Abstract
A chromosomal translocation results in the production of a PAX8-PPARG Fusion Protein (PPFP) in ~35% of follicular thyroid carcinomas. To examine the role of PPFP in thyroid oncogenesis, the fusion protein was stably expressed in the non-transformed rat thyroid cell line PCCL3. PPFP conferred on PCCL3 cells the ability to invade through Matrigel and to form colonies in anchorage independent conditions. PPFP also increased the fraction of cells with Wnt/TCF responsive green fluorescent protein reporter gene expression. This Wnt/TCF-activated population was enriched for colony forming and invading cells. These actions of PPFP required a functional PPARG DNA binding domain within PPFP and were further stimulated by PPARG agonists. The data indicate that PPFP, through its PPARG DNA binding domain, induces Wnt/TCF pathway activation in a subpopulation of cells, and these cells have properties of cellular transformation including increased invasiveness and anchorage-independent growth.
Keywords: thyroid carcinoma, PPFP, Wnt, TCF
INTRODUCTION
The paired box 8 (PAX8) - peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) fusion protein (PPFP) results from a t(2;3)(q13;p25) chromosomal translocation implicated in the etiology of ~35% of follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) (Kroll et al. 2000). The promoter and most of the PAX8 gene is fused to the coding exons of the PPARG gene. Since the PAX8 promoter is highly active in the thyroid, PPFP is expressed at a high level in thyroid carcinomas containing this translocation. Expression of PPFP increases cell growth, viability, and anchorage-independence in thyroid and non-thyroid cell lines (Powell et al. 2004; Au et al. 2006; Li et al. 2012).
Both fusion partners of PPFP play important roles in tissue development and differentiation. PAX8 is a transcription factor required for thyroid development and mature thyroid gene expression (Esposito et al. 1998; Fabbro et al. 1998; Macchia et al. 1998; Mansouri et al. 1998; Ohno et al. 1999; Magliano et al. 2000). PPARG is a nuclear hormone receptor that has been well studied as the master regulator of adipocyte differentiation and as an important therapeutic target for diabetes, atherosclerosis, inflammation and cancer (Tontonoz & Spiegelman 2008). Modulation of PPARG-regulated pathways is thought to be important in PPFP carcinogenesis, and this is consistent with the observation that a different translocation fusing PPARG to the gene CREB3L2 also has been identified in FTC (Lui et al. 2008).
The initial report of PPFP occurrence and subsequent publications demonstrate that PPFP interferes with PPARG transactivation in a dominant negative manner (Kroll et al. 2000; Powell et al. 2004; Yin et al. 2006, 2009).). The hypothesis that PPFP exerts its pro-oncogenic effect via repression of PPARG is bolstered by observations that PPARG is downregulated in other types of thyroid carcinoma, that restoration of PPARG activity has anti-proliferative, pro-differentiation effects, and that heterozygous deletion of Pparg enhances tumorigenesis in an unrelated mouse model of thyroid carcinoma (Aldred et al. 2003; Marques et al. 2004; Park et al. 2005; Kato et al. 2006).
Nonetheless, there is evidence that PPFP also can transactivate some PPARG target genes. Numerous PPARG target genes are upregulated in PPFP tumor samples versus non-PPFP FTC or normal thyroid (Lacroix et al. 2005; Giordano et al. 2006). In vitro, PPFP stimulates the promoters of some PPARG target genes, represses others, or both depending on the cellular context (Powell et al. 2004; Au et al. 2006; Giordano et al. 2006).
Thyroid specific expression of PPFP combined with thyroid specific knockout of Pten in a transgenic mouse model generates spontaneous metastatic FTC (Dobson et al. 2011). In the thyroids of these mice, PPARG target genes can be positively or negatively regulated by PPFP. With administration of the PPARG agonist pioglitazone, however, adipocyte PPARG target genes are broadly upregulated and thyrocytes adopt an adipocyte phenotype, indicating that the functional domains of PPFP retain their capacity to act in a strongly PPARG-like manner. Thus, overall, the actions of PPFP that contribute to thyroid carcinogenesis are poorly understood..
