Abstract
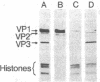
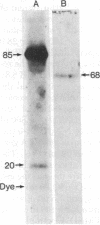
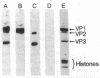
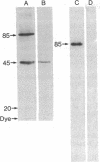
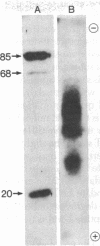
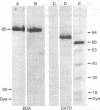
We describe a rapid and very sensitive method for detecting proteins as antigens after their separation in polyacrylamide/agarose composite gels, with or without sodium dodecyl sulfate. The polyacrylamide matrix is crosslinked with a reagent that can be cleaved with periodate or alkali to facilitate transfer of the protein bands to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper, where they are coupled covalently. Specific proteins are detected by autoradiography after sequential incubation with unfractionated, unlabeled specific antiserum and 125I-labeled protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Antibody and protein A can be removed with urea and 2-mercaptoethanol, and the same paper can be probed again with a different antiserum. An antiserum specific for the simian virus 40 virion proteins VP3 and VP2 has been prepared; it does not crossreact with VP1, as demonstrated by this method. An antiserum raised in rabbits against simian virus 40-transformed rabbit kidney cells is shown to be directed primarily against a periodate-sensitive moiety present in tumor (T) antigen from infected or transformed cells, whereas an antiserum raised in rabbits against large T antigen purified from lytically infected monkey kidney cells by electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate [Lane, D.P. & Robbins, A.K. (1978) Virology 87, 182-193] is directed primarily against determinants that are not sensitive to periodate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anker H. S. A solubilizable acrylamide gel for electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 16;7(3):293–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Consigli R. A. Chromatographic separation of the polyoma virus proteins and renaturation of the isolated VP1 major capsid protein. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):436–442. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.436-442.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. Direct identification of specific glycoproteins and antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:54–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain D. F., Pitney R. E. A method for the determination of the relative specific radioactivity of [3H] proteins in acrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen G., Landers T., Griffith J., Berg P. Characterization of components released by alkali disruption of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1079-1084.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Black P. H. Analysis of surface antigens on simian virus 40-transformed cells. II. Exposure of simian virus 40-induced antigens on transformed rabbit kidney and inbred hamster kidney cells by phospholipase C. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jul;51(1):115–134. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Lane D. P. An immune complex assay for SV40 T antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91411-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defendi V., Jensen F. Oncogenicity by DNA tumor viruses: enhancement after ultraviolet and cobalt-60 radiations. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):703–705. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Brocklehurst J. R., Dulbecco R. Virus-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of cells lytically infected or transformed by pol-oma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4666–4670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Flory P. J., Jr Synthesis of the SV40 viral polypeptide Vp1 during infection. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):344–353. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Robbins A. K. An immunochemical investigation of SV40 T antigens. 1. Production properties and specificity of rabbit antibody to purified simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Virology. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):182–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Consigli R. A. Immunological reactivity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1113-1120.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Yamada K. M. Direct detection of antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., McLaughlin B. C., Oxford J. S. Simian virus 40-induced T and tumor antigens. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):574–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.574-579.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R. Transfer of small DNA fragments from polyacrylamide gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection by hybridization with DNA probes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):1104–1112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showe M. K., Isobe E., Onorato L. Bacteriophage T4 prehead proteinase. II. Its cleavage from the product of gene 21 and regulation in phage-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 15;107(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Extraction and fingerprint analysis of simian virus 40 large and small T-antigens. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):140–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.140-153.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen J. M., Yang Y. R., Kirschiner M. W. Preparation of 125 I-Catalytic subunit of asparatate transcarbamylase and its use in studies of the regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3762–3768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Dohan C., Jr, Reznikoff C. Inactivating and mutagenic effects of nitrosoguanidine on simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):745–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Stinchcomb D., Losick R. Antibody directed against Bacillus subtilis rho factor purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate slab gel electrophoresis. Effect on transcription by RNA polymerase in crude extracts of vegetative and sporulating cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8824–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Chumackov P. M., Georgiev G. P. Minichromosome of simian virus 40: presence of histone HI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):2101–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]