Abstract
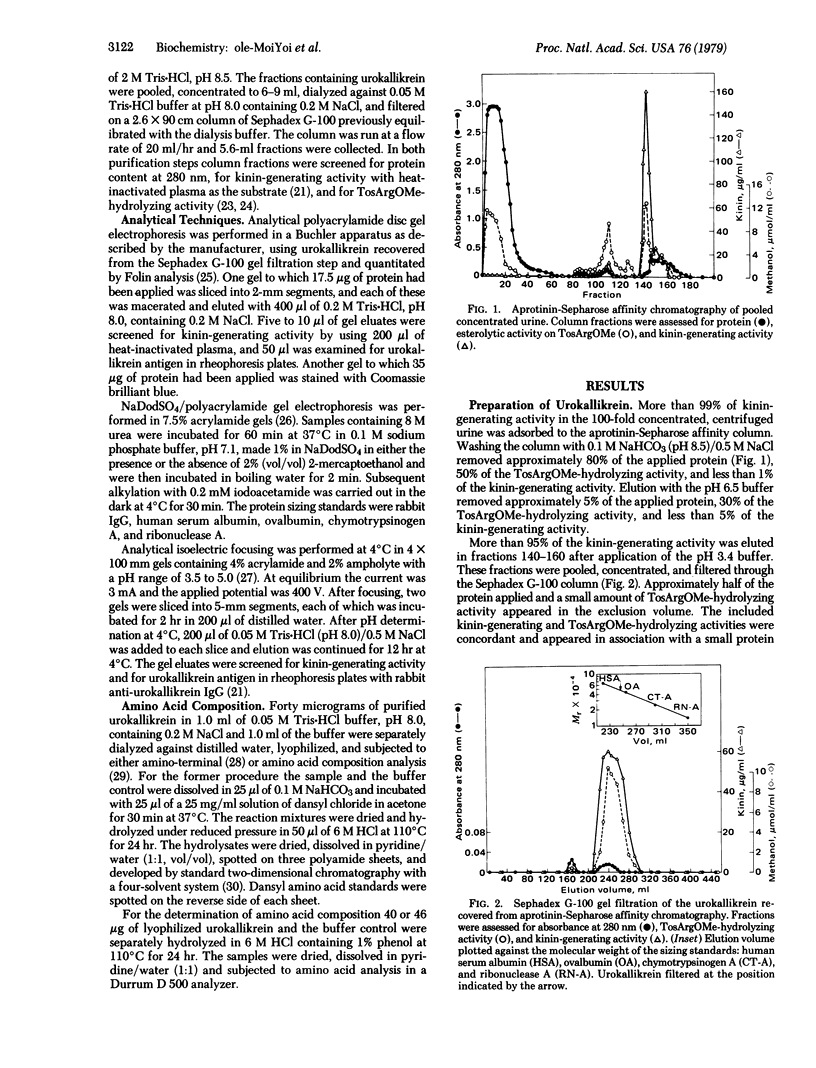
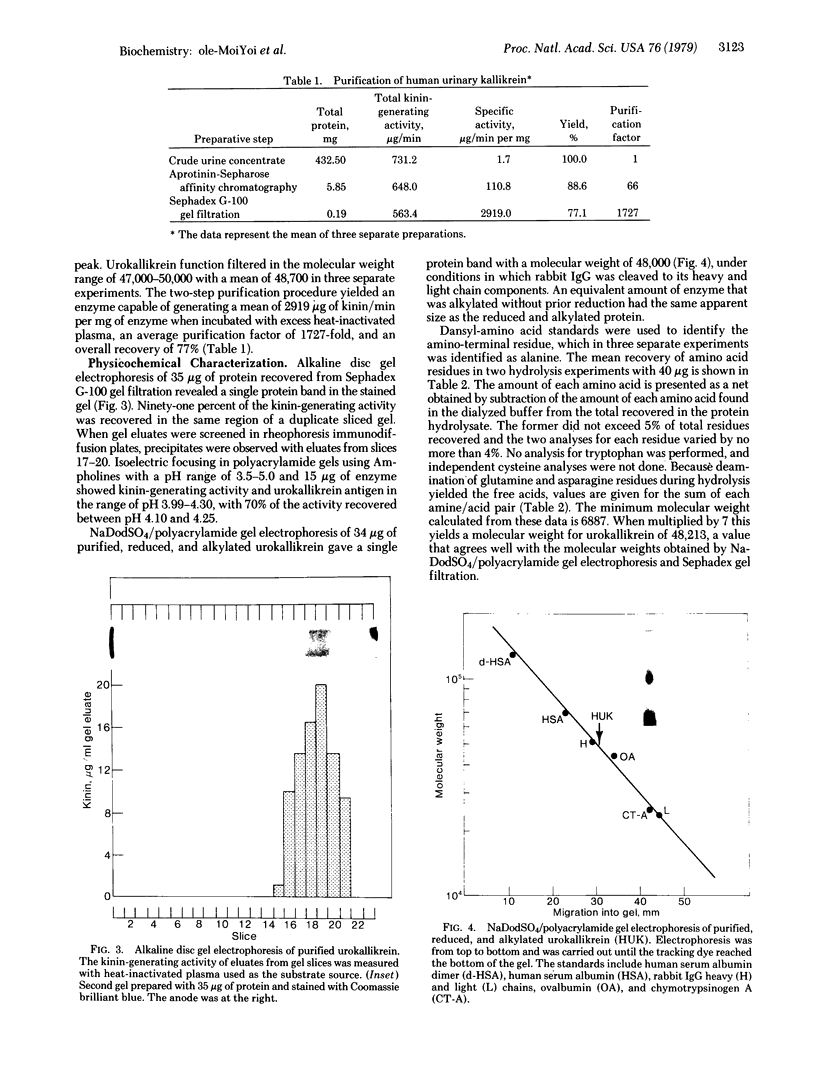
Human urinary kallikrein (urokallikrein) has been purified by affinity chromatography with aprotinin coupled to CH-Sepharose and by gel filtration. The isolation procedure, which was performed under mild conditions, was completed in a 36-hr period and yielded an overall recovery of more than 75% and a purification of 1727-fold. Homogeneity of the urokallikrein was demonstrated by three criteria: the coincidence of the stained protein band and functional urokallikrein in duplicate gels after alkaline disc gel electrophoresis; the appearance of a single stained band of molecular weight 48,000 on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of reduced and unreduced enzyme; and the finding of a single amino-terminal residue, namely alanine after dansylation and acid hydrolysis of purified enzyme. The Km of urokallikrein on N alpha-p-tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester was 400 microM, and the Vmax was 194 mumol/min per mg of protein, which is higher than that observed with any previous preparations. The molecular weight of 48,700 determined on gel filtration and the molecular weight of 48,000 observed by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis are in good agreement with the molecular weight of 48,213 calculated from the amino acid composition. The finding of a molecular weight higher than those previously reported, namely 27,000-43,500, the increased functional activity on tosylarginine methyl ester, and the detection of a single amino-terminal residue are consistent with the isolation of a more native protein by the procedure described in this paper.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adetuyibi A., Mills I. H. Relation between urinary kallikrein and renal function, hypertension, and excretion of sodium and water in man. Lancet. 1972 Jul 29;2(7770):203–207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERALDO W. T., FELDBERG W., HILTON S. M. Experiments on the factor in urine forming substance U. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):558–565. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Amin V. M., Ocholik T., Scicli A. G., Koch J. Urinary kallikrein in rats bred for their susceptibility and resistance to the hypertensive effect of salt. A new radioimmunoassay for its direct determination. Circ Res. 1978 May;42(5):727–731. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.5.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger R., Mann K., Bettels T. Isolation of human urinary kallikrein by affinity chromatography. Determination of human urinary kallikrein, I. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1977 Sep;15(9):479–483. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1977.15.1-12.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Diniz C. R., Mares-Guia M. Purification and properties of a human urinary kallikrein (kininogenase). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4311–4318. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. R., Andrews M. J., Jr, Guyton R. A., Margolius H. S., Pisano J. J. Urinary kallikrein in dogs with constriction of one renal artery. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jan;151(1):53–56. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Geller R., Pisano J. J., Sjoerdsma A. Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet. 1971 Nov 13;2(7733):1063–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Miyazaki K., Moriya H., Fujimoto Y., Hojima Y., Moriwaki C. Studies on urinary kallikreins. I. Purification and characterization of human urinary kallikreins. J Biochem. 1976 Oct;80(4):671–679. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Nasjletti A. Kinins, renal function and blood pressure regulation. Introduction. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):172–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K., Pierce J. V. Purification of rat urinary kallikreins and their specific antibody. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2312–2319. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B., Amin V. M., McGregor R. K., Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A. Isolation of rat urinary kallikrein and properties of its antibodies. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jul 15;25(14):1607–1612. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90471-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B., Ryan J. W. A simple high-yield procedure for isolation of human urinary kallikreins. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):285–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1710285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli G., Marini-Bettòlo G. B., Croxatto H. R., Di Iorio M. Purification and chemical studies on human urinary kallikrein. Ital J Biochem. 1974 Jan;23(1):44–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGELMAN A. M., CARLSON A. S., ROBERTSON T. Investigation of serum trypsin and related substances. I. The quantitative demonstration of trypsinlike activity in human blood serum by a micromethod. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:159–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Oza N. B., Ryan J. W. Human urinary kallikrein converts inactive to active renin and is a possible physiological activator of renin. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):144–145. doi: 10.1038/275144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva E., Diniz C. R., Mares-Guia M. Rat urinary kallikrein: purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4304–4310. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., PIERCE J. V. The nature of the kallidins released from human plasma by kallikreins and other enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:91–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoi O. O., Austen K. F., Spragg J. Kinin-generating and esterolytic activity of purified human urinary kallikrein (urokallikrein). Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 15;26(20):1893–1900. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ole-MoiYoi O. K., Spragg J., Austen K. F. Inhibition of human urinary kallikrein (urokallikrein) by anti-enzyme FAB. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]