In this study we show that expression of PPFP in the rat thyroid PCCL3 cell line induces properties of transformation, including increased anchorage-independent growth and invasiveness. Transformation requires a functional PPARG DNA binding domain (DBD) within PPFP and is further enhanced by PPARG agonists. Our data also show that a small fraction of PCCL3 cells is Wnt/TCF-responsive, that the responsive fraction is expanded by PPFP expression, and that this fraction is enriched in cells with the transformed phenotype.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and Reagents
The PCCL3 differentiated rat thyroid cell line has been described (Fusco et al. 1987). PCCL3 cells and their derivatives were cultured at 5% CO2 in Coon's F-12 media with L-glutamine, 5% fetal bovine serum, antibiotic/antimycotic (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, US), 1 mIU/ml TSH, 10 µg/ml insulin, 5 µg/ml apo-transferrin, 10 nM hydrocortisone (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, US), and prophylactic plasmocin (Invivogen, San Diego, CA, US).
SR1664 was a gift from Drs. Patrick Griffin and Bruce Spiegelman. GW9662 and T0070907 were purchased from Cayman Chemicals (Ann Arbor, MI, US). Bvt.13 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Myc antibody was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, US, catalog #2276) and GAPDH antibody sc-32233 was from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, US).
Stable Transfection
The P box amino acids EGG within the PPARG DBD of PPFP were mutated to AAA by inverse PCR to generate PPFP-AAA, and the entire sequence was verified. PPFP or PPFP-AAA with 3 Myc epitopes at the N terminus was inserted into the pCagen plasmid (Addgene, Cambridge, MA, US, plasmid 11160) (Matsuda & Cepko 2004). pCagen-PPFP, pCagen-PPFP-AAA or pCagen empty vector control plasmid was co-transfected at 10-fold excess with a hygromycin resistance vector (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, US, #631625) into PCCL3 cells using Fugene 6 (Promega, Fitchburg, WI, US). Transfected cells were plated at clonogenic density and subjected to hygromycin B selection at 400 µg/ml. Resistant colonies were assayed for PPFP by RT-PCR and Western blot.
DNA Binding Assay
The DNA binding activities of PPFP and PPFP-AAA were assessed using an avidin biotin complex to DNA assay (Glass et al. 1987) with minor modifications. Whole cell lysates were generated from stably transfected PCCL3 cells using M-PER (Thermo Scientific) supplemented with 0.4 M NaCl and Halt Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Thermo Scientific). Fifty µg of lysate protein were incubated with a double stranded oligonucleotide, biotinylated at the 5’ end of the top strand, containing the mouse Aqp7 gene PPAR response element. The top strand sequence is AGTTCTGTTGTGCTTCTCCAGGGGAGAGGTCAGTAGGGCAGGGGTTT, and the minimal response element is underlined. A mutated sequence was used as a specificity control in which the underlined sequence was changed to ATTTGAGATTTCA. Protein-DNA complexes were pulled down with NeutrAvidin agarose beads (Thermo Scientific), and were then subjected to electrophoresis through an SDS polyacrylamide gel and analyzed for PPFP by Western blot using a Myc antibody.
Lentiviral Construction and Infection
All lentivirus construction was done at the University of Michigan Vector Core. Lentiviral TOP-destabilized green fluorescent protein (dGFP) construct was a gift of Dr. Irving Weissman through Dr. Hasan Korkaya. pGreenFire TCF/LEF lentivirus reporter was obtained from System Biosciences (Mountain View, CA, US). In this construct, dGFP expression is driven by a minimal CMV promoter preceded by four TCF/LEF response elements. The same pGreenFire reporter but lacking TCF binding sites was used as a control to set flow cytometry gates for GFP positivity. Cells were infected with 10X concentrated particles provided by the Core, supplemented with 5 µg/ml polybrene. 5 days after infection, cells were checked for GFP expression. GFP positive cells were isolated via fluorescence activated cell sorting and replaced in culture to obtain 100% transduced cell lines.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometric analysis and sorting was done at the University of Michigan Flow Cytometry Core. Cells to be run on a flow cytometer were filtered through a 40 micron sieve after removal from culture. Cell were resuspended in Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) with propidium iodide (PI) or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) added as a viability indicator. At least 10,000 live cell events were recorded during each run of a cell sample through the flow cytometer. Gates were set at the level of GFP expression in 99.5% of control cells expressing GFP under the control of the minimal CMV promoter without TCF response elements. Test samples with GFP levels higher than gated were considered GFP positive and TCF responsive.
Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
Live trypsinized cells in 0.2% trypan blue were counted on a hemocytometer, where at least 95% of cells were verified as singlets. Five thousand cells were resuspended in 333 µl full media, mixed with 667 µl full media plus 0.5% low melt agarose, and added to a well in a 24 well ultra low attachment plate. After the agarose set, 100 µl of full media was added to cover the well. Media was added every 5 days to maintain coverage. After 21 days, cells were stained with 0.025% crystal violet and colonies counted under a microscope.
Matrigel Invasion Assay
Cell culture inserts for 24 well plates from BD Biosciences (Franklin Lakes, NJ, US) were used with standard tissue culture plates. One hundred µl of 12.5% Matrigel (BD Biosciences) in unsupplemented F-12 media was added to each insert to cover the base of the top chamber. Matrigel was allowed to set in a 37° incubator for 60 minutes. Six hundred µl Coon's F-12 media supplemented with 10% FBS was added directly to the bottom well. Five thousand or 25000 single cells obtained as above were resuspended in 200 µl unsupplemented F-12 media and added to the upper chamber. After 36 hours the experiment was stopped by addition of paraformaldehyde to a final concentration of 1.5%. Afterwards the media were aspirated and a gentle swabbing removed the Matrigel layer and any remaining media. Cells on the bottom of the inserts were stained in a solution of 0.025% crystal violet, washed and stored in distilled water, and counted under a microscope.
Quantitative PCR and RT-PCR
Cells removed from culture by trypsinization were placed directly in RealTime Lysis Buffer (Roche Applied Science, Basel, Switzerland) and cDNA was synthesized directly from lysate using Transcriptor Universal cDNA Master. Primer and probe sets for the respective genes were ordered from Universal Probe Library (Roche). Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) was done on a Lightcycler 480 using Sybr Green I Master. Analysis was done by the LightCycler software at High Sensitivity setting (Roche).
Quantitative PCR for PPFP expression was performed as follows. RNA was isolated using an RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, US). cDNA was synthesized using SuperScript III (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, US). Real-time PCR was performed using an Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA, US) Step One Plus real-time PCR instrument and Power SYBR Green master mix. In general, the cDNA from 100 ng RNA was used in triplicate PCR. To analyze lentiviral GFP reporter construct insertion into cell lines, genomic DNA was prepared using a Wizard SV Genomic DNA Purification kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and subjected to qPCR. Primer sequences are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
PCR primer pairs
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Actb | GCTTCTTTGCAGCTCCTTCGT | GCGCAGCGATATCGTCATC |
| Ccnd1 | CAGACCTTTGTGGCCCTCTG | CTACCATGGAGGGTGGGTTG |
| Cldn1 | AGGTGCAGAAGATGTGGATGG | GGCCACTAATGTCGCCAGA |
| Fgf4 | CACGCAGACACGAGGGAC | CTCCGAAGATGCTCACCACG |
| Fgf18 | CGAGGACGGGGACAAGTATG | CTTGCCCTTGATCCGGACTT |
| Fst | GGATGATTTTCAACGGGGGC | AGTCCACGTTCTCACACGTT |
| GFP | GCCGCATGACCAACAAGATG | AAGTGGTAGAAGCCGTAGCC |
| Gja1 | GTTCCACCACTTTGGCGTG | CAGTCACCCATGTCTGGGC |
| Gusb | CTCACAGAGATTGACCTGCCTCTA | TTTGGCGCACGCCTTTA |
| Nkx2-2 | ACCGAGGGCCTCCAATACT | AGGGCTCTGGGGATTTGGA |
| Pgk1 | GGAAGCGGGTCGTGATGA | TTTGGTTGTTTGTTATCTGGTTGTTC |
| Pparg | AGGCGAGGGCGATCTTG | CATGTCGTAGATGACAAATGGTGAT |
| PPFP | CGGACAGGGCAGCTATGC | TCTCTGTGTCAACCATGGTCATT |
| Vcan | CCATGTCACTGGCTGTGGAT | AGCGGCAAAGTTCAGAGTGT |
| Wisp2 | AACCCACTGATCCATCTTCTGG | TGTCCAAGGACAGGCACAGG |
In vivo studies
All in vivo studies were approved by the University of Michigan Committee on the Use and Care of Animals. FVB/N mice with combined thyroid-specific expression of PPFP and thyroid-specific deletion of Pten (denoted PPFP;PtenFF;Cre) develop FTC that is responsive to pioglitazone, whereas control FVB/N mice with just thyroid-specific Pten deletion (PtenFF;Cre) develop thyroid hyperplasia without neoplasia (Dobson et al. 2011). Thyroid gland RNA from six 10 week old mice of both genotypes was used to evaluate the expression of potentially TCF-responsive genes by RT-qPCR using the methods described above for PPFP.
