Abstract
Objective
To develop a clinical risk scoring system for identifying adolescents with dysglycemia (prediabetes or diabetes) who need further confirmatory testing and to determine whether the addition of non-fasting tests would improve the prediction of dysglycemia.
Study Design
A sample of 176 overweight and obese adolescents (10 – 17 years) had a history/physical exam, a 2-h oral glucose tolerance test, and non-fasting tests [hemoglobin A1c, 1-h glucose challenge test (GCT), and random glucose test] performed. Given the low number of children with diabetes, we created several risk scoring systems combining the clinical characteristics with non-fasting tests for identifying adolescents with dysglycemia and compared the test performance.
Results
Sixty percent of participants were white and 32% were black; 39.2% had prediabetes and 1.1% had diabetes. A basic model including demographics, body mass index percentile, family history of diabetes, and acanthosis nigricans had reasonable test performance [area under the curve (AUC), 0.75; 95% confidence interval (95% CI), 0.68 – 0.82]. The addition of random glucose (AUC, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.87) or 1-h GCT (AUC, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.88) to the basic model significantly improved the predictive capacity, but the addition of hemoglobin A1c did not (AUC, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.68 – 0.83). The clinical score thresholds to consider for the basic plus random glucose model are total score cutoffs of 60 or 65 (sensitivity 86% and 65% and specificity 60% and 78%, respectively) and for the basic plus 1-h GCT model are total score cutoffs of 50 or 55 (sensitivity 87% and 73% and specificity 59% and 76%, respectively).
Conclusions
Pending a validation in additional populations, a risk score combining the clinical characteristics with non-fasting test results may be a useful tool for identifying children with dysglycemia in the primary care setting.
Keywords: adolescents, prediabetes, risk score
INTRODUCTION
Because of the U.S. childhood obesity epidemic, both type 2 diabetes (T2D) (1) and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance), a condition associated with the increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease (2 – 4), are reportedly increasing among the U.S. pediatric population (1, 5, 6). Although the overall burden of T2D is still relatively low (7, 8), as estimated by the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study at 0.02%, the prevalence of prediabetes is much higher, with the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reporting the prevalence rates of 18% and 30% among overweight and obese children in the USA (9), respectively. These childhood prediabetes prevalence estimates foreshadow a concerning trend for the future lifetime burden of T2D in the USA.
The screening for diabetes is endorsed by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the American Academy of Pediatrics, and there is an increasing interest in the screening for the identification of adolescents with prediabetes (10). Children with prediabetes represent a high-risk group who may benefit from the targeted diabetes prevention interventions similar to the Diabetes Prevention Project in adults (11). To effectively target the highest-risk children for such interventions, efficient and valid methods of screening to identify children with prediabetes and diabetes need to be developed. A screening method based on clinical parameters routinely collected in the primary care setting, rather than requiring fasting laboratory tests, is needed.
Therefore, our objectives were (a) to develop a clinical risk score for identifying children with dysglycemia, defined as prediabetes or diabetes, who need further confirmatory glucose testing and (b) to determine whether a clinical risk score combined with non-fasting glucose tests, including a random glucose, a 1-h glucose challenge test (GCT), or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), would improve prediction of dysglycemia.
Patients and Methods
The study population consisted of a convenience sample of overweight or obese [body mass index (BMI) ≥ 85th percentile] adolescents ages 10 – 17 years without known diabetes, the majority of whom (85%) were recruited from pediatric primary care clinics in the southeast Michigan area. We studied both overweight and obese children because the guidelines recommended the screening of both groups of children. The participants had two study visits 1 – 3 weeks apart. The first visit was for a 2-h oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The participants fasted for a minimum of 12 h and were seen in the Michigan Clinical Research Unit (MCRU), where they provided a medical history and underwent a physical examination, a HbA1c test, and an ingestion of 1.75 g/kg glucola to a maximum of 75 g, with glucose values measured every 30 min until 2 h after. During the second visit, the participants returned for a random glucose test (glucose measured in a non-fasting state) and a 1-h GCT (glucose measured 1 h after ingestion of 50 g glucola in a non-fasting state). The test performance of nonfasting biomarkers alone has been previously published using this cohort, along with more detailed information about the protocol (4).
Study Definitions
In constructing the risk score, we attempted to use variables that would be readily available and easily captured by physicians in the primary care setting. We considered demographic characteristics, BMI, and patient self-report of pubertal status (Tanner stage). We also considered the risk factors based on the ADA screening guidelines, including family history of diabetes, maternal history of diabetes, and signs of insulin resistance [acanthosis nigricans, hyperlipidemia, and polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)]. (10). Lastly, we evaluated the abnormalities in blood pressure (BP), given the link between BP, metabolic syndrome, and incident diabetes (12).
