Abstract
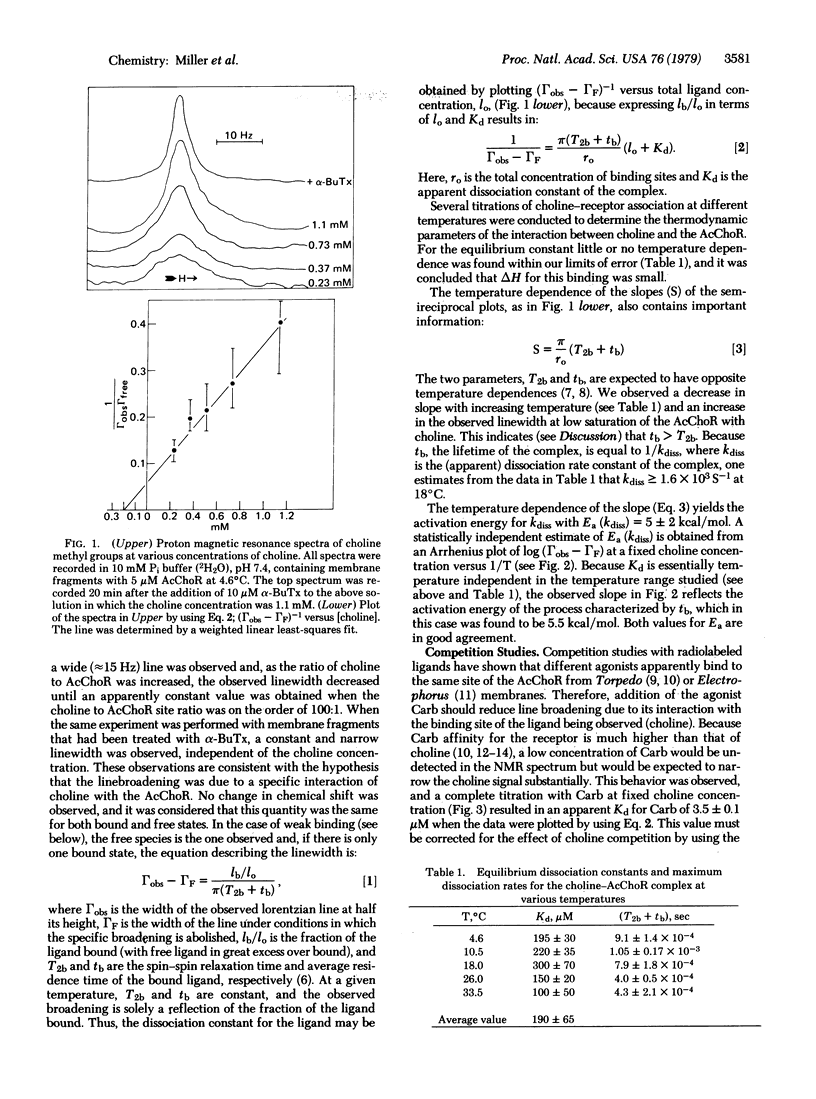
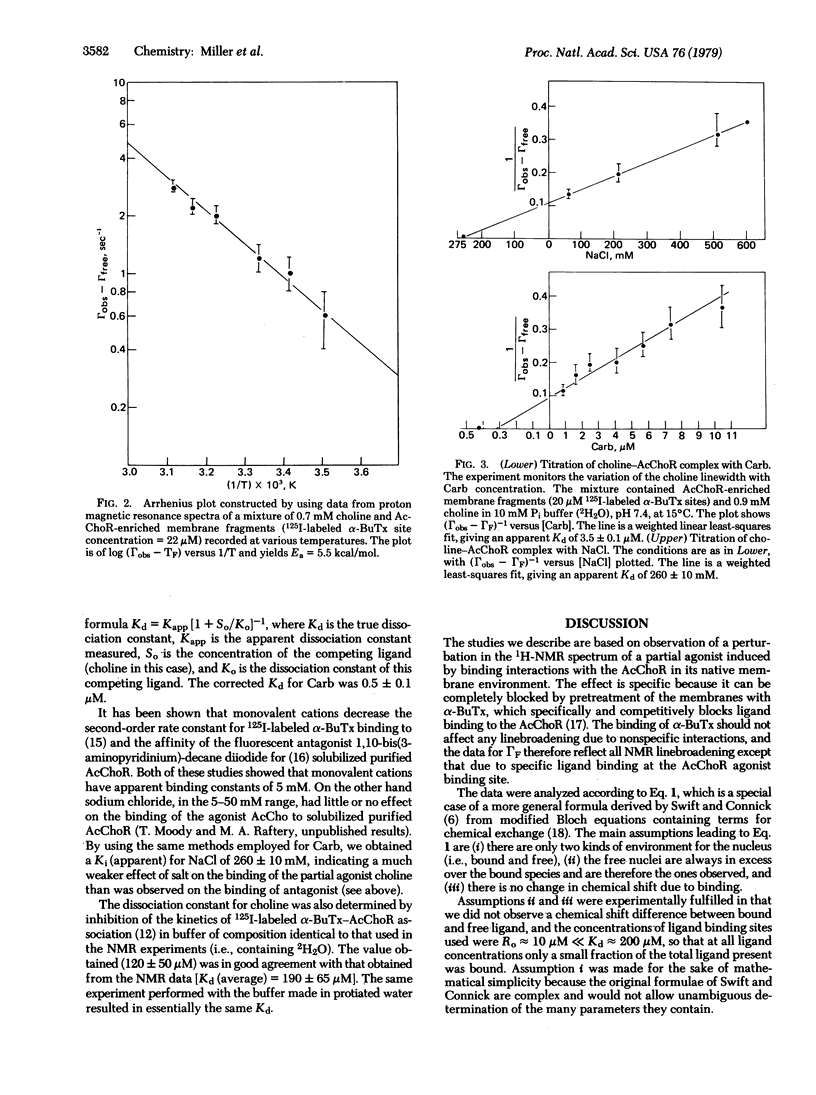
Proton magnetic resonance has been used to monitor binding of choline, a known partial agonist, to acetylcholine receptor-enriched membrane preparations from Torpedo californica electroplax. The interaction between choline and receptor led to a broadening of the resonance of the choline methyl groups and this effect was reversed by alpha-bungarotoxin, a quasi-irreversible antagonist of the acetylcholine receptor. From the concentration dependence of line broadening the equilibrium dissociation constant for choline was obtained (Kd = 190 +/- 65 microM). The temperature dependence of the parameters observed in the choline titrations gave an enthalpy of binding delta H less than 1.5 kcal/mol and allowed estimates for the dissociation rate constant of the receptor-choline complex (kdiss greater than 1.6 x 10(3) S(1) and the respective activation energy, Ea (Kdiss) approximately 5.5 kcal/mol. The association of other ligands with the membrane-bound receptor could also be studied by observing effects of varying concentrations of such ligands on the choline methyl group linewidth at a constant choline concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Sakmann B. A comparison of current-voltage relations for full and partial agonists. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:621–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrantes F. J. Agonist-mediated changes of the acetylcholine receptor in its membrane environment. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard S. G., Quast U., Reed K., Lee T., Schimerlik M. I., Vandlen R., Claudio T., Strader C. D., Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Interaction of [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin with acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1875–1883. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. R., Raftery M. A. Fractionation and partial characterization of membrane particles from Torpedo californica electroplax. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 11;12(19):3593–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00743a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J., Dunn S. M., Blanchard S. G., Raftery M. A. Specific binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin to Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2576–2579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. L., Donner D. B., Moore D. E., Hess G. P. Allosteric interactions between the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor and chemical mediators: equilibrium measurements. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):678–684. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünhagen H. H., Iwatsubo M., Changeux J. P. Fast kinetic studies on the interaction of cholinergic agonists with the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata as revealed by quinacrine fluorescence. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):225–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maelicke A., Fulpius B. W., Klett R. P., Reich E. Acetylcholine receptor. Responses to drug binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4811–4830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Raftery M. A. Use of a fluorescent probe for the study of ligand binding by the isolated cholinergic receptor of Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1156–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Chang H. W. Dynamic properties of isolated acetylcholine receptor protein: kinetics of the binding of acetylcholine and Ca ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3994–3998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Schimerlik M. I., Raftery M. A. Ligand-induced changes in membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor observed by ethidium fluorescence. 2. Stopped-flow studies with agonists and antagonists. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1891–1901. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Schimerlik M., Lee T., Witzemann T. L., Blanchard S., Raftery M. A. Ligand-induced conformation changes in Torpedo californica membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2405–2414. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Vandlen R. L., Reed K. L., Lee T. Characterization of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor: its subunit composition and ligand-binding properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:193–202. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K., Vandlen R., Bode J., Duguid J., Raftery M. A. Characterization of acetylcholine receptor-rich and acetylcholinesterase-rich membrane particles from Torpedo californica electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimerlik M., Quast U., Raftery M. A. Ligand-induced changes in membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor observed by ethidium fluorescence. 1. Equilibrium studies. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1884–1890. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. The cation sensitivity of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):617–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. D., Schmidt P. G., Stark G. R. Aspartate transcarbamylase. A study by transient nuclear magnetic resonance of the binding of succinate to the native enzyme and its catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1180–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


