Abstract
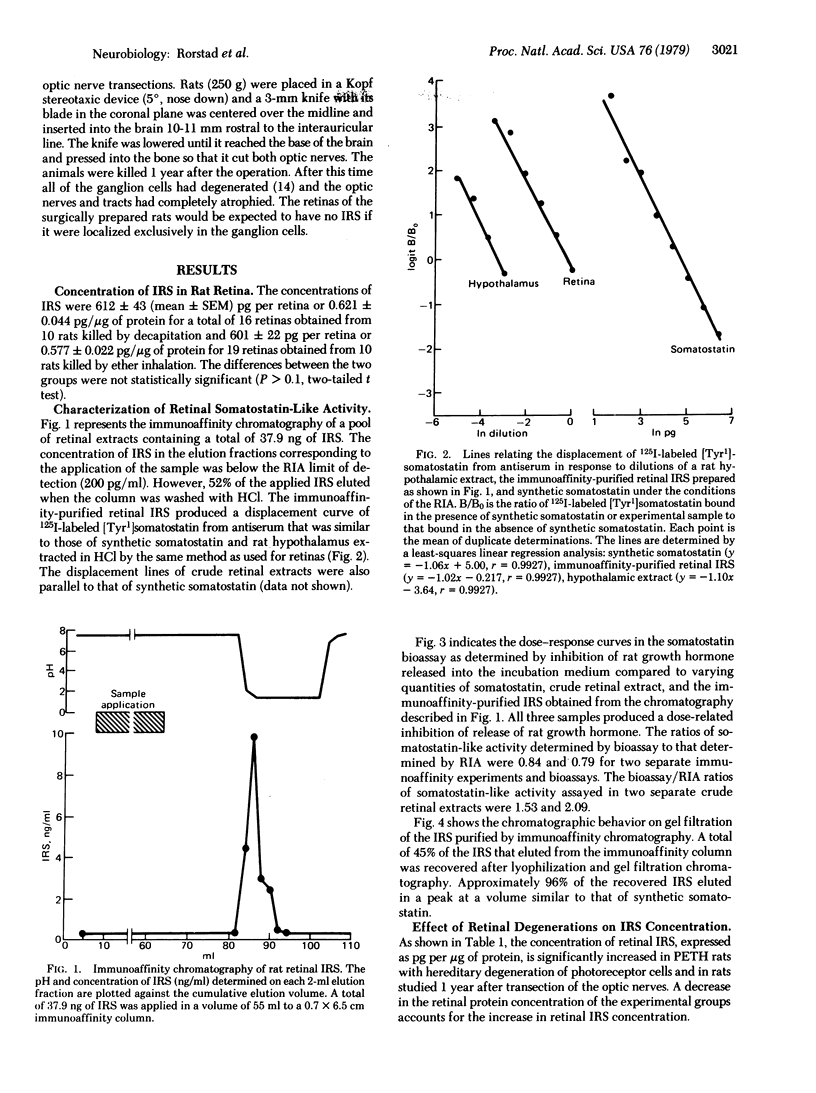
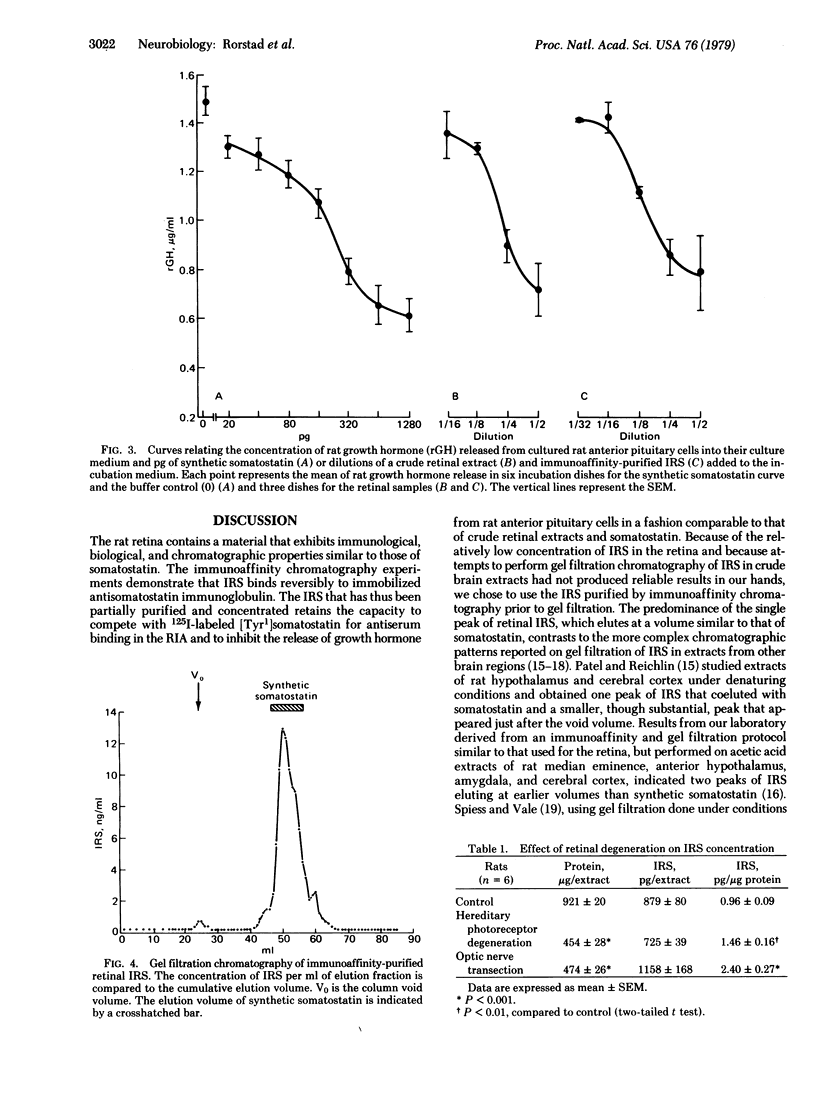
Somatostatin-like activity, as determined by radioimmunoassay and bioassay, is present in HCl extracts of rat retina. The concentrations of immunoreactive somatostatin are 612 +/- 43 (mean +/- SEM)pg per whole retina of 0.621 +/- 0.044 pg/microgram of protein in retinas from rats killed by decapitation, values which are not significantly different from those in retinas from rats killed by ether inhalation. The immunoreactive somatostatin was partially purified and concentrated by immunoaffinity chromatography. Both the crude retinal extracts and the immunoaffinity-purified immunoreactive somatostatin inhibited, in a dose-related manner, the release of rat growth hormone from dispersed rat anterior pituitary cells in culture. When the immunoaffinity-purified immunoreactive somotostatin was subjected to gel filtration chromatography, 96% of the recovered somatostatin eluted as a peak corresponding in position to that of synthetic somatostatin. Retinas from a group of rats with hereditary degeneration of the photoreceptor cells and another group of rats studied 1 year after transection of the optic nerves demonstrated an increased concentration of immunoreactive somatostatin compared to controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd A. E., 3rd, Sanchez-Franco F., Spencer E., Patel Y. C., Jackson I. M., Reichlin S. Characterization of hypophysiotropic hormones in porcine hypothalamic extracts. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1075–1083. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Epelbaum J., Tannenbaum G. S., Rorstad O., Martin J. B. Somatostatin: isolation, characterization, distribution, and blood determination. Metabolism. 1978 Sep;27(9 Suppl 1):1133–1137. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Guillemin R. Isolation of somatostatin (a somatotropin release inhibiting factor) of ovine hypothalamic origin. Can J Biochem. 1974 Nov;52(11):1067–1072. doi: 10.1139/o74-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M., Arimura A., Sato H., Schally A. V., Kizer J. S. The regional distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain. Endocrinology. 1975 Jun;96(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-6-1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epelbaum J., Brazeau P., Tsang D., Brawer J., Martin J. B. Subcellular distribution of radioimmunoassayable somatostatin in rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 May 6;126(2):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elde R., Johansson O., Luft R., Nilsson G., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi R. M., Brown M., Vale W. Regional distribution of neurotensin and somatostatin in rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronheim S., Berelowitz M., Pimstone B. L. A radioimmunoassay for growth hormone release-inhibiting hormone: method and quantitative tissue distribution. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Nov;5(6):619–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail M. M., Sidman R. L., Gerhardt C. O. Congenic strains of RCS rats with inherited retinal dystrophy. J Hered. 1975 Jul-Aug;66(4):242–244. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar R. P. Somatostatin immunoreactive peptides of higher molecular weight in ovine hypothalamic extracts. J Endocrinol. 1978 Jun;77(3):429–430. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0770429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Reichlin S. Somatostatin in hypothalamus, extrahypothalamic brain, and peripheral tissues of the rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):523–530. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Dupont A., Arimura A., Redding T. W., Nishi N., Linthicum G. L., Schlesinger D. H. Isolation and structure of somatostatin from porcine hypothalami. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):509–514. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B., Kronheim S., Pimstone B. The presence of immunoreactive somatostatin in rat retina. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Jan;11(1):79–80. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman R. L., Pearlstein R., Waymouth C. Pink-eyed dilution (p) gene in rodents: increased pigmentation in tissue culture. Dev Biol. 1965 Aug;12(1):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess J., Vale W. Investigation of larger forms of somatostatin in pigeon pancreas and rat brain. Metabolism. 1978 Sep;27(9 Suppl 1):1175–1178. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. The naso-temporal division of the cat's retina. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Apr;126(4):585–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum G. S., Martin J. B. Evidence for an endogenous ultradian rhythm governing growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1976 Mar;98(3):562–570. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-3-562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Brazeau P., Rivier C., Brown M., Boss B., Rivier J., Burgus R., Ling N., Guillemin R. Somatostatin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:365–397. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Ling N., Rivier J., Villarreal J., Rivier C., Douglas C., Brown M. Anatomic and phylogenetic distribution of somatostatin. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1491–1494. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier C., Brown M. Regulatory peptides of the hypothalamus. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:473–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