Children were classified as white vs. non-white for the race/ethnicity variable. BMI, expressed in percentiles based on the 2000 CDC growth curves (13), was grouped into three strata: 85th – 89th percentile, 90th – 94th percentile, and 95th percentile and above. Self- reported sexual development was classified as pubertal (Tanner stage ≥ 2 breast for girls and genital development for boys) versus not pubertal. Family history of T2D was classified as none, first degree (positive family history of T2D in mother, father, or sibling), or second degree (positive family history of T2D in aunts, uncles, or grandparents). Parent report of maternal history of diabetes during gestation was classified as yes or no, and signs of insulin resistance were classified as the presence or absence of acanthosis nigricans, which was identified by trained physician assistants from the MCRU. The presence or absence of hypercholesterolemia and PCOS was based on the patient’s or parent’s report. We used the self-report of these conditions rather than the objective measure, because a physician seeing a patient for the first time would not necessarily know during an initial clinical visit if the patient had elevated fasting cholesterol levels or laboratory findings that were consistent with PCOS. We specifically did not consider fasting insulin measures in our risk score for that reason as well.
To measure the BP, the arm circumference was measured to select the appropriate BP cuff, and systolic and diastolic BP was measured after 5 min of rest using a Dinamap Pro 100 and was repeated twice. The BP was averaged and the two different definitions of elevated BP were created: (a) BP > 95th percentile (systolic or diastolic) for age, sex, and height using traditional BP tables (14) or (b) BP above the normal threshold using simplified age- and sex-specific tables (15).
For the random and 1-h GCT measures, children were grouped into 10 mg/dL strata (60, 70, 80, etc.), and for HbA1c, children were grouped into 0.1% strata (5.5, 5.6, 5.7, etc.). Based on the 2-h OGTT, glucose status was classified as follows: (a) normal glucose metabolism 2-h post-load glucose level <140 mg/dL and a fasting glucose level <100 mg/dL), (b) prediabetes [impaired glucose tolerance (2-h post-load glucose level ≥140 and <200 mg/dL) or impaired fasting glucose (fasting plasma glucose ≥100 and <126 mg/dL)], or (c) diabetes (2-h post-load glucose level ≥200 mg/dL or fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL). We combined the individuals with prediabetes and diabetes into the category of dysglycemia given the low numbers of children with diabetes (n = 2). The information for laboratory assays is detailed in a previous publication (4). The labs were performed by the Michigan Diabetes Research and Training Center Core Labs (DK020572).
Data Analysis and Construction of the Risk Scores
Of the 271 children enrolled in the study, we limited the sample to the 176 individuals with complete data for ADA risk factors, HbA1c, a random glucose, and 1-h GCT. When we compared the children in the sample with those excluded from the sample (n = 95), we did not find significant differences in age (p = 0.80), sex (p = 0.12), race (p = 0.26), or glucose tolerance status (p = 0.69), but we did find a slightly higher BMI percentile for children in our sample (96.97 vs. 96.04; p = 0.03).
We conducted logistic regression analyses, with dysglycemia as the outcome of interest, to evaluate which covariates to include in the models. In our bivariate analyses, no statistically significant associations with dysglycemia were found for abnormal BP, maternal history of diabetes during gestation, patient- or parent-reported PCOS or cholesterol status, or pubertal status. We did find marginal associations for sex (p = 0.05) and race (p = 0.08) and significant associations for BMI percentile (p <0.01), family history of T2D (p <0.01), and the presence of acanthosis nigricans (p = 0.001).
We then performed multiple logistic regression models using standardized coefficients, so that one covariate would not hold greater weight over another based on its numeric scale (i.e., BMI expressed in percentiles vs. dichotomous categories such as family history). The score contribution of each predictor was calculated by multiplying a given z-score value of the predictor by 10 times the β coefficient, rounding the product to a whole number, and then subtracting 10 to set the reference level of each predictor to zero. We calculated the risk scores for each individual in the sample, performed receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis curves for various risk score cutoff s, and then calculated the area under the ROC curve (AUC) for each risk score. We first created (a) a basic model of clinical characteristics that included all demographic variables, BMI, and only risk factors that were statistically significant at the p <0.05 level in the bivariate analyses (only acanthosis nigricans and family history) and (b) an extended model that contained all demographic variables, BMI, and all risk factors outlined by the ADA screening criteria regardless of statistical significance. We did not find significant differences in test performance based on a comparison of AUC when comparing the basic versus the full ADA model (AUC, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.68 – 0.82) for the basic model and AUC, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69 – 0.83 for the ADA model; p = 0.51). Therefore, we elected to focus on the basic model given that it would be easier for clinicians to implement in practice. We constructed additional models that also included non-fasting measures of glucose: (a) the basic model plus a random glucose level, (b) the basic model plus a 1-h glucose tolerance test, (c) the basic model plus HbA1c, (d) the basic model plus random glucose and HbA1c, and (e) the basic model plus 1-h GCT and HbA1c. We compared the AUC for each model with the basic model.
The study was approved by the University of Michigan institutional review board. We performed our statistical analyses using Stata 10.0 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). The authors have complied with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki regarding the ethical conduct of research involving human subjects.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the overall study sample and the characteristics stratified by glucose tolerance status. The overall prevalence of dysglycemia in our sample of overweight and obese children was 40.3%. Of the 71 children with dysglycemia, 97.2% had prediabetes and 2.8% had diabetes. Overall, there was an equal representation of males and females, close to one-third were black, and the majority of children were obese and postpubertal. A similar percentage of children (10%) had a maternal history of diabetes, reported having hyperlipidemia, and had evidence of acanthosis nigricans, and a very small proportion of girls reported having PCOS. The prevalence of abnormal BP was similar to other studies of hypertension prevalence among overweight and obese children (16).
