Abstract
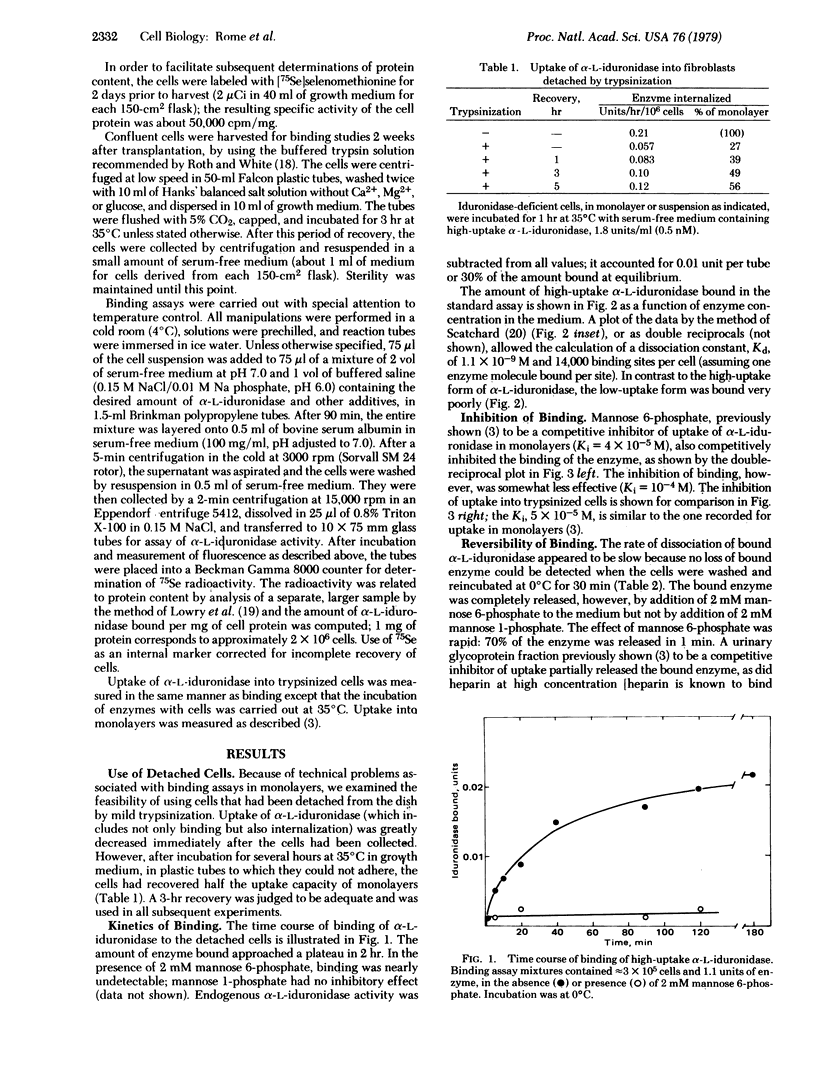
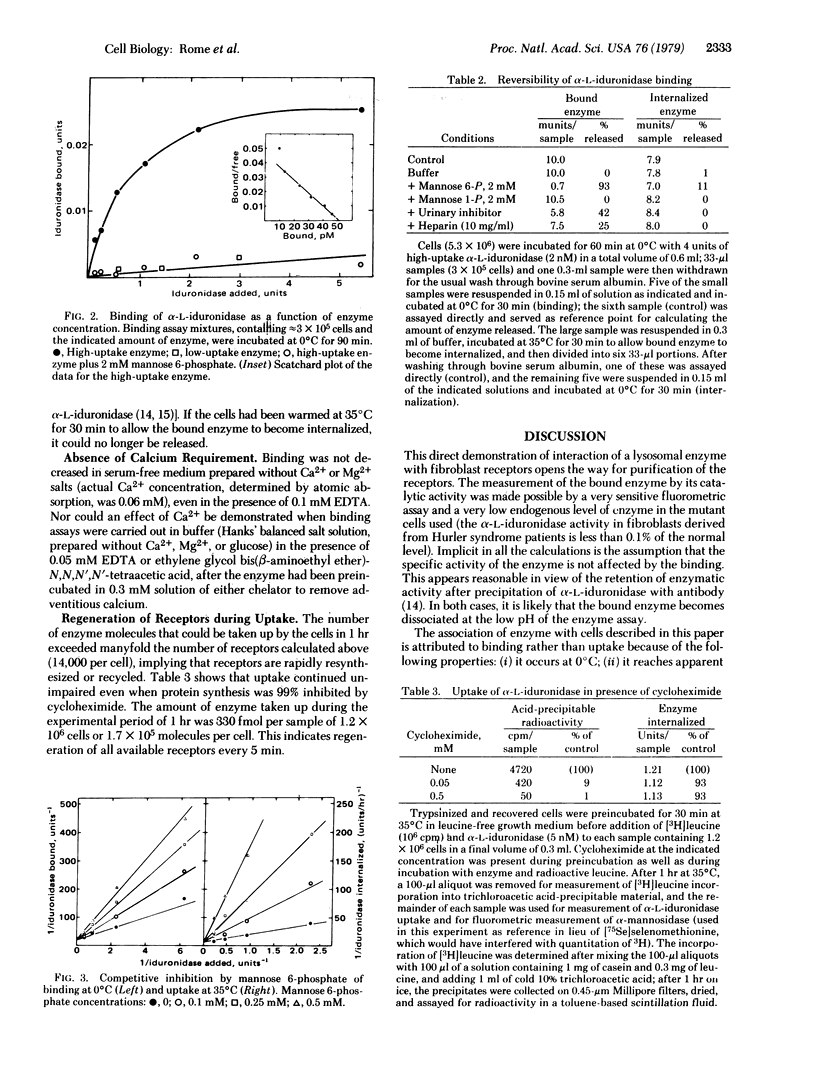
Receptor-binding of "high-uptake" forms of lysosomal enzymes to human diploid skin fibroblasts had been predicted from the Michaelis--Menten kinetics of uptake of these enzymes [e.g., Sando, G.N. & Neufeld, E.F. (1977) Cell 12, 619--627]. We have now demonstrated such binding directly by using a sensitive assay for the bound enzyme. Cells deficient in alpha-L-iduronidase were detached from plastic dishes by mild trypsinization, allowed to recover, and used in suspension. They were incubated with urinary alpha-L-iduronidase at 0 degrees C for 90 minutes and then washed by centrifugation through concentrated bovine serum albumin; the activity of the cell-associated enzyme was measured with 4-methylumbelliferyl alpha-L-iduronide as substrate. A Scatchard analysis showed 14,000 binding sites per cell and a Kd of 1 x 10(-9) M for high-uptake alpha-L-iduronidase; binding of the low-uptake form was barely detectable. Mannose 6-phosphate, a known competitive inhibitor of uptake, inhibited the binding competitively, with Ki = 1 x 10(-4) M. Unexpectedly, mannose 6-phosphate greatly accelerated the dissociation of bound enzyme. During uptake of alpha-L-iduronidase at 35 degrees C, the receptors were regenerated every few minutes, even in the absence of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Characterization of the low density lipoprotein receptor in membranes prepared from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3852–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot F. E., Glaser J. H., Roozen K. J., Sly W. S., Stahl P. D. In vitro correction of deficient human fibroblasts by beta-glucuronidase from different human sources. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORHAM L. W., WAYMOUTH C. DIFFERENTIATION IN VITRO OF EMBRYONIC CARTILAGE AND BONE IN A CHEMICALLY-DEFINED MEDIUM. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:287–290. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. W., Liebaers I., Di Natale P., Neufeld E. F. Enzymic diagnosis of the genetic mucopolysaccharide storage disorders. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:439–456. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Shapiro L. J., Neufeld E. F. A recognition marker required for uptake of a lysosomal enzyme by cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieber V., Distler J., Myerowitz R., Schmickel R. D., Jourdian G. W. The role of glycosidically bound mannose in the assimilation of beta-galactosidase by generalized gangliosidosis fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90868-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Achord D. T., Sly W. S. Phosphohexosyl components of a lysosomal enzyme are