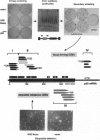
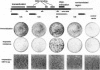
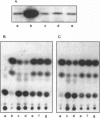
Abstract
p53 is a multifunctional tumor suppressor protein involved in the negative control of cell growth. Mutations in p53 cause alterations in cellular phenotype, including immortalization, neoplastic transformation, and resistance to DNA-damaging drugs. To help dissect distinct functions of p53, a set of genetic suppressor elements (GSEs) capable of inducing different p53-related phenotypes in rodent embryo fibroblasts was isolated from a retroviral library of random rat p53 cDNA fragments. All the GSEs were 100-300 nucleotides long and were in the sense orientation. They fell into four classes, corresponding to the transactivator (class I), DNA-binding (class II), and C-terminal (class III) domains of the protein and the 3'-untranslated region of the mRNA (class IV). GSEs in all four classes promoted immortalization of primary cells, but only members of classes I and III cooperated with activated ras to transform cells, and only members of class III conferred resistance to etoposide and strongly inhibited transcriptional transactivation by p53. These observations suggest that processes related to control of senescence, response to DNA damage, and transformation involve different functions of the p53 protein and furthermore indicate a regulatory role for the 3'-untranslated region of p53 mRNA.
Full text
PDF

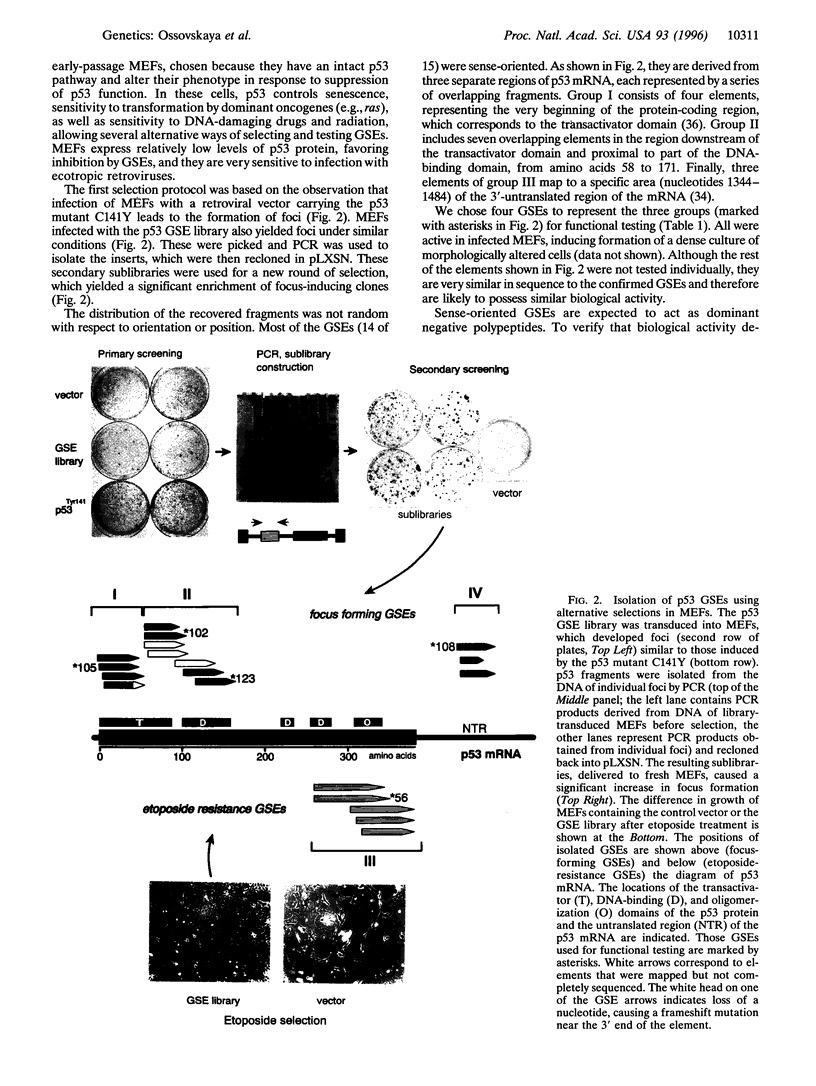


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atadja P., Wong H., Garkavtsev I., Veillette C., Riabowol K. Increased activity of p53 in senescing fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8348–8352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox L. S., Hupp T., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. A direct effect of activated human p53 on nuclear DNA replication. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2099–2105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber T. G., Osmanian C., Jacks T., Housman D. E., Koch C. J., Lowe S. W., Giaccia A. J. Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature. 1996 Jan 4;379(6560):88–91. doi: 10.1038/379088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudkov A. V., Kazarov A. R., Thimmapaya R., Axenovich S. A., Mazo I. A., Roninson I. B. Cloning mammalian genes by expression selection of genetic suppressor elements: association of kinesin with drug resistance and cell immortalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3744–3748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudkov A. V., Zelnick C. R., Kazarov A. R., Thimmapaya R., Suttle D. P., Beck W. T., Roninson I. B. Isolation of genetic suppressor elements, inducing resistance to topoisomerase II-interactive cytotoxic drugs, from human topoisomerase II cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3231–3235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey D. M., Levine A. J. p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2375–2385. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Rowan S., Shaulian E., Vousden K. H., Oren M. Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by trans-activation-deficient p53. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2170–2183. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks G. G., Egan S. E., Greenberg A. H., Mowat M. Mutant p53 tumor suppressor alleles release ras-induced cell cycle growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1344–1352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmayer T. A., Pestov D. G., Roninson I. B. Isolation of dominant negative mutants and inhibitory antisense RNA sequences by expression selection of random DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):711–717. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Sparks A., Lane D. P. Small peptides activate the latent sequence-specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi K., Bartel P. L., Li B., Marraccino R., Fields S. Two cellular proteins that bind to wild-type but not mutant p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6098–6102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondratov R. V., Kuznetsov N. V., Pugacheva E. N., Almazov V. P., Prasolov V. S., Kopnin B. P., Chumakov P. M. Funktsional'naia geterogennost' p53-responsivnykh élementov. