Abstract
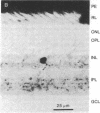
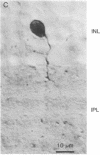
The distribution of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity within the avian retina was studied by immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase techniques with antiserum to [Met5]enkephalin and [Leu5]enkephalin. Formaldehyde-fixed retinae were sectioned and incubated in antiserum to either [Met5]- or [Leu5]enkephalin. Specificity to the antiserum was established by absorption of the antiserum with synthetic [Met5]- or [Leu5]enkephalin at 1 mM. Positive immunohistochemical staining for enkephalin was observed in the somata of amacrine cells and their processes within the inner plexiform layer. A large number of enkephalin-containing amacrine cells were distributed throughout the retina, and their density appeared to be greatest within central retinal regions. The majority of labeled amacrine cells were about 7.5 micrometers in diameter although, occasionally, amacrine cells were observed that were 12--15 micrometers in diameter. Amacrine cells had a cell-to-cell spacing of approximately 40 micrometers within central retinal regions. Labeled processes of the amacrine cells were observed to project into the inner plexiform layer where they arborized as a fine plexus, within laminae 1, 3--5 of the inner plexiform layer. These observations demonstrate the existence of opioid peptides in seemingly select populations of amacrine cells within the retina. The localization of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity within the retina suggests that opioid peptides play a specific and unique functional role in retinal processing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. II. The brain stem. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 24;129(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90965-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman R. W., Bader C. R. Biochemical characterization and cellular localization of the cholinergic system in the chicken retina. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 23;138(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN W. M., POWELL T. P. CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE AVIAN VISUAL SYSTEM. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Sep 17;158:232–252. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. Y., Naka K. The amacrine cell. Vision Res. 1976;16(10):1119–1129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland W. J., Hughes C. P. Observations on the afferent and efferent connections of the avian isthmo-optic nucleus. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 28;145(2):239–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90860-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E. Synaptic organization of the frog retina: an electron microscopic analysis comparing the retinas of frogs and primates. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):205–228. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin M. W. The inner plexiform layer of the vertebrate retina: a quantitative and comparative electron microscopic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Dec;140(4):479–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.901400406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galifret Y. Les diverses aires fonctionnelles de la rétine du pigeon. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;86(4):535–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild D. C., Laties A. M. An indoleamine-containing cell in chick retina. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973 Jul;12(7):537–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yang H. Y., Fratta W., Costa E. Determination of methionine enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karten J. H., Fite K. V., Brecha N. Specific projection of displaced retinal ganglion cells upon the accessory optic system in the pigeon (Columbia livia). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. G., Potts A. M., Mangnall Y. Dopamine: a retinal neurotransmitter. II. Autoradiographic localization of H3-dopamine in the retina. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971 Aug;10(8):617–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATURANA H. R., FRENK S. DIRECTIONAL MOVEMENT AND HORIZONTAL EDGE DETECTORS IN THE PIGEON RETINA. Science. 1963 Nov 15;142(3594):977–979. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3594.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturana H. R., Frenk S. Synaptic connections of the centrifugal fibers in the pigeon retina. Science. 1965 Oct 15;150(3694):359–361. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3694.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill J. I., Powell T. P., Cowan W. M. The organization of the projection of the centrifugal fibres to the retina in the pigeon. J Anat. 1966 Jan;100(Pt 1):35–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles F. A. Centrifugal control of the avian retina. I. Receptive field properties of retinal ganglion cells. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:65–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Cooper B., Cuatrecasas P. Radioimmunoassay and characterization of enkephalins in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Leighton J., Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of iodinated enkephalin analogues with opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1978 Feb;22(5):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols C. W., Koelle G. B. Comparison of the localization of acetylcholinesterase and non-specific cholinesterase activities in mammalian and avian retinas. J Comp Neurol. 1968 May;133(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/cne.901330102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman A. L., Hughes C. P. Functional role of efferents to the avian retina. I. Analysis of retinal ganglion cell receptive fields. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Mar 1;166(1):111–122. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Autoradiograhic localization of the opiate receptor in rat brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1849–1853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEN S. C., GREENFIELD P., BOELL E. J. Localization of acetylcholinesterase in chick retina during histogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 1956 Dec;106(2):433–461. doi: 10.1002/cne.901060211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sar M., Stumpf W. E., Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 1;182(1):17–37. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer J. M., Brownstein M. J., Axelrod J. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-like material in the rat retina: changes due to environmental lighting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3579–3581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. The regional distribution of a morphine-like factors enkephalin in monkey brain. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Nirenberg M. Localization of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis in retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Sullivan S., Barchas J. D. Immunocytochemical localization of methionine enkephalin: preliminary observations. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Hong J. S., Costa E. Regional distribution of LEU and MET enkephalin in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Apr;16(4):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Schmidt J. Radioautographic localization of 125I alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites in the retinas of goldfish and turtle. Vision Res. 1976;16(8):878–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Schmidt J. Two types of receptors for alpha-bungarotoxin in the synaptic layers of the pigeon retina. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 9;138(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]