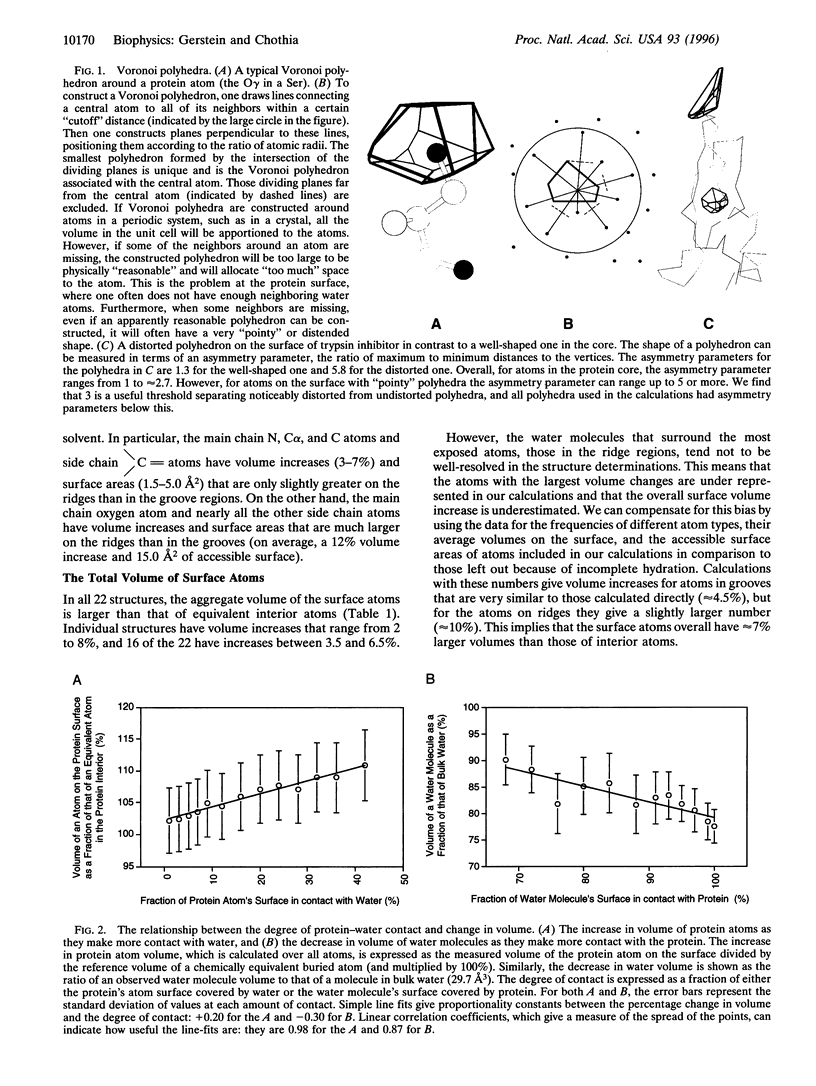
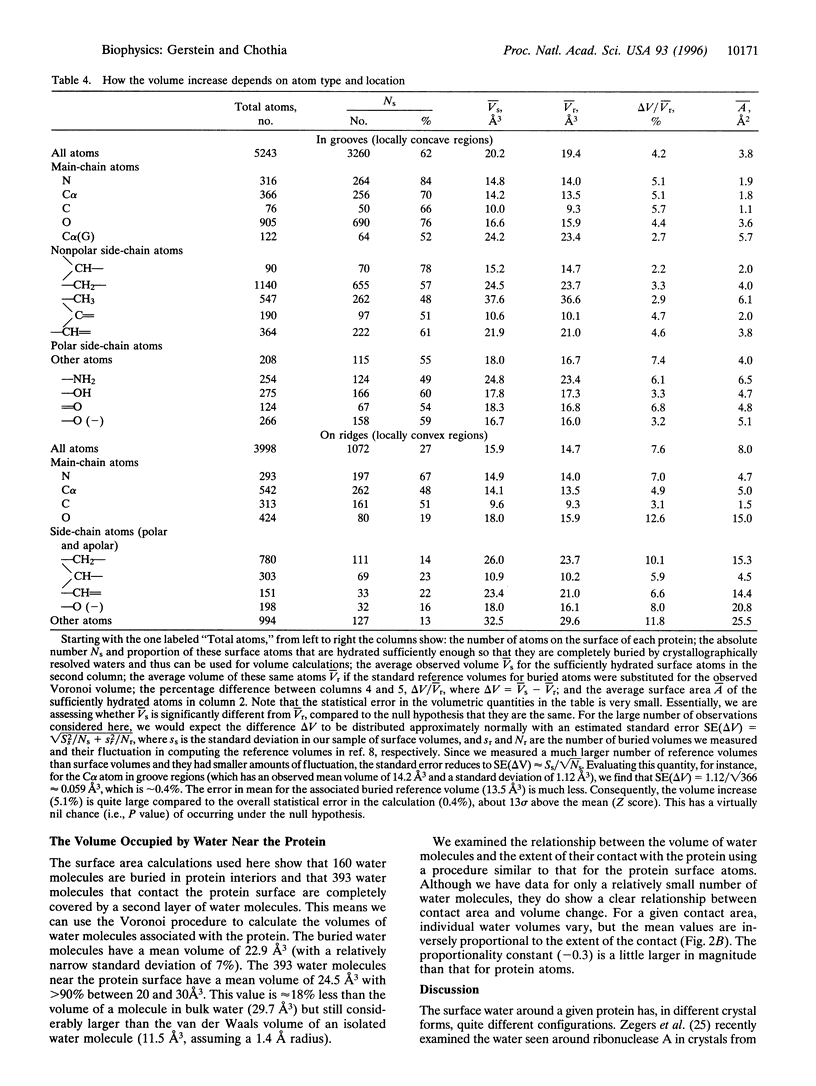

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed F. R., Przybylska M., Rose D. R., Birnbaum G. I., Pippy M. E., MacManus J. P. Structure of oncomodulin refined at 1.85 A resolution. An example of extensive molecular aggregation via Ca2+. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):127–140. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N., Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. M., Hubbard R. E., Isaacs N. W., Reynolds C. D. The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 A resolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1195):369–456. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Pulford W. C., Artymiuk P. J. X-ray studies of water in crystals of lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):693–723. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burling F. T., Weis W. I., Flaherty K. M., Brünger A. T. Direct observation of protein solvation and discrete disorder with experimental crystallographic phases. Science. 1996 Jan 5;271(5245):72–77. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5245.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Structural invariants in protein folding. Nature. 1975 Mar 27;254(5498):304–308. doi: 10.1038/254304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrick J. P., Wigley D. B. The third IgG-binding domain from streptococcal protein G. An analysis by X-ray crystallography of the structure alone and in a complex with Fab. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 11;243(5):906–918. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edsall J. T., McKenzie H. A. Water and proteins. II. The location and dynamics of water in protein systems and its relation to their stability and properties. Adv Biophys. 1983;16:53–183. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(83)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J. S., Kossiakoff A. A., Hurley J. H., Earnest T., Stroud R. M. Solvent structure in crystals of trypsin determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Proteins. 1992 Mar;12(3):203–222. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein M., Lynden-Bell R. M. What is the natural boundary of a protein in solution? J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 20;230(2):641–650. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein M., Tsai J., Levitt M. The volume of atoms on the protein surface: calculated from simulation, using Voronoi polyhedra. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 23;249(5):955–966. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddette D. W., Paech C., Yang S. S., Mielenz J. R., Bystroff C., Wilke M. E., Fletterick R. J. The crystal structure of the Bacillus lentus alkaline protease, subtilisin BL, at 1.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):580–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90843-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss J. M., Bartunik H. D., Freeman H. C. Accuracy and precision in protein structure analysis: restrained least-squares refinement of the structure of poplar plastocyanin at 1.33 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr B. 1992 Dec 1;48(Pt 6):790–811. doi: 10.1107/s0108768192004270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harata K. X-ray structure of monoclinic turkey egg lysozyme at 1.3 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Sep 1;49(Pt 5):497–504. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993005542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz Y., Gerstein M., Chothia C. Volume changes on protein folding. Structure. 1994 Jul 15;2(7):641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housset D., Habersetzer-Rochat C., Astier J. P., Fontecilla-Camps J. C. Crystal structure of toxin II from the scorpion Androctonus australis Hector refined at 1.3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 22;238(1):88–103. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauzmann W., Moore K., Schultz D. Protein densities from X-ray crystallographic coordinates. Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):447–449. doi: 10.1038/248447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn L. A., Siani M. A., Pique M. E., Fisher C. L., Getzoff E. D., Tainer J. A. The interdependence of protein surface topography and bound water molecules revealed by surface accessibility and fractal density measures. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Jr, Kauzmann W. Hydration of proteins and polypeptides. Adv Protein Chem. 1974;28:239–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan B., Lee B. Role of hydrogen bonds in hydrophobicity: the free energy of cavity formation in water models with and without the hydrogen bonds. Biophys Chem. 1994 Aug;51(2-3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)00049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez C., De Geus P., Lauwereys M., Matthyssens G., Cambillau C. Fusarium solani cutinase is a lipolytic enzyme with a catalytic serine accessible to solvent. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):615–618. doi: 10.1038/356615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. T., Shaffie F., Yu C., Satyshur K. A., Stockman B. J., Markley J. L., Sundarlingam M. Structure of the oxidized long-chain flavodoxin from Anabaena 7120 at 2 A resolution. Protein Sci. 1992 Nov;1(11):1413–1427. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Calculation of molecular volumes and areas for structures of known geometry. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:440–464. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: total volume, group volume distributions and packing density. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90570-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Nicholls A., Fine R. F., Honig B. Reconciling the magnitude of the microscopic and macroscopic hydrophobic effects. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):106–109. doi: 10.1126/science.2011744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigemann W., Weber E. Structure of erythrocruorin in different ligand states refined at 1.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):309–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teplyakov A. V., Kuranova I. P., Harutyunyan E. H., Vainshtein B. K., Frömmel C., Höhne W. E., Wilson K. S. Crystal structure of thermitase at 1.