Abstract
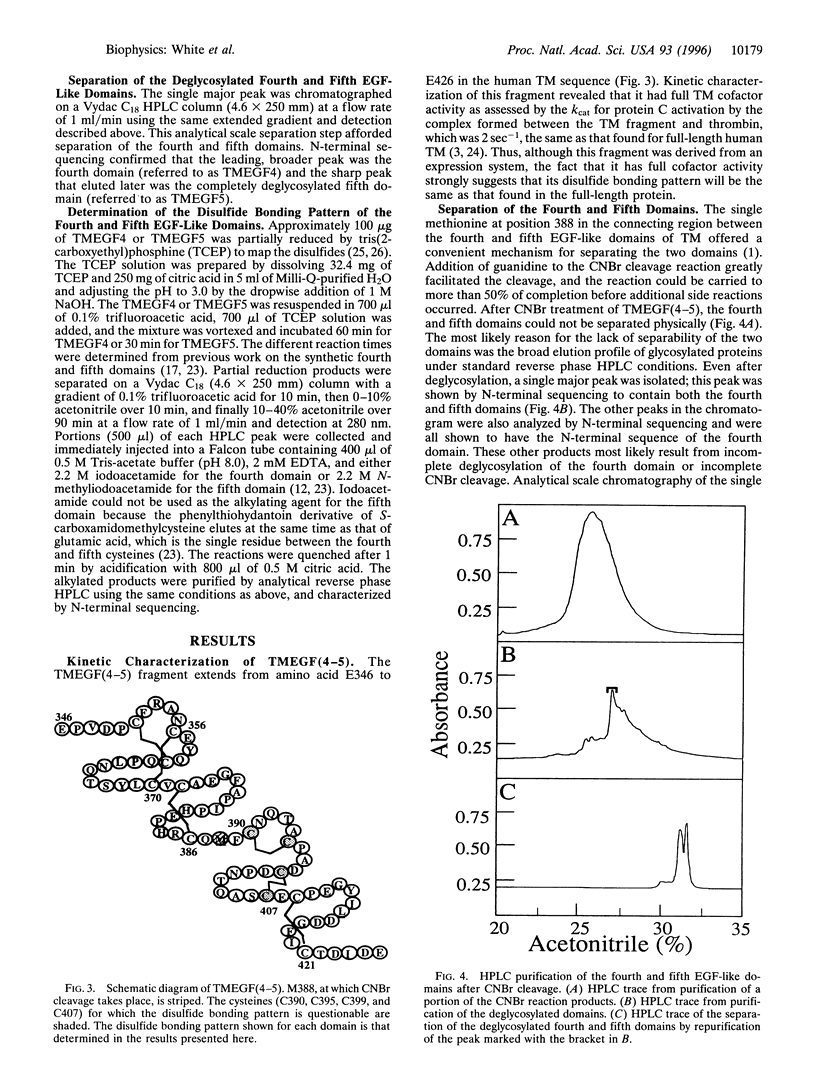
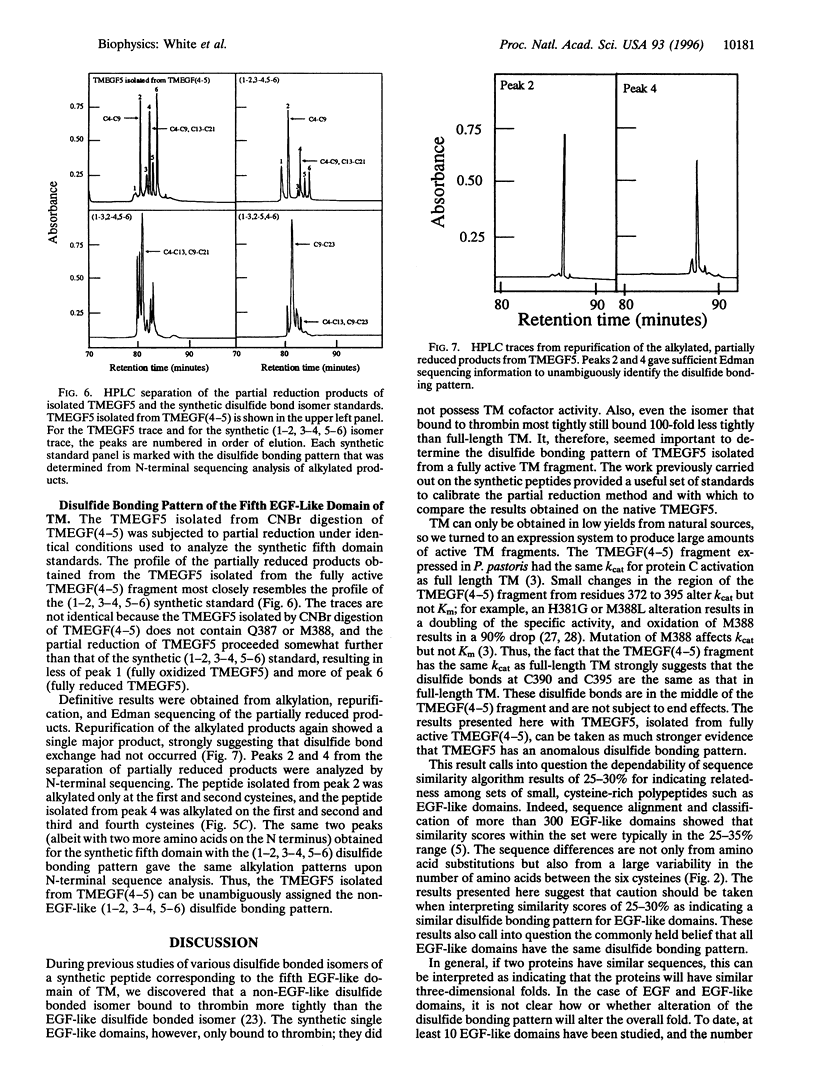
The disulfide bonding pattern of the fourth and fifth epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains within the smallest active fragment of thrombomodulin have been determined. In previous work, this fragment was expressed and purified to homogeneity, and its cofactor activity, as measured by Kcat for thrombin activation of protein C, was the same as that for full-length thrombomodulin. CNBr cleavage at the single methionine in the connecting region between the domains and subsequent deglycosylation yielded the individual EGF-like domains. The disulfide bonds were mapped by partial reduction with tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine according to the method of Gray [Gray, W. R. (1993) Protein Sci. 2, 1732-1748], which provides unambiguous results. The disulfide bonding pattern of the fourth EGF-like domain was (1-3, 2-4, 5-6), which is the same as that found previously in EGF and in a synthetic version of the fourth EGF-like domain. Surprisingly, the disulfide bonding pattern of the fifth domain was (1-2, 3-4, 5-6), which is unlike that found in EGF or in any other EGF-like domain analyzed so far. This result is in line with an earlier observation that the (1-2, 3-4, 5-6) isomer bound to thrombin more tightly than the EGF-like (1-3, 2-4, 5-6) isomer. The observation that not all EGF-like domains have an EGF-like disulfide bonding pattern reveals an additional element of diversity in the structure of EGF-like domains.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler M., Seto M. H., Nitecki D. E., Lin J. H., Light D. R., Morser J. The structure of a 19-residue fragment from the C-loop of the fourth epidermal growth factor-like domain of thrombomodulin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23366–23372. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Norman D. G., Harvey T. S., Handford P. A., Mayhew M., Tse A. G., Brownlee G. G., Campbell I. D. The three-dimensional structure of the first EGF-like module of human factor IX: comparison with EGF and TGF-alpha. Protein Sci. 1992 Jan;1(1):81–90. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G. The many faces of epidermal growth factor repeats. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):410–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S. Computer-based characterization of epidermal growth factor precursor. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):558–560. doi: 10.1038/307558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface. FASEB J. 1995 Jul;9(10):946–955. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.10.7615164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser C. B., Morser J., Clarke J. H., Blasko E., McLean K., Kuhn I., Chang R. J., Lin J. H., Vilander L., Andrews W. H. Oxidation of a specific methionine in thrombomodulin by activated neutrophil products blocks cofactor activity. A potential rapid mechanism for modulation of coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2565–2573. doi: 10.1172/JCI116151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Crowther R. L., Chandran C., Rumberger J. M., Li S., Huang K. S., Presky D. H., Familletti P. C., Wolitzky B. A., Burns D. K. Insight into E-selectin/ligand interaction from the crystal structure and mutagenesis of the lec/EGF domains. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):532–538. doi: 10.1038/367532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R. Disulfide structures of highly bridged peptides: a new strategy for analysis. Protein Sci. 1993 Oct;2(10):1732–1748. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R. Echistatin disulfide bridges: selective reduction and linkage assignment. Protein Sci. 1993 Oct;2(10):1749–1755. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. P., Petros A. M., Meadows R. P., Nettesheim D. G., Mazar A. P., Olejniczak E. T., Xu R. X., Pederson T. M., Henkin J., Fesik S. W. Solution structure of the amino-terminal fragment of urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 26;33(16):4847–4864. doi: 10.1021/bi00182a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Henikoff J. G. Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10915–10919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel U., Harvey T. S., Driscoll P. C., Campbell I. D. Human epidermal growth factor. High resolution solution structure and comparison with human transforming growth factor alpha. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90697-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrabal R., Komives E. A., Ni F. Structural resiliency of an EGF-like subdomain bound to its target protein, thrombin. Protein Sci. 1996 Feb;5(2):195–203. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560050202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. H., Ke X. H., Sweeney W., Tam J. P. Calcium binding and putative activity of the epidermal growth factor domain of blood coagulation factor IX. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91631-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. J., Komives E. A. Thrombin-binding affinities of different disulfide-bonded isomers of the fifth EGF-like domain of thrombomodulin. Protein Sci. 1995 Oct;4(10):2129–2137. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Magnusson S. Disulphide bridges of bovine factor X. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj2450887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lougheed J. C., Bowman C. L., Meininger D. P., Komives E. A. Thrombin inhibition by cyclic peptides from thrombomodulin. Protein Sci. 1995 Apr;4(4):773–780. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meininger D. P., Hunter M. J., Komives E. A. Synthesis, activity, and preliminary structure of the fourth EGF-like domain of thrombomodulin. Protein Sci. 1995 Sep;4(9):1683–1695. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Burgess A. W., Nice E. C., Wagner G., Gibson K. D., Scheraga H. A. Solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor determined by NMR spectroscopy and refined by energy minimization with restraints. