Abstract
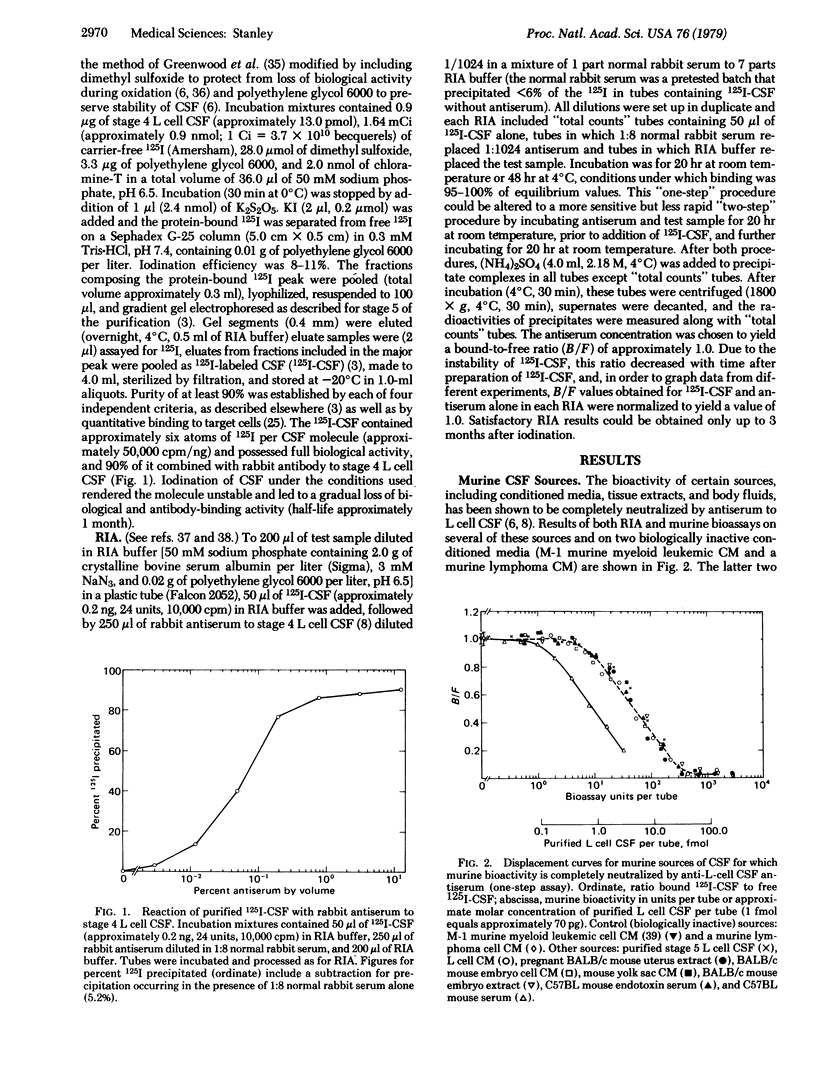
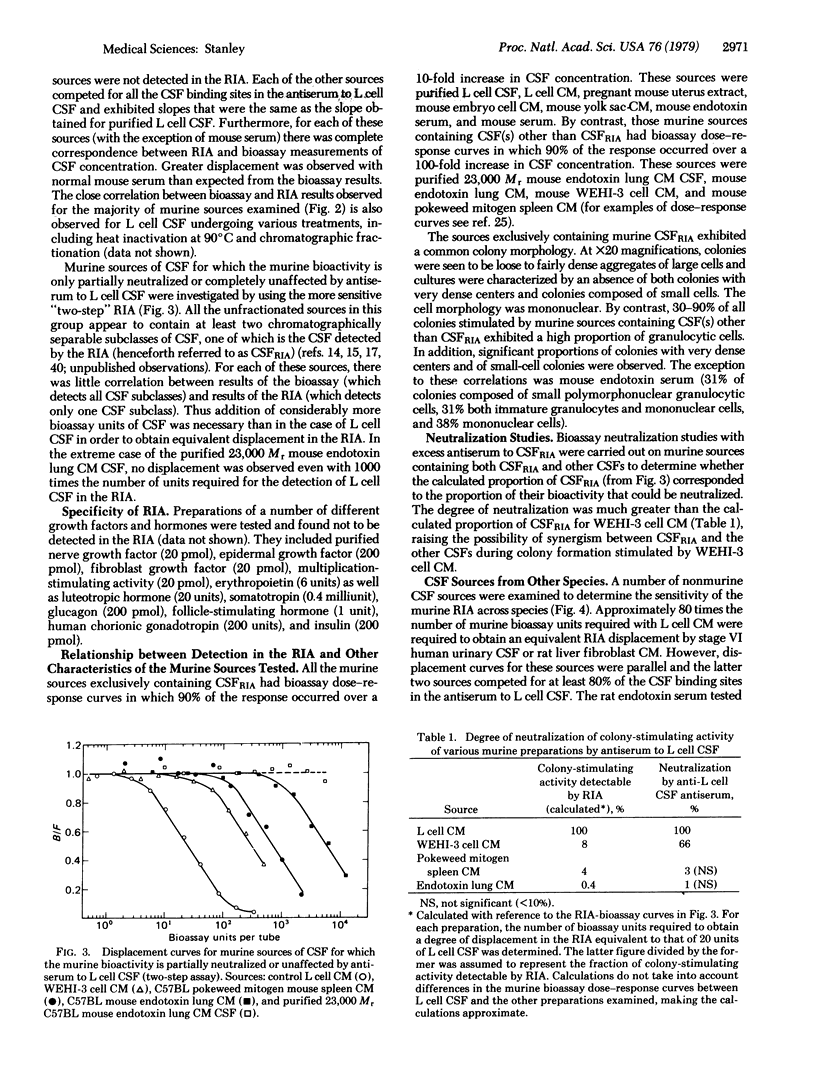
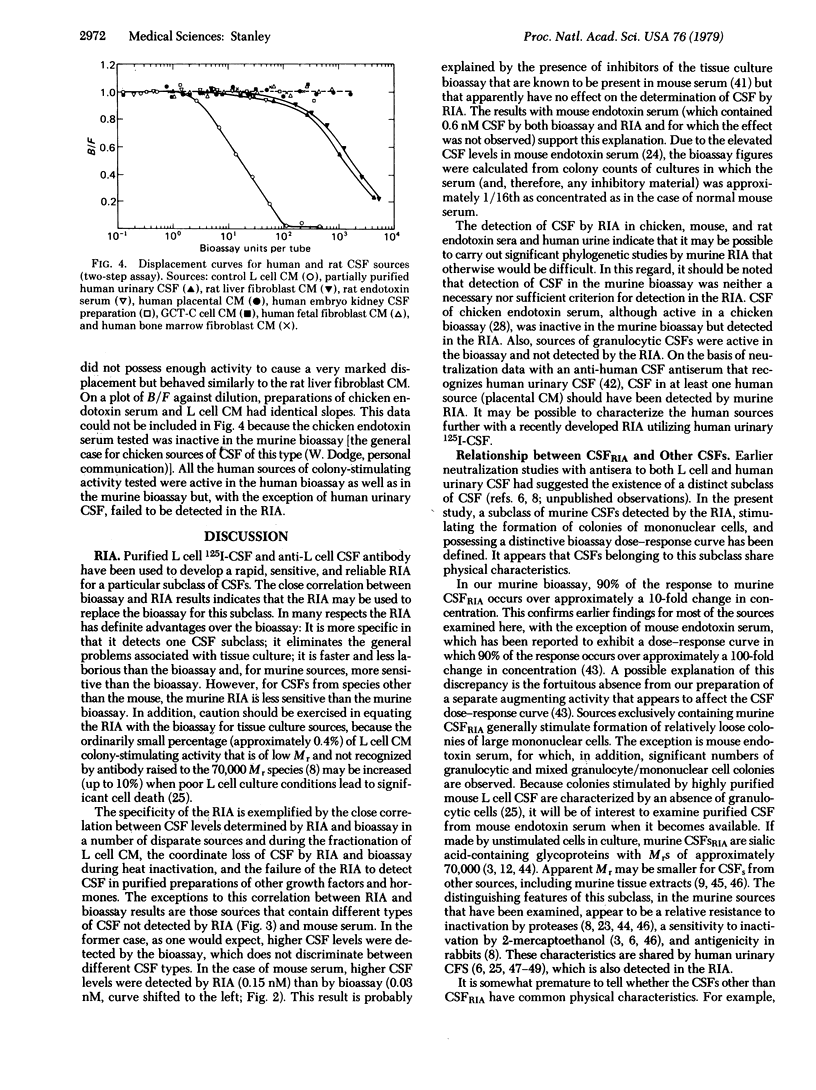
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) stimulate the differentiation of immature precursor cells to mature granulocytes and macrophages. Purified 125I-labeled murine L cell CSF has been used to develop a radioimmunoassay (RIA) that detects a subclass of CSFs that stimulates macrophage production. Murine CSF preparations that contain this subclass of CSF complete for all of the CSF binding sites on anti-L cell CSF antibody. With the exception of mouse serum, which can contain inhibitors of the bioassay, there is complete correspondence between activities determined by RIA and those determined by bioassay. The RIA is slightly more sensitive than the bioassay, detecting approximately 0.3 fmol of purified L cell CSF. It also detect this subclass of CSF in chickens, rats, and humans. In the mouse, the subclass is distinguished from other CSFs by a murine cell bioassay dose-response curve in which 90% of the response occurs over a 10-fold (rather than a 100-fold) increase in concentration, by stimulating the formation of colonies containing a high proportion of mononuclear (rather than granulocytic) cells, and by certain physical characteristics.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin P. E., McCulloch E. A., Till J. E. Characterization of the factor in L-cell conditioned medium capable of stimulating colony formation by mouse marrow cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):121–134. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. General principles of radioimmunoassay. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;22(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Stanley E. R., Sumner M. A. Factors from mouse tissues stimulating colony growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Dec;49(6):595–603. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Sumner M. A. Stimulation of mouse bone marrow colony growth in vitro by conditioned medium. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Oct;46(5):607–618. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull F. G., Rosendaal M. Macrophage colony development: properties of colony stimulating factors from murine embryo and pregnant uterus. Immunology. 1978 Mar;34(3):479–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Camakaris J., Metcalf D. Purification and properties of colony-stimulating factor from mouse lung-conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Wilson E. M., Metcalf D. Stimulation by human placental conditioned medium of hemopoietic colony formation by human marrow cells. Blood. 1977 Apr;49(4):573–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne P., Heit W., Kubanek B. The in vitro differentiation of density sub-populations of colony-forming cells under the influence of different types of colony-stimulating factor. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 Jul;10(4):341–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1977.tb00302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Persio J. F., Brennan J. K., Lichtman M. A., Speiser B. L. Human cell lines that elaborate colon-stimulating activity for the marrow cells of man and other species. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):507–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge W. H., Hansell C. C. The marrow colony forming cell and serum colony stimulating factor of the chicken. Exp Hematol. 1978 Sep;6(8):661–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Wu M. C., Gross M. A., Purcell Y., Yunis A. A. Purification and characterization of a colony stimulating factor from human lung. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3109–3116. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Ichikawa Y. Control of macrophage and granulocyte colony formation by two different factors. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Nov;110(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y. Differentiation of a cell line of myeloid leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Burgess A. W. Molecular and biological properties of a macrophage colony-stimulating factor from mouse yolk sacs. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):35–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner H. A., McCulloch E. A. Interacting cell populations affecting granulopoietic colony formation by normal and leukemic human marrow cells. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Acute antigen-induced elevation of serum colony stimulating factor (CFS) levels. Immunology. 1971 Sep;21(3):427–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., MacDonald H. R. Heterogeneity of in vitro colony- and cluster-forming cells in the mouse marrow: segregation by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Jun;85(3):643–654. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Russell S., Burgess A. W. Production of hemopoietic stimulating factors by pokeweed-mitogen-stimulated spleen cells. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Studies on colony formation in vitro by mouse bone marrow cells. II. Action of colony stimulating factor. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):89–99. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Kung C. K., Goldwasser E. Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5558–5564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth D. N. General considerations for radioimmunoassay of peptide hormones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:22–38. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Robinson W. A. Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol. 1970 Aug;76(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040760111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senn J. S., Messner H. A., Stanley E. R. Analysis of interacting cell populations in cultures of marrow from patients with neutropenia. Blood. 1974 Jul;44(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. W., Metcalf D. A low molecular weight factor in lung-conditioned medium stimulating granulocyte and monocyte colony formation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Feb;81(1):11–23. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. W., Metcalf D., Stanley E. R. Further studies on the factor in lung-conditioned medium stimulating granulocyte and monocyte colony formation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Aug;84(1):147–158. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. W., Stanley E. R. Tissue sources of bone marrow colony stimulating factor. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Dec;78(3):451–460. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagg B. H., Temperley J. W., Rochman H., Morley J. S. Iodination and the biological activity of gastrin. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):58–59. doi: 10.1038/228058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Bradley T. R., Sumner M. A. Properties of the mouse embryo conditioned medium factor(s) stimulationg colony formation by mouse bone marrow cells grown in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):301–317. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Chen D. M., Lin H. S. Induction of macrophage production and proliferation by a purified colony stimulating factor. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):168–170. doi: 10.1038/274168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Cifone M., Heard P. M., Defendi V. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth: identity of colony-stimulating factor and macrophage growth factor. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):631–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Hansen G., Woodcock J., Metcalf D. Colony stimulating factor and the regulation of granulopoiesis and macrophage production. Fed Proc. 1975 Dec;34(13):2272–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., McNeill T. A., Chan S. H. Antibody production to the factor in human urine stimulating colony formation in vitro by bone marrow cells. Br J Haematol. 1970 May;18(5):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Metcalf D. Enzyme treatment of colony stimulating factor: evidence for a peptide component. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Jun;49(3):281–290. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Metcalf D., Maritz J. S., Yeo G. F. Standardized bioassay for bone marrow colony stimulating factor in human urine: levels in normal man. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Apr;79(4):657–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Robinson W. A., Ada G. L. Properties of the colony stimulating factor in leukaemic and normal mouse serum. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Dec;46(6):715–726. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Eger R. R., Moore M. A., Mendelsohn N. Differentiation of mouse bone marrow precursor cells into neutrophil granulocytes by an activity separation from WEHI-3 cell-conditioned medium. Differentiation. 1978 Jul 24;11(1):59–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1978.tb00970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Jackson H. Analysis of populations of macrophage-granulocyte progenitor cells stimulated by activities in mouse lung-conditioned medium. Exp Hematol. 1977 Nov;5(6):523–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G., Bol S. The presence of a CSF enhancing activity in the serum of endotoxin-treated mice. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1975 Nov;8(6):579–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1975.tb01244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