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):261–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90160-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teplyakov A., Wilson K. S., Orioli P., Mangani S. High-resolution structure of the complex between carboxypeptidase A and L-phenyl lactate. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Nov 1;49(Pt 6):534–540. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993007267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunasawa S., Masaki T., Hirose M., Soejima M., Sakiyama F. The primary structure and structural characteristics of Achromobacter lyticus protease I, a lysine-specific serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3832–3839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassylyev D. G., Katayanagi K., Ishikawa K., Tsujimoto-Hirano M., Danno M., Pähler A., Matsumoto O., Matsushima M., Yoshida H., Morikawa K. Crystal structures of ribonuclease F1 of Fusarium moniliforme in its free form and in complex with 2'GMP. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):979–996. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassi M., Steif C., Weber P., Tsernoglou D., Wilson K. S., Hinz H. J., Kokkinidis M. Restored heptad pattern continuity does not alter the folding of a four-alpha-helix bundle. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Oct;1(10):706–716. doi: 10.1038/nsb1094-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watenpaugh K. D., Margulis T. N., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Water structure in a protein crystal: rubredoxin at 1.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 25;122(2):175–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watenpaugh K. D., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Crystallographic refinement of rubredoxin at 1 x 2 A degrees resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):615–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Nachman J., Gilliland G. L., Gallagher W., Woodward C. Structure of form III crystals of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Svensson L. A., Sjölin L., Gilliland G. L. Structure of phosphate-free ribonuclease A refined at 1.26 A. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2705–2717. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Walter J., Huber R., Sjölin L. Structure of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Results of joint neutron and X-ray refinement of crystal form II. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):301–329. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zegers I., Maes D., Dao-Thi M. H., Poortmans F., Palmer R., Wyns L. The structures of RNase A complexed with 3'-CMP and d(CpA): active site conformation and conserved water molecules. Protein Sci. 1994 Dec;3(12):2322–2339. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B., Carson M., Ealick S. E., Bugg C. E. Structure of scorpion toxin variant-3 at 1.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):239–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90694-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]