Beginning at 8 weeks of age and continuing for 14 days, PPFP;PtenFF;Cre mice were treated with either a control diet, or pioglitazone in the chow at 200 parts per million, or SR1664 by IP injection at 30 mg/kg body weight every 12 hours. SR1664 at 20 mg/kg is strongly insulin-sensitizing (Choi et al. 2011). Thyroid size was measured by ultrasound at the start and end of the two week treatment period as described (Dobson et al. 2011).
Statistical Analyses
Statistical differences for colony growth, invasion, TCF activation, and gene expression were determined using the Student’s t-test with p<0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
The PPARG DBD within PPFP is essential for the ability of PPFP to induce a transformed cell phenotype
The PCCL3 rat thyroid cell line (Fusco et al. 1987) was stably transfected to express Myc-tagged PPFP or Myc-tagged PPFP with a mutated, non-functional DBD, described in more detail below. Expression of PPFP at the RNA level was 21 ± 2.1 fold above endogenous PPARG by RT-qPCR (n=3), which is within the range of 10–50 fold typically seen in PPFP expressing thyroid carcinomas (Giordano et al. 2006).
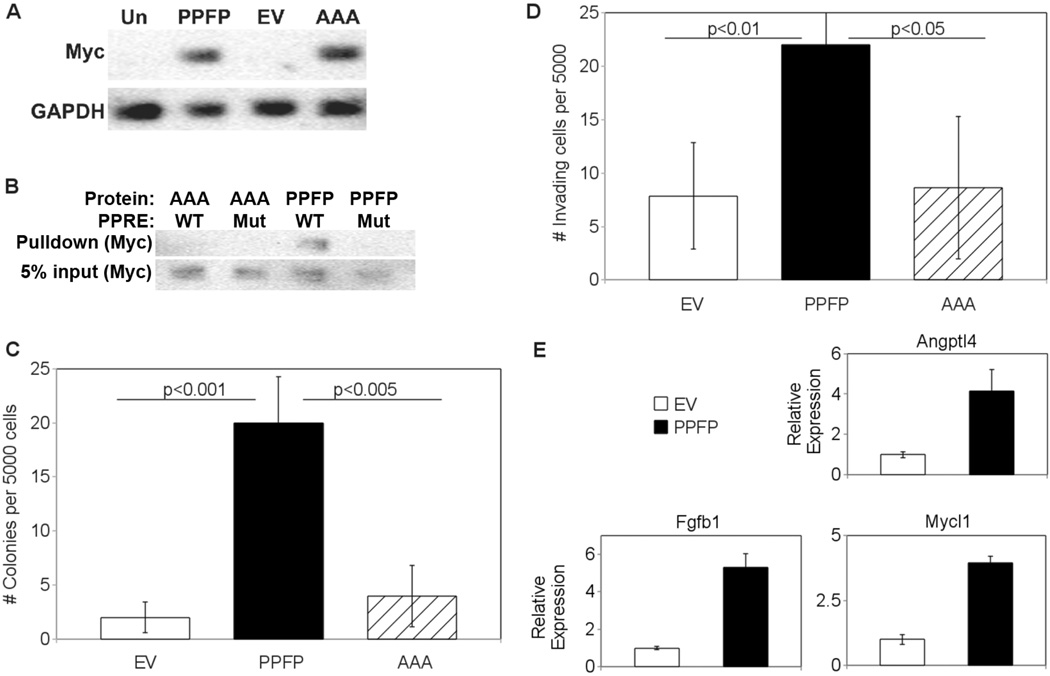
To determine whether PPFP activities depend on retention of a functional PPARG DBD, we mutated the P box amino acids EGG at the base of the first zinc finger to AAA, and stably expressed this mutant PPFP protein in PCCL3 cells. Henceforth, the protein will be denoted PPFP-AAA and the cell line PCCL3-AAA. The PPFP and PPFP-AAA proteins were expressed at similar levels in their respective cell lines [Fig. 1A]. As expected given that P box amino acids contact the bases in the DNA response element (Umesono & Evans 1989), the AAA mutation prevented binding to a PPAR response element [Fig. 1B].
