Abstract
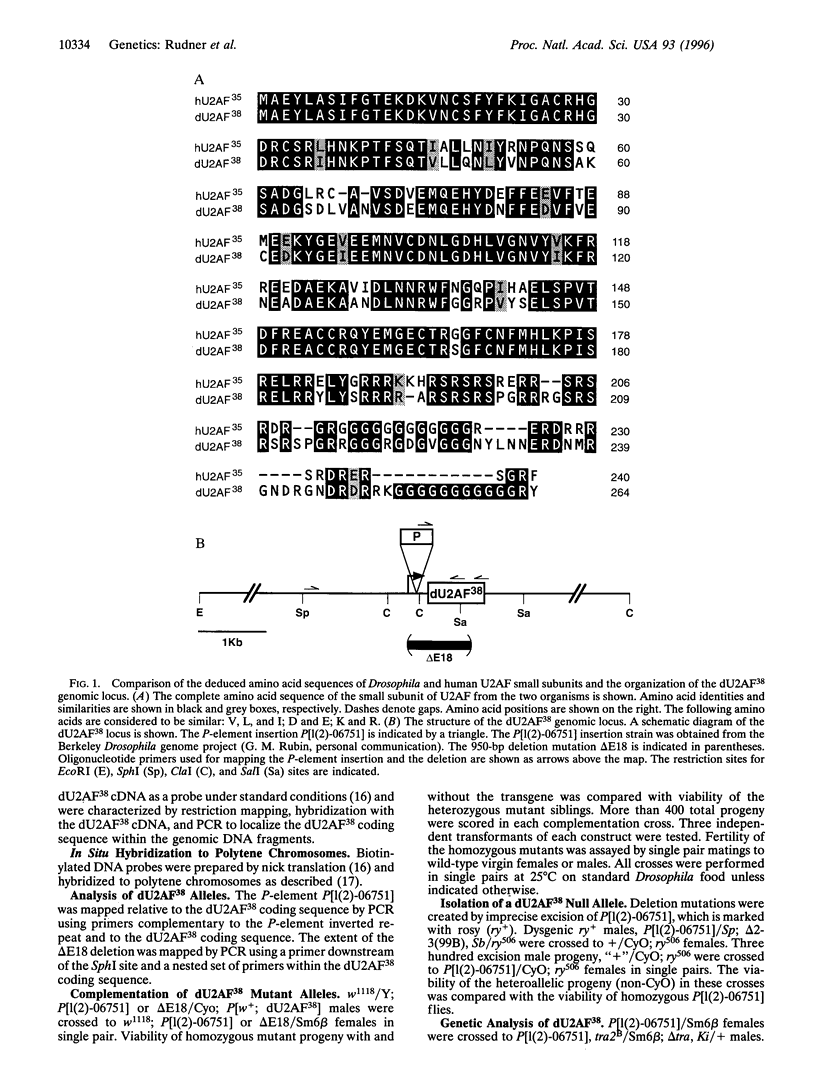
The essential eukaryotic pre-mRNA splicing factor U2AF (U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor) is required to specify the 3' splice at an early step in spliceosome assembly. U2AF binds site-specifically to the intron polypyrimidine tract and recruits U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein to the branch site. Human U2AF (hU2AF) is a heterodimer composed of a large (hU2AF65) and small (hU2AF35) subunit. Although these proteins associate in a tight complex, the biochemical requirement for U2AF activity can be satisfied solely by the large subunit. The requirement for the small subunit in splicing has remained enigmatic. No biochemical activity has been found for hU2AF35 and it has been implicated in splicing only indirectly by its interaction with known splicing factors. In the absence of a biochemical assay, we have taken a genetic approach to investigate the function of the small subunit in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. A cDNA clone encoding the small subunit of Drosophila U2AF (dU2AF38) has been isolated and sequenced. The dU2AF38 protein is highly homologous to hU2AF35 containing a conserved central arginine- and serine-rich (RS) domain. A recessive P-element insertion mutation affecting dU2AF38 causes a reduction in viability and fertility and morphological bristle defects. Consistent with a general role in splicing, a null allele of dU2AF38 is fully penetrant recessive lethal, like null alleles of the Drosophila U2AF large subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):521–524. doi: 10.1038/340521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Wolfner M. F. A molecular analysis of doublesex, a bifunctional gene that controls both male and female sexual differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):477–489. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond B. J., Davidson N. The Drosophila melanogaster actin 5C gene uses two transcription initiation sites and three polyadenylation sites to express multiple mRNA species. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2080–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaar R., Roche S. E., Beall E. L., Green M. R., Rio D. C. The conserved pre-mRNA splicing factor U2AF from Drosophila: requirement for viability. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):569–573. doi: 10.1126/science.7692602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. E., Lis J. T. The concentration of B52, an essential splicing factor and regulator of splice site choice in vitro, is critical for Drosophila development. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5360–5370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra S., Rio D. C. Cytotype control of Drosophila P element transposition: the 66 kd protein is a repressor of transposase activity. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):269–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90365-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng X., Mount S. M. Genetic enhancement of RNA-processing defects by a dominant mutation in B52, the Drosophila gene for an SR protein splicing factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):6273–6282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.11.6273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin J., Naik K., Wentz-Hunter K. U2AF homolog required for splicing in vivo. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):573–575. doi: 10.1126/science.8211184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. The organization of 3' splice-site sequences in mammalian introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2113–2123. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring H. Z., Lis J. T. The SR protein B52/SRp55 is essential for Drosophila development. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7499–7506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Maine E. M., Keyes L. N., Samuels M. E., Cline T. W., Schedl P. The Drosophila female-specific sex-determination gene, Sex-lethal, has stage-, tissue-, and sex-specific RNAs suggesting multiple modes of regulation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):708–719. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebel C. W., Admon A., Rio D. C. Soma-specific expression and cloning of PSI, a negative regulator of P element pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1995 Feb 1;9(3):269–283. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebel C. W., Kanaar R., Rio D. C. Regulation of tissue-specific P-element pre-mRNA splicing requires the RNA-binding protein PSI. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1713–1725. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Biochemical characterization of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor: an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor with a novel intranuclear distribution. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Patton J. G., Green M. R. Cloning and domain structure of the mammalian splicing factor U2AF. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):609–614. doi: 10.1038/355609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M., Zamore P. D., Carmo-Fonseca M., Lamond A. I., Green M. R. Cloning and intracellular localization of the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor small subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8769–8773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo P., Maniatis T. The splicing factor U2AF35 mediates critical protein-protein interactions in constitutive and enhancer-dependent splicing. Genes Dev. 1996 Jun 1;10(11):1356–1368. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.11.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]