recognized by pinocytosis receptors on human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Fischer D., Achord D., Sly W. Phosphohexosyl recognition is a general characteristic of pinocytosis of lysosomal glycosidases by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1172/JCI108860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Isolation and characterization of an avian hepatic binding protein specific for N-acetylglucosamine-terminated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6536–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Lim T. W., Shapiro L. J. Inherited disorders of lysosomal metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:357–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Sando G. N., Garvin A. J., Rome L. H. The transport of lysosomal enzymes. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):95–101. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome L. H., Garvin A. J., Neufeld E. F. Human kidney alpha-L-iduronidase: purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Aug;189(2):344–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., White D. Intercellular contact and cell-surface galactosyl transferase activity (cell culture-mouse-radioautography-contact inhibition-cis-and trans-galactosylation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando G. N., Neufeld E. F. Recognition and receptor-mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-l-iduronidase, by cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. J., Hall C. W., Leder I. G., Neufeld E. F. The relationship of alpha-L-iduronidase and Hurler corrective factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular membrane topology and turnover of a rat hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P., Schneider Y. J., Trouet A. The fate of the plasma membrane during endocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(6):1809–1815. doi: 10.1042/bst0051809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K., Mersmann G., Weber E., Von Figura K. Evidence for lysosomal enzyme recognition by human fibroblasts via a phosphorylated carbohydrate moiety. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1700643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann B. Synthetic substrates for alpha-L-iduronidase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:141–150. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Weber E. An alternative hypothesis of cellular transport of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Effect of inhibitors of lysosomal enzyme endocytosis on intra- and extra-cellular lysosomal enzyme activities. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):943–950. doi: 10.1042/bj1760943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