Table 1.
Characteristics of the Study Population.
| Overall population (n=176) | Normal glucose tolerance (n=105) | Dysglycemia (n=71) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) age | 13.7 (2.1) | 13.6 (2.1) | 13.7 (2.0) | 0.93 |
| Sex, % (n) | ||||
| Female | 50.0 (88) | 56.2 (59) | 40.9 (29) | |
| Male | 50.0 (88) | 43.8 (46) | 59.1 (42) | 0.05 |
| Race,%(n) | ||||
| White | 59.7 (105) | 65.7 (69) | 50.7 (36) | |
| Black | 31.8 (56) | 27.6 (29) | 38.0 (27) | |
| Other | 8.5 (15) | 6.7 (7) | 11.3 (8) | 0.13 |
| Weight status, % (n) | ||||
| Overweight (BMI ≥85th and <95th percentiles) | 17.6 (31) | 24.8 (26) | 7.0 (5) | |
| Obese (BMI ≥95th percentile) | 82.4 (145) | 75.2 (79) | 93.0 (66) | <0.01 |
| Family history of T2 D, % (n) | ||||
| First-degree relative | 25.6 (45) | 18.1 (19) | 36.6 (26) | |
| Second-degree relative | 46.0 (81) | 46.7 (49) | 45.1 (32) | |
| No family history | 28.4 (50) | 35.2 (37) | 18.3 (13) | <0.01 |
| Self-report of hyperlipidemia, % (n) | 11.4 (20) | 12.4 (13) | 9.9 (7) | 0.61 |
| Self-report of PCOSa, % (n) | 3.4 (3) | 1.7 (1) | 6.9 (2) | 0.21 |
| Maternal history of diabetes, %(n) | 10.8 (19) | 8.6 (9) | 14.1 (10) | 0.25 |
| % Abnormal BP (14), % (n) | 29.0 (51) | 28.6 (30) | 29.6 (21) | 0.89 |
| % Abnormal BP using modified guidelines (15), % (n) | 42.1 (74) | 42.9 (45) | 40.9 (29) | 0.79 |
| Presence of acanthosis nigricans, % (n) | 10.2 (18) | 2.9 (3) | 21.1 (15) | <0.01 |
| Tanner stageb (n=134), % (n) | ||||
| 1 | 7.5 (10) | 7.3 (6) | 7.7 (4) | |
| 2 | 11.9 (16) | 12.2 (10) | 11.5 (6) | |
| 3 | 22.4 (30) | 24.4 (20) | 19.2 (10) | |
| 4 | 32.1 (43) | 30.5 (25) | 34.6 (18) | |
| 5 | 26.1 (35) | 25.6 (21) | 26.9 (14) | 0.97 |
| Median (range) Tanner stage | 4 (1–5) | 4 (1–5) | 4 (1–5) | |
| Pubertal, % (n) | 92.5 (124) | 92.7 (76) | 92.3 (48) | |
| Prepubertal, % (n) | 7.5 (10) | 7.3 (6) | 7.7 (4) | 0.94 |
| Mean (SD) random glucose, mg/dL | 97.7 (16.6) | 92.9 (13.7) | 104.8 (18.0) | <0.001 |
| Mean (SD) 1-h glucose challenge test | 113.3 (28.7) | 104.0 (22.0) | 127.0 (32.0) | <0.001 |
| Mean (SD) HbA1c, % | 5.5 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.4) | 5.6 (0.5) | 0.11 |
Prevalence among females only.
For those with self-reported pubertal measures (n=134).
Compared with the basic model (AUC, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.68 – 0.82), there were significant improvements in AUC for the basic model with random glucose (AUC, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.87; p = 0.02) and for the basic model with 1-h GCT (AUC, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.88; p <0.01). However, the addition of HbA1c to the basic model (AUC, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.68 – 0.83; p = 0.54) did not lead to statistically significant improvements in predictive capacity. The addition of HbA1c to the basic with random glucose or the basic with 1-h GCT models also did not lead to improvements in test discrimination.
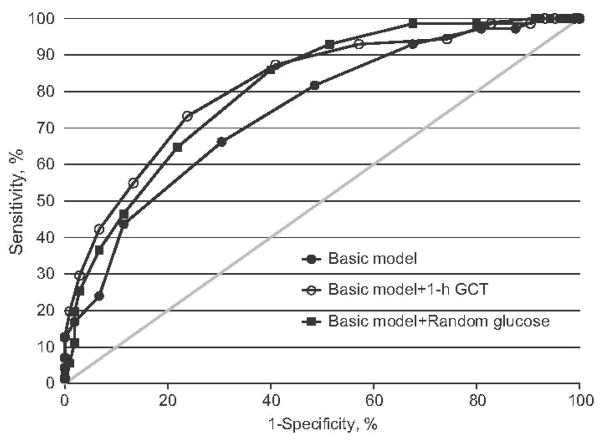
Figure 1 shows a comparison of ROC curves of the basic model and the best-performing models: basic plus random glucose and basic plus 1-h GCT. Table 2 shows a user-friendly example of a risk scoring sheet for each of these models and Table 3 shows the test performance characteristics of each of these models. The appendix provides similar scoring and test performance information for the additional risk scoring systems that we evaluated.