Figure 1.
(A) Expression of PPFP in stably transfected PCCL3 cells. Whole cell lysates were made from untransfected PCCL3 cells (Un), or PCCL3 cells stably transfected with either PPFP, empty vector (EV), or PPFP in which the P Box amino acids EGG were mutated to AAA (AAA). Twenty micrograms of protein per lysate were analyzed by Western blot for Myc, after which the blot was reprobed for GAPDH. PPFP is ~100 kDa and GAPDH is ~36 kDa. (B) P Box mutation AAA prevents binding of PPFP to a PPAR response element (PPRE). PCCL3-PPFP or PCCL3-AAA whole cell lysates were incubated with a biotinylated PPRE from the mouse Aqp7 gene (WT) or a mutated version (Mut), as described in Methods. Protein-DNA complexes were isolated with NeutrAvidin agarose beads and were analyzed for PPFP by Western blot using anti-Myc (top row). Five percent of input also was analyzed (bottom row). (C) Increased soft agar colony formation by PCCL3-PPFP cells. PCCL3-EV, -PPFP or -AAA cells were suspended in soft agar at 5000 cells per well and colony formation after 21 days was determined as described in Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SD and repeated with independent cell lines. (D) Increased invasion by PCCL3-PPFP cells. PCCL3-EV, -PPFP, or –AAA cells were plated on Matrigel-coated transwells with serum-free media and placed in tissue culture wells containing 10% FBS as attractant. After 36 hours, cells that invaded through the transwell membrane were counted under a microscope. Results are expressed as means ± SD and repeated with independent cell lines. (E) Upregulation in PCCL3-PPFP cells of genes overexpressed in human PPFP FTC. Five genes common to 2 published profiles of genes overexpressed in human PPFP FTC were analyzed by RT-qPCR in lysates from PCCL3-EV and PCCL3-PPFP cells. The 3 genes shown here had increased expression in the PCCL3-PPFP cells; the other two genes had no change (data not shown). Results are means ± SD.
Compared to PCCL3 cells stably transfected with empty vector (PCCL3-EV), PCCL3-PPFP cells exhibited a more transformed phenotype. Thus, PCCL3-PPFP cells generated 8 times more colonies in soft agar [Fig. 1C] and 3 times as many PCCL3-PPFP cells invaded through Matrigel-coated transwells [Fig. 1D]. PCCL3-AAA cells did not exhibit increased colony formation or invasion [Fig. 1C, 1D], indicating that the PPARG DBD within PPFP is important for these activities.
PPFP target genes overlap those from agonist induced PPARG activation
Gene expression profiles of human PPFP thyroid carcinomas have been reported by Lacroix and Giordano (Lacroix et al. 2005; Giordano et al. 2006). Giordano identified 55 genes that were highly over-expressed specifically in PPFP carcinomas, and 17 of those 55 also were found by Lacroix to be over-expressed in PPFP tumors versus normal thyroids (ACAA1, ALDH1L1, ANGPTL4, AQP7, CHIA, CXCR7, DHCR24, ENO3, PMP22, FBN2, FBP1, FGFBP1, MYCL1, PPARG, RAB15, TNFRSF21, XK). We tested the expression of 5 of the 17 intersection genes by RT-qPCR and found that 3 of the 5 are induced in PCCL3-PPFP cells versus PCCL3-EV cells. The results for these 3 genes, Angiopoietin like 4 (Angptl4), Fibroblast Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 (Fgfbp1), and Myelocytomatosis Viral Oncogene Homolog 1 (Mycl1), are shown in Fig. 1E. The expression of the other 2 genes, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (Cxcr7) and Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 (Tnfrsf21), was not significantly changed (data not shown). These data indicate that the transcriptional effects of PPFP expression in this rat thyroid cell line overlap with the changes seen in human PPFP carcinomas.
