Abstract
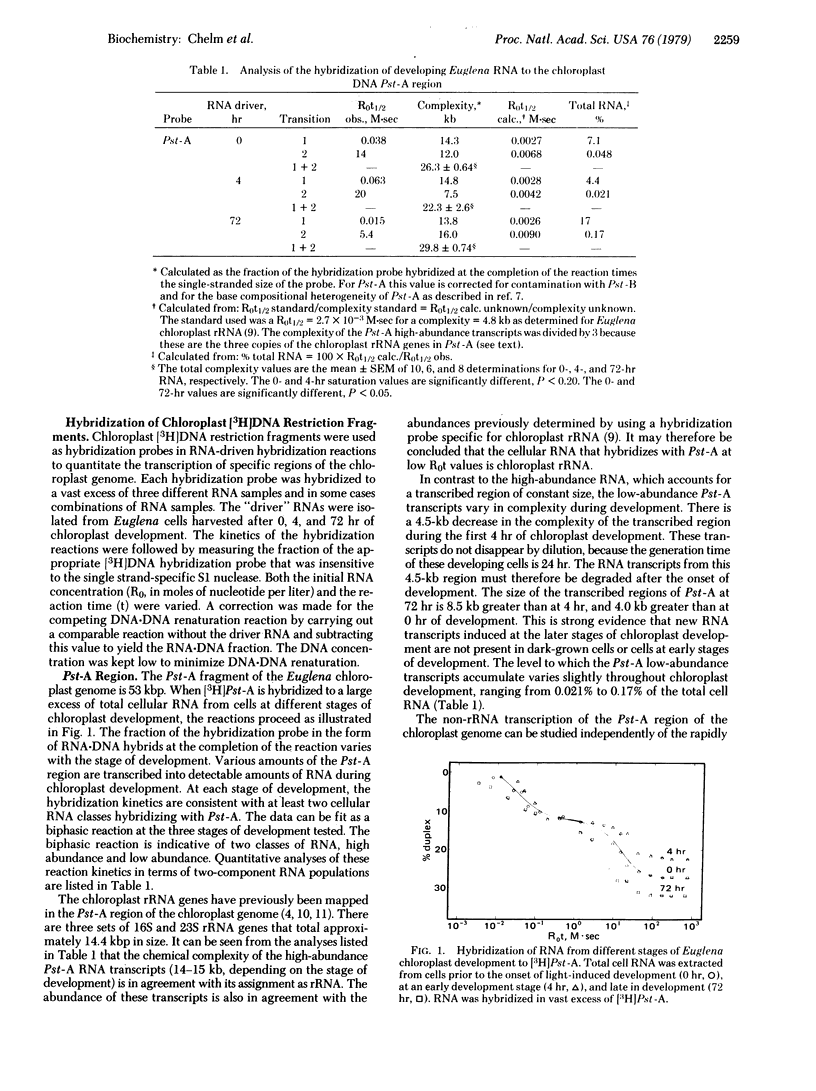
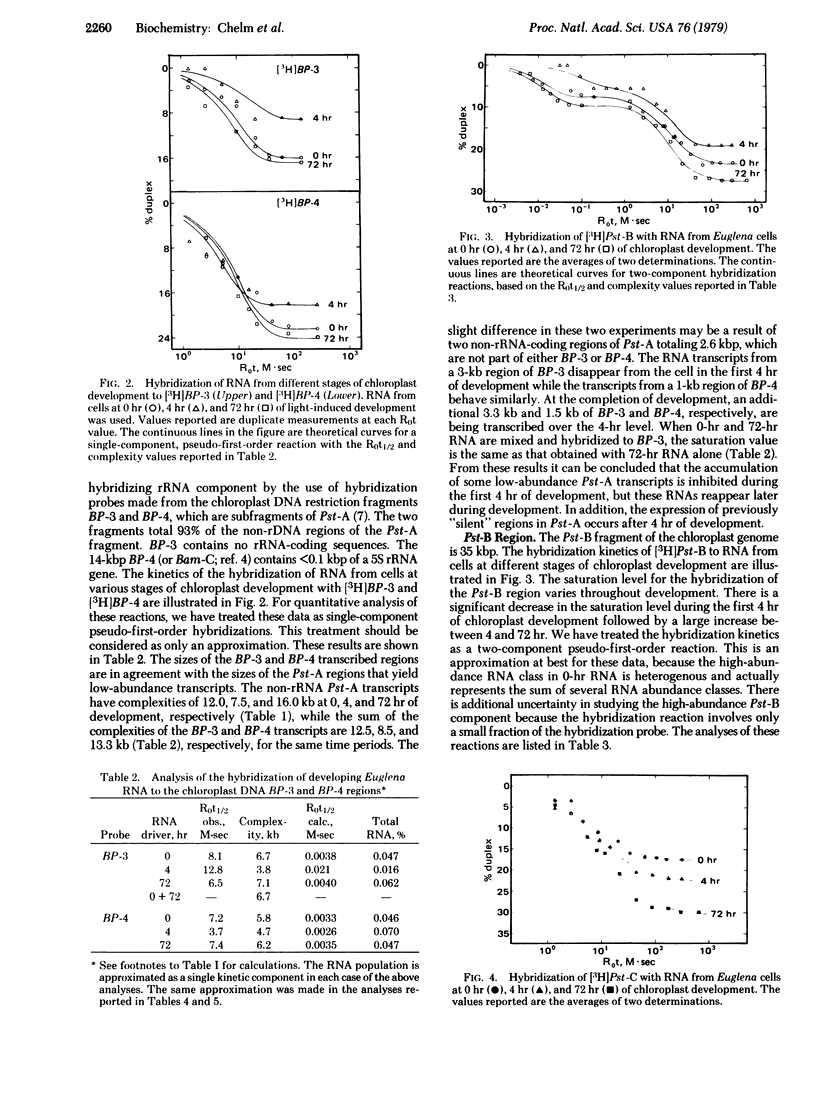
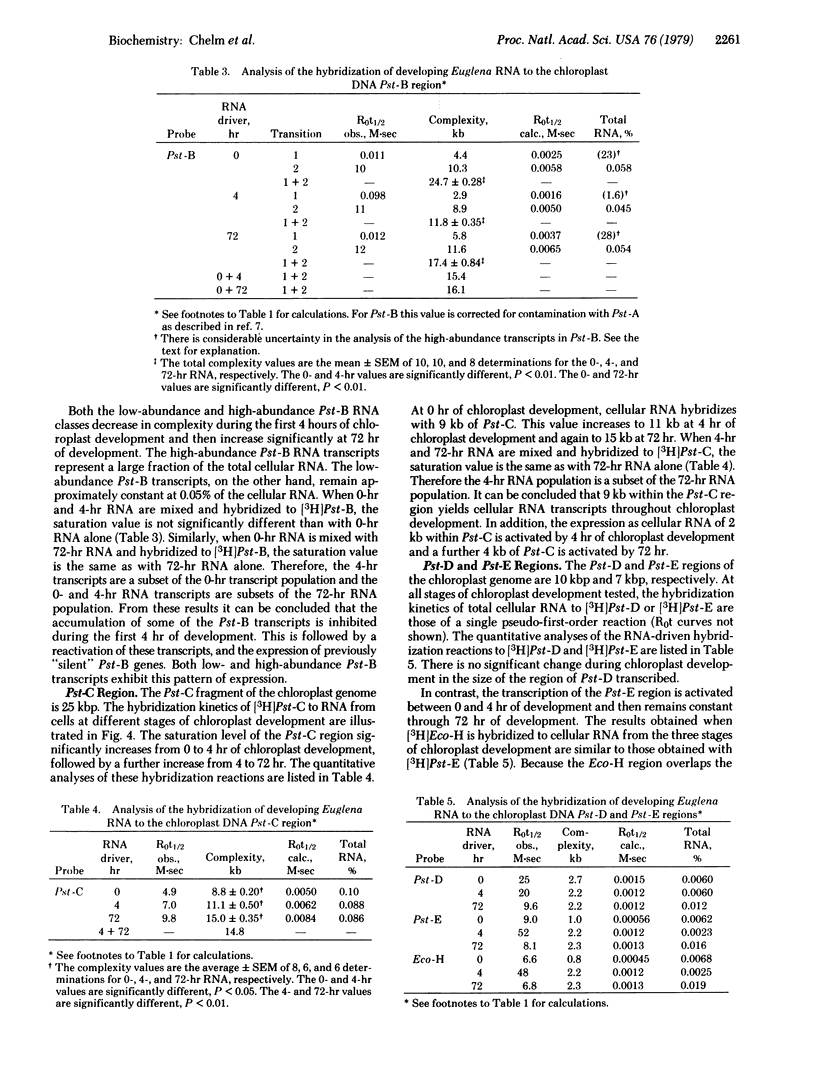
RNA transcription in Euglena gracilis chloroplasts has been characterized by hybridization of RNA from cells at different stages of chloroplast development to 3H-labeled chloroplast DNA restriction endonuclease fragments. Chloroplast DNA was digested into five fragments of 53,000, 35,000, 25,000, 10,000, and 6900 base pairs with Pst I. The 53,000-base-pair DNA was further cleaved by BamHI digestion. Eight different DNA fragments, of known restriction nuclease map location and accounting for the entire genome, were labeled in vitro by means of the nick translation reaction of DNA polymerase I with [3H]dTTP as a substrate. RNA was isolated from dark-adapted Euglena cells, and from cells at an early (4 hr) and a late (72 hr) stage of light-induced chloroplast development. The RNAs were hybridized in solution to each 3H-labeled chloroplast DNA fragment. From the extents and kinetics of the reactions, a temporal program for RNA transcription from defined regions of the chloroplast genome could be described. Different classes of transcription units are present, including RNAs (i) continuously present throughout development, (ii) induced at the onset of development, (iii) repressed early in development, and (iv) induced late in development.