Figure 1.
ROC curves for predicting dysglycemia for the basic model (AUC, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.68 – 0.82) and the two additional best-performing models: the basic plus random glucose test model (AUC, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.87) and the basic plus 1-h GCT model (AUC, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.75 – 0.88).
Table 2.
Sample Risk Scoring Sheet: for example, a girl who is 10 years old is white and has a BMI ≥ 95th percentile with a positive family history in her grandparents and acanthosis on exam would receive a score of 56 for the basic model.
| Basic model (maximum score=83) |
Basic plus random glucose model (maximum score=126) |
Basic plus 1-h GCT model (maximum score=109) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | Age, years | Age, years | |||
| 10–11 | 0 | 10–11 | 0 | 10–11 | 0 |
| 12–13 | 3 | 12–13 | 2 | 12–13 | 2 |
| 14–15 | 5 | 14–15 | 5 | 14–15 | 4 |
| 16–17 | 8 | 16–17 | 7 | 16–17 | 6 |
| Sex | Sex | Sex | |||
| Female | 0 | Female | 0 | Female | 0 |
| Male | 9 | Male | 8 | Male | 11 |
| Race | Race | Race | |||
| White | 0 | White | 0 | White | 0 |
| Non-white | 3 | Non-white | 3 | Non-white | 4 |
| BMI percentile | BMI percentile | BMI percentile | |||
| 85th–89th | 0 | 85th–89th | 0 | 85th–89th | 0 |
| 90th–94th | 14 | 90th–94th | 13 | 90th–94th | 11 |
| ≥95th | 28 | ≥95th | 25 | ≥95th | 22 |
| Family history of diabetes | Family history of diabetes | Family history of diabetes | |||
| No | 0 | No | 0 | No | 0 |
| Yes, grandparents | 6 | Yes, grandparents | 6 | Yes, grandparents | 7 |
| Yes, parents/siblings | 13 | Yes, parents/siblings | 12 | Yes, parents/siblings | 13 |
| Acanthosis nigricans | Acanthosis nigricans | Acanthosis nigricans | |||
| No | 0 | No | 0 | No | 0 |
| Yes | 22 | Yes | 23 | Yes | 18 |
| Random glucose | 1-hGCT | ||||
| 50–59 | 0 | 60–69 | 0 | ||
| 60–69 | 5 | 70–79 | 3 | ||
| 70–79 | 11 | 80–89 | 6 | ||
| 80–89 | 16 | 90–99 | 10 | ||
| 90–99 | 21 | 100–109 | 13 | ||
| 100–109 | 27 | 110–119 | 16 | ||
| 110–119 | 32 | 120–129 | 19 | ||
| 120–129 | 38 | 130–139 | 22 | ||
| 130–139 | 43 | 140–149 | 25 | ||
| ≥140 | 48 | 150–159 | 29 | ||
| 160–169 | 32 | ||||
| ≥170 | 35 |
Table 3.
Test Characteristics for Various Models.
| Threshold | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Positive likelihood ratio | Negative likelihood ratio | Positive predictive value, % | Negative predictive value, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic model (demographics, BMI percentile, family history, and acanthosis nigricans) | ||||||
| 0 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 5 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 10 | 100 | 2 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 15 | 100 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 20 | 100 | 8 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 25 | 97 | 12 | 1.11 | 0.23 | 43 | 87 |
| 30 | 97 | 19 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 45 | 91 |
| 35 | 93 | 32 | 1.37 | 0.22 | 48 | 87 |
| 40 | 82 | 51 | 1.68 | 0.36 | 53 | 81 |
| 45 | 66 | 70 | 2.17 | 0.49 | 59 | 75 |
| 50 | 44 | 89 | 3.82 | 0.64 | 72 | 70 |
| 55 | 24 | 93 | 3.59 | 0.81 | 71 | 64 |
| 60 | 17 | 98 | 8.87 | 0.85 | 86 | 64 |
| 65 | 13 | 100 | – | 0.87 | 100 | 63 |
| 70 | 7 | 100 | – | 0.93 | 100 | 61 |
| 75 | 4 | 100 | – | 0.96 | 100 | 61 |
| 80 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
| Basic plus random glucose test model | ||||||
| 10 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 20 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 3 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 35 | 100 | 6 | 1.06 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 40 | 100 | 9 | 1.09 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 45 | 99 | 20 | 1.23 | 0.07 | 45 | 95 |
| 50 | 99 | 32 | 1.46 | 0.04 | 50 | 97 |
| 55 | 93 | 49 | 1.81 | 0.15 | 55 | 91 |
| 60 | 86 | 60 | 2.15 | 0.23 | 59 | 86 |
| 65 | 65 | 78 | 2.96 | 0.45 | 67 | 77 |
| 70 | 46 | 89 | 4.07 | 0.60 | 73 | 71 |
| 75 | 37 | 93 | 5.49 | 0.68 | 79 | 69 |
| 80 | 25 | 97 | 8.87 | 0.77 | 86 | 66 |
| 85 | 20 | 98 | 10.35 | 0.82 | 88 | 64 |
| 90 | 11 | 98 | 5.92 | 0.90 | 80 | 62 |
| 95 | 6 | 99 | 5.92 | 0.95 | 80 | 61 |
| 105 | 4 | 100 | – | 0.96 | 100 | 61 |
| 110 | 3 | 100 | – | 0.97 | 100 | 60 |
| 125 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
| Basic plus 1-h GCT model | ||||||
| 10 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 15 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 20 | 100 | 5 | 1.05 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 7 | 1.07 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 30 | 99 | 10 | 1.09 | 0.15 | 42 | 91 |
| 35 | 99 | 17 | 1.19 | 0.08 | 45 | 95 |
| 40 | 94 | 26 | 1.27 | 0.22 | 46 | 87 |
| 45 | 93 | 43 | 1.63 | 0.16 | 52 | 90 |
| 50 | 87 | 59 | 2.13 | 0.21 | 59 | 87 |
| 55 | 73 | 76 | 3.08 | 0.35 | 68 | 81 |
| 60 | 55 | 87 | 4.12 | 0.52 | 74 | 74 |
| 65 | 42 | 93 | 6.34 | 0.62 | 81 | 71 |
| 70 | 30 | 97 | 10.35 | 0.72 | 87 | 67 |
| 75 | 20 | 99 | 20.70 | 0.81 | 93 | 65 |
| 80 | 13 | 100 | – | 0.87 | 100 | 63 |
| 90 | 7 | 100 | – | 0.93 | 100 | 61 |
| 95 | 4 | 100 | – | 0.96 | 100 | 61 |
| 100 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
DISCUSSION