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1996 May-Jun;30(3):613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Levine A. J. Human TAFII31 protein is a transcriptional coactivator of the p53 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5154–5158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Park S. H., Thompson T. C., Lane D. P. Ras-induced hyperplasia occurs with mutation of p53, but activated ras and myc together can induce carcinoma without p53 mutation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90541-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Vartikar J., Pipas J. M., Laimins L. A. Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):281–283. doi: 10.1038/363281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Czyzyk L. UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. C., Levine A. J. The properties of p53 proteins selected for the loss of suppression of transformation. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jan;5(1):61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pear W. S., Nolan G. P., Scott M. L., Baltimore D. Production of high-titer helper-free retroviruses by transient transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. How loops, beta sheets, and alpha helices help us to understand p53. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):543–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Conboy M. J., Rando T. A., Blau H. M. Tumor suppression by RNA from the 3' untranslated region of alpha-tropomyosin. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1107–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90320-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M., Wang Y., Mayr G., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: suppression, transformation, and transactivation. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):95–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M., Woelker B., Wang P., Wang Y., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. The C-terminal domain of p53 recognizes DNA damaged by ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9455–9459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Haviv I., Shaul Y., Oren M. Transcriptional repression by the C-terminal domain of p53. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):671–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Ginsberg D., Oren M. Identification of a minimal transforming domain of p53: negative dominance through abrogation of sequence-specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5581–5592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Milner J., Davies E. A., Oren M. Tight DNA binding and oligomerization are dispensable for the ability of p53 to transactivate target genes and suppress transformation. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2789–2797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., Breugnot C., May E. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the rat p53 nuclear oncoprotein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11384–11384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thukral S. K., Blain G. C., Chang K. K., Fields S. Distinct residues of human p53 implicated in binding to DNA, simian virus 40 large T antigen, 53BP1, and 53BP2. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8315–8321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishler R. B., Lamppu D. M., Park S., Price B. D. Microtubule-active drugs taxol, vinblastine, and nocodazole increase the levels of transcriptionally active p53. Cancer Res. 1995 Dec 15;55(24):6021–6025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truant R., Xiao H., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct interaction between the transcriptional activation domain of human p53 and the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2284–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Tomooka Y., Takai S., Ueda Y., Nishikawa S., Yagi T., Tokunaga T., Takeda N., Suda Y., Abe S. Enhanced proliferative potential in culture of cells from p53-deficient mice. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3313–3322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Nau M. M., Segal S., Minna J. D. p53: a transdominant regulator of transcription whose function is ablated by mutations occurring in human cancer. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y., Tainsky M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Strong L. C., Wahl G. M. Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]