Abstract
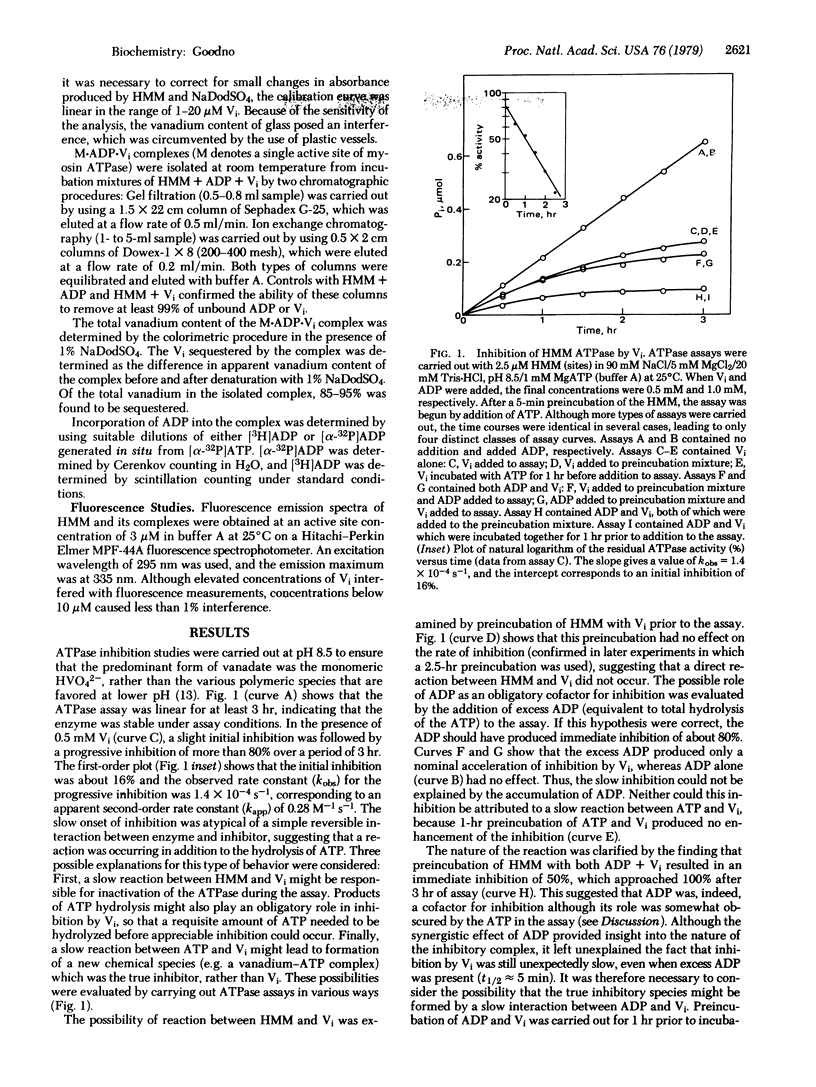
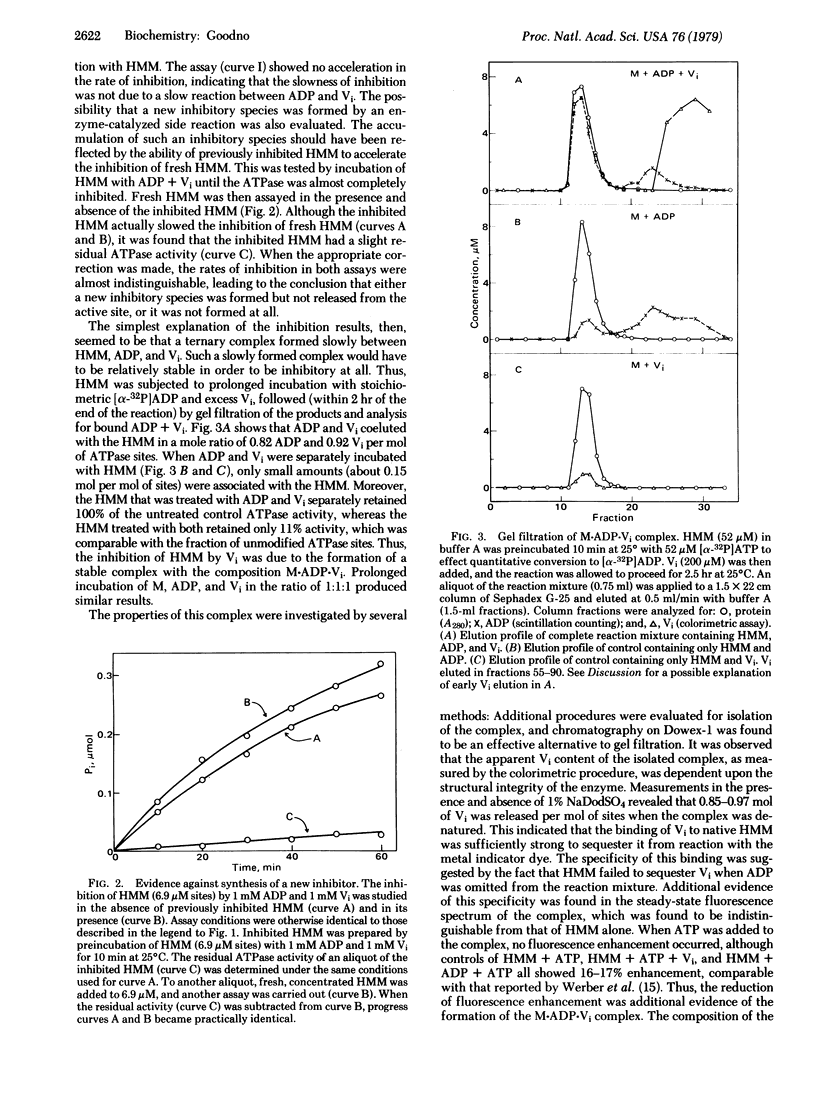
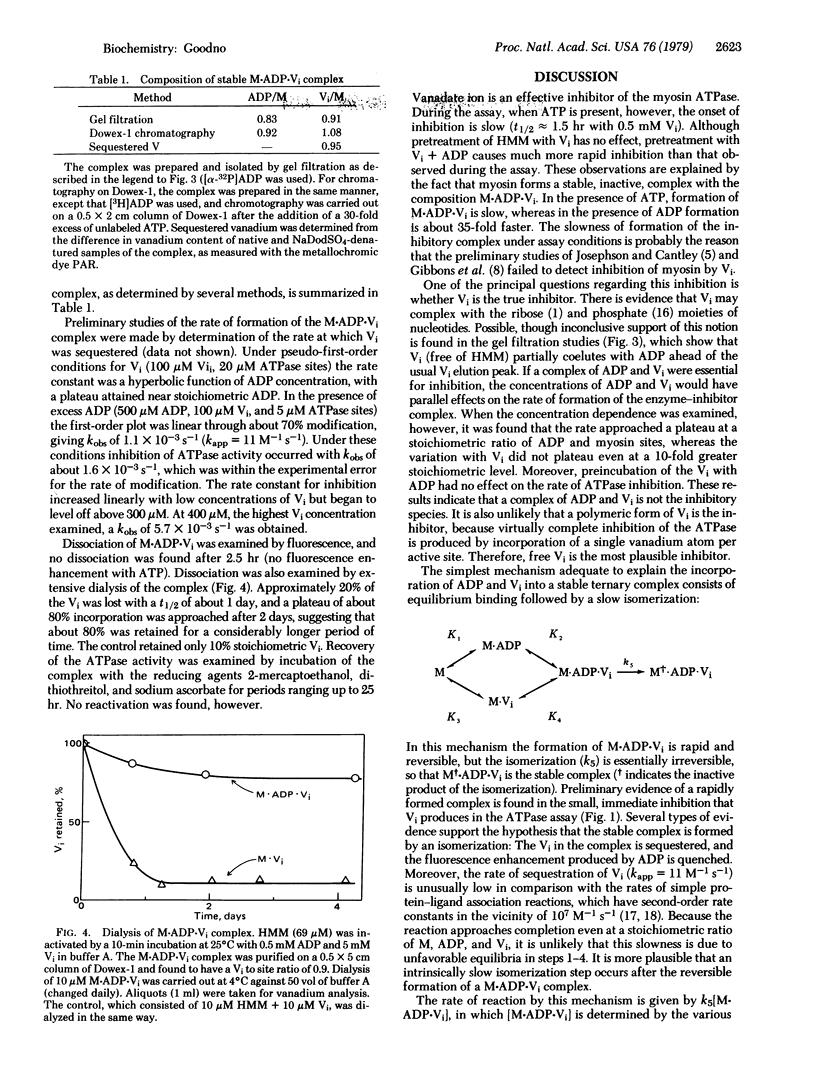
Inhibition of the myosin ATPase by vanadate ion (Vi) has been studied in 90 mM NaCl/5 mM MgCl2/20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, at 25 degrees C. Although the onset of inhibition during the assay is slow and dependent upon Vi concentration (kapp approximately 0.3 M-1 s-1), the final level of inhibition approaches 100%, provided the Vi concentration is in slight excess over the concentration of ATPase sites. Inhibition is not reversible by dialysis or the addition of reducing agents. The source of this irreversible inhibition consists of the formation of a stable, inactive complex with the composition M . ADP . Vi (where M represents a single myosin active site). The complex has been isolated, and its mechanism of formation from M, ADP, and Vi has been studied. Omission of ATP increases the rate of formation by about 35-fold (kapp approximately 11 M-1 s-1), yet this rate is still low in comparison with the rates of simple protein-ligand association reactions. This slowness is interpreted in terms of a rate-limited isomerization step that follows the association of M+, ADP, and Vi: M+ . ADP . Vi leads to M+. ADP . Vi (+ indicates the inactive product of the isomerization). The properties of M.ADP.Vi are compared with those of the ATPase intermediate M**.ADP . Pi, and the possible role of Vi as an analog of Pi is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagshaw C. R., Eccleston J. F., Eckstein F., Goody R. S., Gutfreund H., Trentham D. R. The magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of myosin. Two-step processes of adenosine triphosphate association and adenosine diphosphate dissociation. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):351–364. doi: 10.1042/bj1410351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R., Trentham D. R. The characterization of myosin-product complexes and of product-release steps during the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase reaction. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):331–349. doi: 10.1042/bj1410331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Cantley L. G., Josephson L. A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na,K)-ATPase. Mechanistic and regulatory implications. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7361–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMaster E. G., Mitchell A. A comparison of arsenate and vanadate as inhibitors or uncouplers of mitochondrial and glycolytic energy metabolism. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 11;12(19):3616–3621. doi: 10.1021/bi00743a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Cosson M. P., Evans J. A., Gibbons B. H., Houck B., Martinson K. H., Sale W. S., Tang W. J. Potent inhibition of dynein adenosinetriphosphatase and of the motility of cilia and sperm flagella by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H. Kinetic analysis of the properties and reactions of enzymes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(2):161–195. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H. Transients and relaxation kinetics of enzyme reactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:315–344. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson L., Cantley L. C., Jr Isolation of a potent (Na-K)ATPase inhibitor from striated muscle. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4572–4578. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Secemski I. I., Koehler K. A., Lindquist R. N. Enzymatic catalysis and the transition state theory of reaction rates: transition state analogs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:45–51. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. N., Lynn J. L., Jr, Lienhard G. E. Possible transition-state analogs for ribonuclease. The complexes of uridine with oxovanadium(IV) ion and vanadium(V) ion. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Dec 26;95(26):8762–8768. doi: 10.1021/ja00807a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez V., Stevens T., Lindquist R. N. Vanadium ion inhibition of alkaline phosphatase-catalyzed phosphate ester hydrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-White E. J., Watts D. C. Inhibition of adenosine 5'-triphosphate-creatine phosphotransferase by substrate-anion complexes. Evidence for the transition-state organization of the catalytic site. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):727–740. doi: 10.1042/bj1220727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUSSKY H. H., SHORR E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R., Eccleston J. F., Bagshaw C. R. Kinetic analysis of ATPase mechanisms. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 May;9(2):217–281. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanEtten R. L., Waymack P. P., Rehkop D. M. Letter: Transition metal ion inhibition of enzyme-catalyzed phosphate ester displacement reactions. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Oct 16;96(21):6782–6785. doi: 10.1021/ja00828a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werber M. M., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Fasman G. D. Fluorescence studies on heavy meromyosin-substrate interaction. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2872–2883. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG D. M., HIMMELFARB S., HARRINGTON W. F. ON THE STRUCTURAL ASSEMBLY OF THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS OF HEAVY MEROMYOSIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2428–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