Our goal was to create a risk score based on clinical characteristics and non-fasting tests that could be used by clinicians in the primary care setting to determine which children are at greatest risk for having dysglycemia; these children could then be referred for confirmatory testing such as a fasting plasma glucose or a 2-h glucose tolerance test. Although a simple model based solely on clinical characteristics (demographics, BMI, family history, and the presence or absence of acanthosis nigricans) had reasonable discrimination for identifying children with dysglycemia, the predictive capacity of the model was further enhanced by the inclusion of a random glucose or a 1-h GCT to the model.
The possible clinical score thresholds to consider for the basic plus random glucose risk score are cutoffs of 60 or 65, which would result in the ability to identify 86 % and 65 % of children screened (i.e., 14% and 35% of cases would be missed). The false-positive rates would be 40% and 22%. Of those children with a positive test, the percentage of children with actual disease (positive predictive value) would be 59% and 67%. The thresholds to consider for the basic plus 1 h GCT risk score are cutoffs of 50 or 55, which would result in the ability to identify 87% and 73% of children screened (i.e., 13% and 27% of cases would be missed). The false-positive rates would be 41% and 24%, and of those children with a positive test, the percentage of children with actual disease would be 59% and 68%.
The 1-h GCT is routinely used for gestational diabetes screening among obstetric providers. Patients are given a bottle of 50 g glucola to drink and then are instructed to have their venous blood draw 1 h later. Providers could adopt a similar screening practice for the pediatric clinical setting, although this may be more difficult to achieve in school settings without a blood drawing facility.
We found that the addition of HbA1c to the clinical risk score did not lead to improvements in predictive capacity compared with the basic model. This is consistent with the findings of previous studies demonstrating that HbA1c has less than optimal test performance for identifying children with prediabetes (AUC, 0.53 – 0.54) (4,17). We acknowledge that further studies need to be performed to validate these risk scoring systems in larger, more diverse clinical populations, because diabetes risk scores in adults have been shown to have varying levels of test performance depending on the population (18).
The previous studies in U.S. populations have attempted to use a combination of clinical characteristics and fasting laboratory studies to generate a dysglycemia risk score for children. Reinehr et al. (19) generated a prediabetes risk score based on two different cohorts of children referred to obesity centers in Germany. In contrast to our findings, when developing their risk score, they did not find significant associations of a positive history of T2D in second-degree relatives or the presence of acanthosis nigricans with having prediabetes. The risk score they developed assigned two points for a family history of diabetes, one point for extreme obesity (defined as a BMI z-score ≥2.54), and one point for pubertal stage. A score of ≥2 was considered positive, resulting in a sensitivity of 87% – 88% and a specificity of 55% – 56%.
The Reinehr et al. study focused on two different populations of German children referred to obesity clinics; the use of a very high-risk population could bias the risk score. In contrast, the majority of children in our study were recruited from primary care clinics. Furthermore, we did not find a significant association between pubertal status and dysglycemia, but the majority of children in our study were pubertal, with a mean age of 13.7 years, which is slightly higher than mean age of 13.1 years for the German study. Furthermore, the German study did not assess the incremental value of adding non-fasting laboratory studies such as a random glucose or HbA1c, which is particularly relevant given the recent change in ADA guidelines, recommending that HbA1c be exclusively used for the diagnosis of diabetes in children.
One U.S. study of obese minority youth evaluated a variety of risk factors for dysglycemia (20). Their criteria for determining risk consisted of a measure of insulin resistance [homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR)] for both girls and boys and cholesterol and HbA1c for boys. We specifically did not include HOMA-IR or cholesterol in our risk score because these measures require the patient to be fasting. Given the large number of children in the USA who are eligible for diabetes screening (21), our goal was to create a risk score that would obviate the need for initial fasting labs for the vast majority of children, given the inconvenience and difficulty of obtaining fasting labs (22). Furthermore, there is a concern regarding the reliability and comparability of insulin levels among various laboratories (23). Finally, given the increasing focus on obesity prevention within school and community settings, the basic risk score may represent a non-invasive and inexpensive strategy that could be used by school nurses and community partners to identify at-risk populations for referral.
