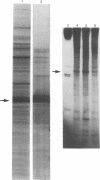
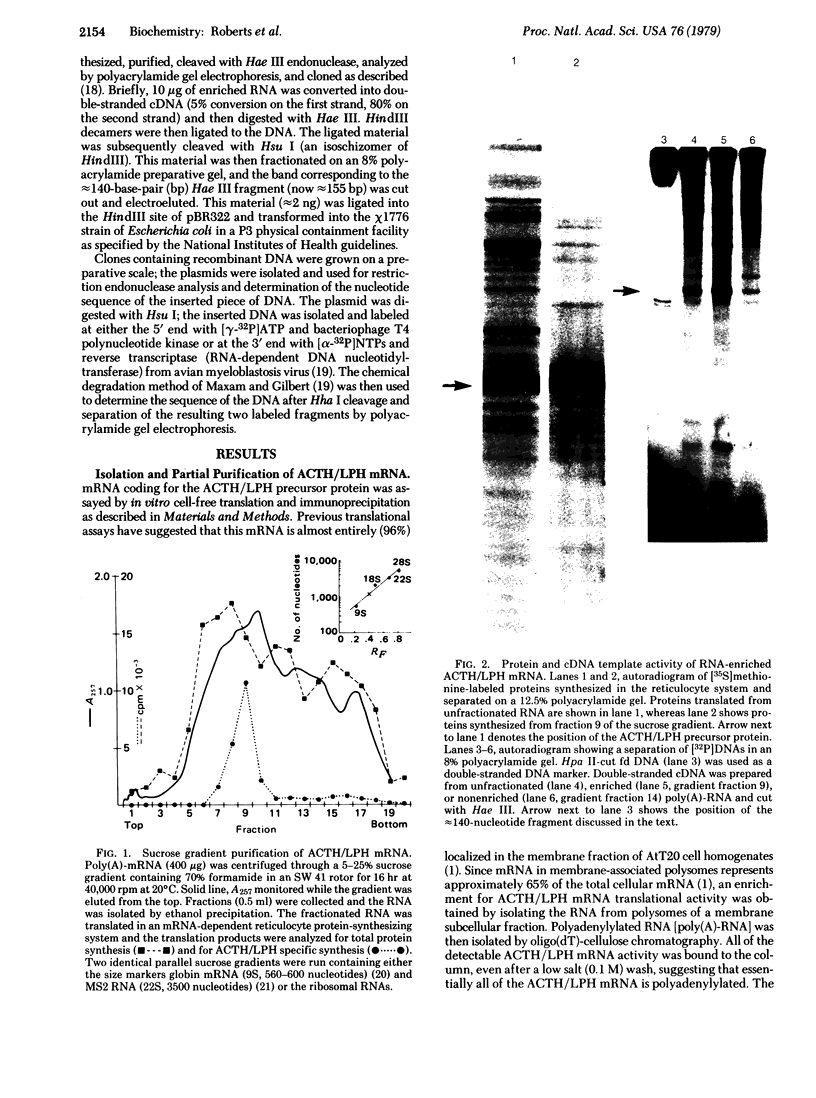
Abstract
A cDNA fragment synthesized from mouse mRNA (ACTH/LPH mRNA) that codes for the precursor polypeptide containing corticotropin (ACTH), beta-lipotropin (LPH), and several other peptides has been cloned in bacteria. The mRNA was enriched for ACTH/LPH mRNA translational activity (to about 75%) prior to cDNA synthesis. It appears to contain about 1200 bases, of which approximately 450 bases are not translated. The cloned DNA fragment is complementary to the region of the mRNA coding for the protein fragment beta-LPH-(44--90); this contains all of the amino acids of [Met]-enkephalin (residues 61--65 of beta-LPH), most of the amino acids of beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, and all but the carboxy-terminal amino acid of beta-endorphin. Based on assignment of the amino acid sequence of mouse beta-LPH from the nucelic acid sequence, it appears that there is extensive homology of mouse beta-LPH with human and porcine beta-LPH. The data also establish the linkage between beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and beta-endorphin as a Lys-Arg sequence. It is hoped that this cloned DNA can be used as a probe to study the expression and structure of the ACTH/LPH gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A., Mains R. E. Analysis of the common precursor to corticotropin and endorphin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5732–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., Grunberger D. Characterization and cell-free translation of mouse pituitary tumor messenger RNA which directs the synthesis of a corticotropin precursor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):476–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., Pulkrabek P., Grunberger D. Mouse pituitary tumor mRNA directed cell-free synthesis of polypeptides that are cross-reactive with adrenocorticotropic hormone antiserum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1490–1495. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90610-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Liotta A., Brownstein M. J. Presence of corticotropin in brain of normal and hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Liotta A., Suda T., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Presence of immunoassayable beta-lipotropin in bovine brain and spinal cord: lack of concordance with ACTH concentrations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):930–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Biosynthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone in mouse pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4115–4120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A., Ling N. Common precursor to corticotropins and endorphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Numa S., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Nunberg J., Schimke R. T. Construction of bacterial plasmids that contain the nucleotide sequence for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6021–6025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Taii S., Hirata Y., Matsukura S., Imura H. A large product of cell-free translation of messenger RNA coding for corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4319–4323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Herbert E. Characterization of a common precursor to corticotropin and beta-lipotropin: cell-free synthesis of the precursor and identification of corticotropin peptides in the molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4826–4830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Herbert E. Characterization of a common precursor to corticotropin and beta-lipotropin: identification of beta-lipotropin peptides and their arrangement relative to corticotropin in the precursor synthesized in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5300–5304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Phillips M., Rosa P. A., Herbert E. Steps involved in the processing of common precursor forms of adrenocorticotropin and endorphin in cultures of mouse pituitary cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3609–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Vargo T. M., Minick S., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Regional dissociation of beta-endorphin and enkephalin contents in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5162–5165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabol S. L. Regulation of endorphin production by glucocorticoids in cultured pituitary tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):560–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90911-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. P., Ratcliffe J. G., Rees L. H., Landon J., Bennett H. P., Lowry P. J., McMartin C. Pituitary peptide. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 18;244(133):65–67. doi: 10.1038/newbio244065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence and amplification in bacteria of structural gene for rat growth hormone. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):486–494. doi: 10.1038/270486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Gage L. P., Brown D. D. The genes for silk fibroin in Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90563-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]