Keywords: restriction endonuclease fragments, nick translation, RNA·DNA hybridization kinetics, transcription mapping
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Shaul Y., Schiff J. A., Epstein H. T. Studies of Chloroplast Development in Euglena. VII. Fine Structure of the Developing Plastid. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):231–240. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Haselkorn R. Chloroplast RNA populations in dark-grown, light-grown, and greening Euglena gracilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2536–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Mapping of transcribed regions of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4239–4244. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Hallick R. B. Changes in the expression of the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis during chloroplast development. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):593–599. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Hoben P. J., Hallick R. B. Cellular content of chloroplast DNA and chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes in Euglena gracilis during chloroplast development. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):782–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Schiff J. A. Events surrounding the early development of Euglena chloroplasts. Photoregulation of the transcription of chloroplastic and cytoplasmic ribosomal RNAs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Physical mapping of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA and ribosomal RNA gene region. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):284–289. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Restriction endonuclease map of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1665–1671. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenni B., Stutz E. Physical mapping of the ribosomal DNA region of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Richards O. C. Isolation and molecular weight of circular chloroplast DNA from Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 15;259(3):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawson J. R., Boerma C. L. A measurement of the fraction of chloroplast DNA transcribed during chloroplast development in Euglena gracilis. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):588–592. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. A., Zeldin M. H., Rubman J. Chlorophyll Formation and Photosynthetic Competence in Euglena During Light-Induced Chloroplast Development in the Presence of 3, (3,4-dichlorophenyl) 1,1-Dimethyl Urea (DCMU). Plant Physiol. 1967 Dec;42(12):1716–1725. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.12.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