A number of studies of U.S. children have reported a high risk of dysglycemia in the populations of patients with hypercholesterolemia, PCOS (24), and maternal history of diabetes during the pregnancy (25). These risk factors, however, were not significantly associated with dysglycemia presumably because of the low prevalence of these conditions in the general pediatric overweight population.
We acknowledge the limitations of our study. Although diabetes is an important independent outcome to evaluate, there were only two individuals with diabetes in our sample, precluding our ability to create a risk score for diabetes alone. Second, because of the limited number of individuals for whom we had complete data, we were unable to validate the risk scoring systems in an independent population of children or in substrata of overweight and obese children. Third, we recognize that the accuracy of the medical history variables could be affected by the reporter; that is, if the risk score were implemented in a school setting, children may not be aware of their full medical history. Fourth, although the majority of studies use a 2-h glucose tolerance test to identify children with prediabetes and diabetes (7, 26 – 28); we acknowledge that some studies have shown a lack of reproducibility using the 2-h OGTT (29). Finally, we recruited a convenience sample of overweight and obese children from southeast Michigan, which had adequate representation of both black and white children. However, the white vs. nonwhite classification grouped Asian and Black children together, and studies have shown that the racial groups carry different levels of health risk for a given BMI (30). As a result, the generalizations must be made accordingly.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of a relatively simple dysglycemia risk score based on clinical characteristics and non-fasting measures of glycemia presents pediatric providers with the opportunity to identify high-risk children who may be referred for confirmatory testing for glucose abnormalities and diabetes prevention interventions. A future validation of this risk score may obviate the need for initial fasting laboratory testing for children with dysglycemia.
Acknowledgments
Grant support: This study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (K08-DK-082386), Clinical Sciences Scholars Program, Michigan Clinical Research Unit (UL1RR024986), Michigan Institute for Clinical and Health Research (UL1RR024986), Michigan Diabetes Research and Training Center (5P60-DK-20572), Blue Cross Blue Shield Foundation of Michigan, and Elizabeth Kennedy Award/Elizabeth Crosby Funds/Office of the Vice President for Research from the University of Michigan.
Appendix Table 1.
Comparison of Risk Scoring Systems and Test Performance for Each Model.
| Basic model | ADA model | Basic model+1-h GCT | Basic model+random glucose | Basic model+HbA1c | Basic model+1-h GCT+HbA1c | Basic model+random glucose+HbA1c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95%CI) | 0.75 (0.68–0.82) | 0.76 (0.69–0.83) | 0.82 (0.75–0.88) | 0.81 (0.75–0.87) | 0.76 (0.68–0.83) | 0.82 (0.76–0.88) | 0.82 (0.76–0.88) |
| Age, years | |||||||
| 10–11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 12–13 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 14–15 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 16–17 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Female | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Male | 9 | 9 | 11 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 9 |
| Race | |||||||
| White | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-white | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| BMI percentile | |||||||
| 85–89 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 90–94 | 14 | 14 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 10 | 12 |
| ≥95 | 28 | 29 | 22 | 25 | 26 | 21 | 23 |
| Family history | |||||||
| No | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yes, grandparents | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 |
| Yes, parents/siblings | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Acanthosis nigricans | |||||||
| No | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yes | 22 | 21 | 18 | 23 | 22 | 18 | 23 |
| Self-report of low cholesterol | |||||||
| No | 0 | ||||||
| Yes | 4 | ||||||
| Self-report of PCOS | |||||||
| No | 0 | ||||||
| Yes | 11 | ||||||
| Maternal history of diabetes during pregnancy | |||||||
| No | 0 | ||||||
| Yes | 4 | ||||||
| 1-h GCT, mg/dL | |||||||
| 60–69 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 70–79 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 80–89 | 6 | 6 | |||||
| 90–99 | 10 | 9 | |||||
| 100–109 | 13 | 12 | |||||
| 110–119 | 16 | 16 | |||||
| 120–129 | 19 | 19 | |||||
| 130–139 | 22 | 22 | |||||
| 140–149 | 25 | 25 | |||||
| 150–159 | 29 | 28 | |||||
| 160–169 | 32 | 31 | |||||
| ≥170 | 35 | 34 | |||||
| Random glucose, mg/dL | |||||||
| 50–59 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 60–69 | 5 | 5 | |||||
| 70–79 | 11 | 11 | |||||
| 80–89 | 16 | 16 | |||||
| 90–99 | 21 | 21 | |||||
| 100–109 | 27 | 26 | |||||
| 110–119 | 32 | 32 | |||||
| 120–129 | 38 | 37 | |||||
| 130–139 | 43 | 42 | |||||
| ≥140 | 48 | 47 | |||||
| HbA1c, % | |||||||
| 4.3–4.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 4.6–4.8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 4.9–5.1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 5.2–5.4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| 5.5–5.7 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 5.8–6.0 | 6 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| 6.1–6.3 | 7 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| 6.4–6.6 | 9 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 6.7–6.9 | 10 | 5 | 7 | ||||
| ≥7.0 | 11 | 5 | 8 | ||||
| Total score | 83 | 100 | 109 | 126 | 91 | 112 | 132 |
Appendix Table 2A.
