Abstract
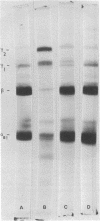
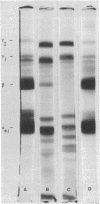
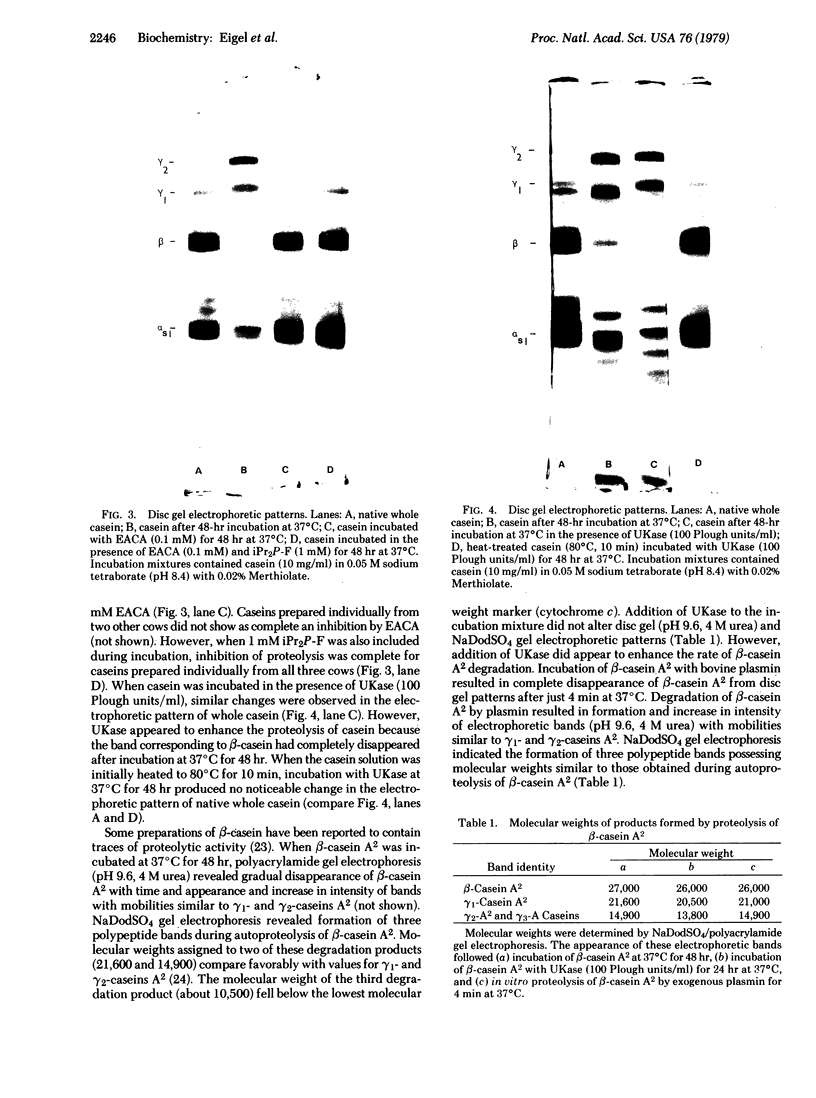
Plasminogen was found to be present in bovine milk by crossreactivity between rabbit antiserum to plasminogen and casein prepared from milk by acid precipitation. This result was further supported by recovery of intact 125I-labeled plasminogen from rabbit milk after its intravenous injection. Freshly isolated whole bovine casein was observed to undergo slow autoproteolysis at 37 degrees C. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed gradual disappearance of major caseins accompanied by appearance and increase in intensity of numerous electrophoretic bands. This autoproteolysis was inhibited by low concentrations of epsilon-aminocaproic acid (0.1 mM) and diisopropyl fluorophosphate (1 mM); catalytic amounts of urokinase accelerated the process. Autoproteolysis of isolated bovine beta-casein was shown by both urea and sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis to result in formation of gamma 1- and gamma 2-caseins. Similar electrophoretic bands were formed when beta-casein was degraded by plasmin prepared from bovine blood serum. These results support the hypothesis that bovine plasmin occurs in milk and is identical to alkaline milk protease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRECHTSEN O. K. The fibrinolytic activity of human tissues. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):284–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., STERNDORFF I. A fibrinolytic system in human milk. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):605–608. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Tissue activators of plasminogen. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):42–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B., Kwaan H. C. Plasminogen activator activity in cultures from human tissues. An immunological and histochemical study. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1740–1753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino F. J., Sodetz J. M. Rabbit plasminogen and plasmin isozymes. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:273–286. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibber B. A., Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Affinity chromatography of plasminogen. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:424–432. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., HORBETT A. P. Human gamma globulin fractionation on anion exchange cellulose columns. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2645–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon W. G., Groves M. L., Greenberg R., Jones S. B., Kalan E. B., Peterson R. F., Townend R. E. Probable identification of -, TS-, R- and S-caseins as fragments of -casein. J Dairy Sci. 1972 Feb;55(2):261–263. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(72)85469-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon W. G., Groves M. L. Primary sequence of beta, gamma, and caseins. J Dairy Sci. 1975 Apr;58(4):574–582. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(75)84613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. L., Gordon W. G. Evidence from amino acid analysis for a relationship in the biosynthesis of gamma- and beta-caseins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 23;194(2):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. L., Kiddy C. A. Polymorphism of gamma-casein in cow's milk. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):188–193. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90573-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto M., Abiko Y., Shimizu M. Plasminogen-plasmin system. 3. Kinetics of plasminogen activation and inhibition of plasminogen-plasmin system by some synthetic inhibitors. J Biochem. 1968 Dec;64(6):759–767. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. J., Kline D. L., Alkjaersig N. Assay methods and standard preparations for plasmin, plasminogen and urokinase in purified systems, 1967-1968. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Apr 30;21(2):259–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peaker M., Taylor J. C. Milk secretion in the rabbit: changes during lactation and the mechanism of ion transport. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):527–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribadeau Dumas B., Brignon G., Grosclaude F., Mercier J. C. Structure primaire de la caséine beta bovine. Séquence complète. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Hsieh B., Groskopf W. R., Robbins K. C. The isolation and characterization of the S-carboxymethyl beta (light) chain derivative of human plasmin. The localization of the active site on the beta (light) chain. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5046–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther P. J., Steinman H. M., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Activation of human plasminogen by urokinase. Partial characterization of a pre-activation peptide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1173–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney R. M., Brunner J. R., Ebner K. E., Farrell H. M., Jr, Josephson R. V., Morr C. V., Swaisgood H. E. Nomemclature of the proteins of cow's milk: fourth revision. J Dairy Sci. 1976 May;59(5):795–815. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(76)84280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]