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):236–249. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy F. J., Li Y. C., Rauenbuehler P., Winkler M. E., Scheraga H. A., Montelione G. T. Solution structure of human type-alpha transforming growth factor determined by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy and refined by energy minimization with restraints. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7334–7353. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Kohda D., Hatanaka H., Ichikawa S., Matsuda S., Yamamoto T., Suzuki A., Inagaki F. Solution structure of the epidermal growth factor-like domain of heregulin-alpha, a ligand for p180erbB-4. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3517–3523. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan K., Padmanabhan K. P., Tulinsky A., Park C. H., Bode W., Huber R., Blankenship D. T., Cardin A. D., Kisiel W. Structure of human des(1-45) factor Xa at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):947–966. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. F., Grinnell B. W., Moore R. E., Hoskins J., Vlahos C. J., Bang N. U. Stable expression of a secretable deletion mutant of recombinant human thrombomodulin in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12602–12610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander-Sunnerhagen M., Ullner M., Persson E., Teleman O., Stenflo J., Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642–19649. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ccf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. O., Downing A. K., Driscoll P. C., Dudgeon T. J., Campbell I. D. The solution structure and backbone dynamics of the fibronectin type I and epidermal growth factor-like pair of modules of tissue-type plasminogen activator. Structure. 1995 Aug 15;3(8):823–833. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan J., Hu S., Hrabal R., Zhu Y., Komives E. A., Ni F. Thrombin-bound structure of an EGF subdomain from human thrombomodulin determined by transferred nuclear Overhauser effects. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13553–13560. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns D. J., Kurosawa S., Esmon C. T. Microthrombomodulin. Residues 310-486 from the epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain of thrombomodulin will accelerate protein C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3352–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. E., Hunter M. J., Meininger D. P., White L. R., Komives E. A. Large-scale expression, purification and characterization of small fragments of thrombomodulin: the roles of the sixth domain and of methionine 388. Protein Eng. 1995 Nov;8(11):1177–1187. doi: 10.1093/protein/8.11.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Bringman T., Marks B. J. The purification of fully active recombinant transforming growth factor alpha produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13838–13843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