Test Characteristics of the ADA Model.
| Threshold | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Positive likelihood ratio | Negative likelihood ratio | Positive predictive value, % | Negative predictive value, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 15 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 20 | 100 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 10 | 1.12 | 0.00 | 43 | 100 |
| 30 | 99 | 15 | 1.16 | 0.09 | 44 | 94 |
| 35 | 97 | 22 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 46 | 92 |
| 40 | 93 | 35 | 1.44 | 0.20 | 49 | 88 |
| 45 | 79 | 63 | 2.12 | 0.34 | 59 | 81 |
| 50 | 65 | 71 | 2.27 | 0.49 | 61 | 75 |
| 55 | 44 | 87 | 3.27 | 0.65 | 69 | 69 |
| 60 | 24 | 94 | 4.19 | 0.81 | 74 | 65 |
| 65 | 17 | 97 | 5.92 | 0.86 | 80 | 63 |
| 70 | 11 | 100 | – | 0.89 | 100 | 63 |
| 75 | 7 | 100 | – | 0.93 | 100 | 61 |
| SO | 3 | 100 | – | 0.97 | 100 | 60 |
| 85 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
Appendix Table 2B.
Test Characteristics of the Basic Plus HbA1c Model.
| Threshold | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Positive likelihood ratio | Negative likelihood ratio | Positive predictive value, % | Negative predictive value, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 10 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 15 | 100 | 3 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 20 | 100 | 5 | 1.05 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 11 | 1.13 | 0.00 | 43 | 100 |
| 30 | 97 | 15 | 1.15 | 0.18 | 44 | 89 |
| 35 | 97 | 26 | 1.31 | 0.11 | 47 | 93 |
| 40 | 87 | 45 | 1.58 | 0.28 | 52 | 84 |
| 45 | 72 | 63 | 1.93 | 0.45 | 57 | 77 |
| 50 | 54 | 79 | 2.55 | 0.59 | 63 | 72 |
| 55 | 38 | 93 | 5.70 | 0.66 | 79 | 69 |
| 60 | 20 | 97 | 6.90 | 0.83 | 82 | 64 |
| 65 | 14 | 98 | 7.39 | 0.88 | 83 | 63 |
| 70 | 10 | 100 | – | 0.90 | 100 | 62 |
| 75 | 7 | 100 | – | 0.93 | 100 | 61 |
| 80 | 3 | 100 | – | 0.97 | 100 | 60 |
Appendix Table 2C.
Test Characteristics of the Basic Plus 1-h GCT Plus HbA1c Model.
| Threshold | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Positive likelihood ratio | Negative likelihood ratio | Positive predictive value, % | Negative predictive value,% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | 40 | ||
| 20 | 100 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 8 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 30 | 99 | 10 | 1.09 | 0.15 | 42 | 91 |
| 35 | 99 | 17 | 1.19 | 0.08 | 45 | 95 |
| 40 | 94 | 26 | 1.27 | 0.22 | 46 | 87 |
| 45 | 93 | 42 | 1.60 | 0.17 | 52 | 90 |
| 50 | 87 | 54 | 1.91 | 0.23 | 56 | 86 |
| 55 | 75 | 77 | 3.27 | 0.33 | 69 | 82 |
| 60 | 59 | 86 | 4.14 | 0.48 | 74 | 76 |
| 65 | 46 | 92 | 6.10 | 0.58 | 80 | 72 |
| 70 | 34 | 97 | 11.83 | 0.68 | 89 | 68 |
| 75 | 20 | 99 | 20.70 | 0.81 | 93 | 65 |
| 80 | 13 | 100 | – | 0.87 | 100 | 63 |
| 85 | 8 | 100 | – | 0.92 | 100 | 62 |
| 90 | 7 | 100 | – | 0.93 | 100 | 61 |
| 95 | 6 | 100 | – | 0.94 | 100 | 61 |
| 100 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
Appendix Table 2D.
Test Characteristics of the Basic Plus Random Glucose Plus HbA1c Model.
| Threshold | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | Positive likelihood ratio | Negative likelihood ratio | Positive predictive value, % | Negative predictive value, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 100 | 0 | 1.00 | – | 40 | – |
| 20 | 100 | 1 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 25 | 100 | 3 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 30 | 100 | 5 | 1.05 | 0.00 | 41 | 100 |
| 35 | 100 | 6 | 1.06 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 40 | 100 | 8 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 42 | 100 |
| 45 | 100 | 18 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 45 | 100 |
| 50 | 99 | 31 | 1.44 | 0.04 | 49 | 97 |
| 55 | 94 | 45 | 1.71 | 0.13 | 54 | 92 |
| 60 | 86 | 59 | 2.10 | 0.24 | 59 | 86 |
| 65 | 70 | 78 | 3.21 | 0.38 | 68 | 80 |
| 70 | 49 | 88 | 3.98 | 0.58 | 73 | 72 |
| 75 | 39 | 92 | 5.18 | 0.66 | 78 | 69 |
| 80 | 28 | 97 | 9.86 | 0.74 | 87 | 67 |
| 85 | 20 | 98 | 10.35 | 0.82 | 88 | 64 |
| 90 | 14 | 98 | 7.39 | 0.88 | 83 | 63 |
| 95 | 6 | 99 | 5.92 | 0.95 | 80 | 61 |
| 100 | 6 | 100 | – | 0.94 | 100 | 61 |
| 115 | 3 | 100 | – | 0.97 | 100 | 60 |
| 125 | 1 | 100 | – | 0.99 | 100 | 60 |
Footnotes
Financial disclosure/conflict of interest: All authors have nothing to disclose.
References
- 1.Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Daniels SR, Standiford D, Khoury PR, et al. Increased incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among adolescents. J Pediatr. 1996;128:608–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(96)80124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Vegt F, Dekker JM, Jager A, Hienkens E, Kostense PJ, et al. Relation of impaired fasting and postload glucose with incident type 2 diabetes in a Dutch population: the Hoorn study. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;285:2109–13. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.16.2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barr EL, Zimmet PZ, Welborn TA, Jolley D, Magliano DJ, et al. Risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in individuals with diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance: the Australian Diabetes, Obesity, and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab) Circulation. 2007;116:151–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.685628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee JM, Gebremariam A, Wu EL, Larose J, Gurney JG. Evaluation of nonfasting tests to screen for childhood and adolescent dysglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2597–602. doi: 10.2337/dc11-0827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lipton RB, Drum M, Burnet D, Rich B, Cooper A, et al. Obesity at the onset of diabetes in an ethnically diverse population of children: what does it mean for epidemiologists and clinicians? Pediatrics. 2005;115:e553–60. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lipton R, Keenan H, Onyemere KU, Freels S. Incidence and onset features of diabetes in African-American and Latino children in Chicago, 1985–1994. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18:135–42. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dolan LM, Bean J, D’Alessio D, Cohen RM, Morrison JA, et al. Frequency of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism and diabetes in a population-based screening of adolescents. J Pediatr. 2005;146:751–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee JM. Why young adults hold the key to assessing the obesity epidemic in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008;162:682–7. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.162.7.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li C, Ford ES, Zhao G, Mokdad AH. Prevalence of pre-diabetes and its association with clustering of cardiometabolic risk factors and hyperinsulinemia among U.S. adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005 – 2006. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:342–7. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.American Diabetes Association. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2000;105:671–80. doi: 10.1542/peds.105.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:393–403. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Izzo R, de Simone G, Chinali M, Iaccarino G, Trimarco V, et al. Insufficient control of blood pressure and incident diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:845–50. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM, et al. 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital Health Stat. 2002;246:1–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114:555–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaelber DC, Pickett F. Simple table to identify children and adolescents needing further evaluation of blood pressure. Pediatrics. 2009;123:e972–4. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-2680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J, Poffenbarger T, Portman RJ. Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics. 2004;113:475–82. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee JM, Wu EL, Tarini B, Herman WH, Yoon E. Diagnosis of diabetes using hemoglobin A1c: should recommendations in adults be extrapolated to adolescents ? J Pediatr. 2011;158:947–52. e1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.11.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gl u mer C, Vistisen D, Borch-Johnsen K, Colagiuri S. Risk scores for type 2 diabetes can be applied in some populations but not all. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:410–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-0945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reinehr T, Wabitsch M, Kleber M, De Sousa G, Denzer C, et al. Parental diabetes, pubertal stage, and extreme obesity are the main risk factors for prediabetes in children and adolescents: a simple risk score to identify children at risk for prediabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009;10:395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Puri M, Freeman K, Garcia M, Nussbaum H, DiMartino-Nardi JR. Criteria for oral glucose tolerance testing of obese minority youth. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007;20:703–10. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2007.20.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fagot-Campagna A, Saaddine JB, Engelgau MM. Is testing children for type 2 diabetes a lost battle? Diabetes Care. 2000;23:1442–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.23.9.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rhodes ET, Finkelstein JA, Marshall R, Allen C, Gillman MW, et al. Screening for type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents: attitudes, barriers, and practices among pediatric clinicians. Ambul Pediatr. 2006;6:110–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ambp.2005.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Robbins DC, Andersen L, Bowsher R, Chance R, Dinesen B, et al. Report of the American Diabetes Association’s Task Force on standardization of the insulin assay. Diabetes. 1996;45:242–56. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Palmert MR, Gordon CM, Kartashov AI, Legro RS, Emans SJ, et al. Screening for abnormal glucose tolerance in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1017–23. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.3.8305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dabelea D, Pettitt DJ. Intrauterine diabetic environment confers risks for type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in the offspring, in addition to genetic susceptibility. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2001;14:1085–91. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2001-0803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:393–403. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Phillips L, Ziemer D, Kolm P, Weintraub W, Vaccarino V, et al. Glucose challenge test screening for prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52:1798–807. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Banyas B, et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:802–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Libman IM, Barinas-Mitchell E, Bartucci A, Robertson R, Arslanian S. Reproducibility of the oral glucose tolerance test in overweight children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4231–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Freedman DS, Wang J, Thornton JC, Mei Z, Pierson RN, Jr, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in body fatness among children and adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16:1105–11. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]