The Connectivity Map (CMAP) is a collection of gene expression data from cultured human cell lines treated with various small molecules, combined with analysis algorithms to facilitate the identification of connections between drugs, diseases, signaling pathways and gene expression changes (Lamb et al. 2006). We conducted a search on CMAP to identify bioactive small molecules that induce a set of gene expression changes similar to the set common to the Lacroix and Giordano PPFP profiles. The PPARG agonist pioglitazone was among the top results returned (p=0.014 overall, p=0.006 for human prostate PC3 cells) [Table 2]. Other thiazolidinediones - rosiglitazone and troglitazone - also elicited significantly similar responses in PC3 cells (p<0.05) but their overall rankings in CMAP were diminished by large variance in the MCF7 cell responses (data not shown).
Table 2.
Connectivity Map results showing the congruence of the common PPFP profile and gene expression changes caused by pioglitazone treatment.
| rank | cmap name | dose | cell | score | up | down |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 111 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | PC3 | 0.841 | 0.393 | −0.743 |
| 228 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | PC3 | 0.793 | 0.399 | −0.672 |
| 259 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | PC3 | 0.786 | 0.245 | −0.817 |
| 501 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | 0.73 | 0.308 | −0.678 |
| 599 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | 0.713 | 0.139 | −0.824 |
| 648 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | PC3 | 0.705 | 0.277 | −0.676 |
| 1141 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | PC3 | 0.625 | 0.222 | −0.623 |
| 2191 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | 0 | 0.236 | 0.598 |
| 2240 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | 0 | 0.229 | 0.718 |
| 3349 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | 0 | −0.118 | −0.681 |
| 5816 | pioglitazone | 10 µM | MCF7 | −0.783 | −0.144 | 0.89 |
Each row represents a CMAP instance - a treatment and control pair subjected to gene expression profiling to derive a set of differentially expressed genes. The score is a value between 1 and −1 indicating the level of overlap between a CMAP instance and the query signature. A high positive score indicates a treatment which induced a set of gene expression changes similar to the query. A low negative score indicates a treatment which reversed the gene expression changes in the query. A 0 score indicates no self-consistent correlation between the two sets. The up and down columns indicate the enrichment scores for the induced and repressed gene set, respectively. Considering all 11 instances together, pioglitazone induced genes were enriched in the common PPFP profile (p = 0.014, as calculated by CMAP).
PPFP is a potential modulator of the Wnt pathway
Another emergent theme from the CMAP results was Wnt pathway modulation. Among the 70 bioactive small molecules eliciting responses significantly enriched for PPFP profile genes, 16 were standard hits in Chembank high-throughput screens for Wnt inhibitors, Wnt/Lithium modulators, or β-catenin inducers/translocators [Table 3]. Of the 16, simvastatin, azacytidine, methotrexate, amiloride and anisomycin also were reported to impact on the Wnt pathway elsewhere in the literature (Shim et al. 2004; Lin et al. 2008; Klinghoffer et al. 2009; Qiao et al. 2011; Qiu et al. 2011; Shang et al. 2011; Georgiou et al. 2012; Serafino et al. 2012).
Table 3.
Small molecules which elicited similar gene expression changes to the common PPFP profile, which were also Chembank HTS standard hits for Wnt inhibitor, Wnt/Lithium modulators, or β-catenin inducer/translocator.
| name | mean score | n | enrichment | p | specificity | % non-null |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| verteporfin | −0.851 | 3 | −0.969 | 0.00008 | 0.0058 | 100 |
| colforsin | 0.481 | 5 | 0.725 | 0.00364 | 0.0101 | 80 |
| hymecromone | −0.479 | 4 | −0.749 | 0.0079 | 0.0121 | 75 |
| bisacodyl | −0.615 | 4 | −0.748 | 0.00812 | 0.0403 | 75 |
| simvastatin | 0.6 | 4 | 0.742 | 0.00849 | 0.0247 | 100 |
| amiloride | −0.603 | 5 | −0.668 | 0.00953 | 0.0052 | 80 |
| altizide | −0.315 | 4 | −0.691 | 0.01971 | 0.0131 | 50 |
| methotrexate | 0.397 | 8 | 0.507 | 0.02008 | 0.1024 | 62 |
| azacitidine | 0.606 | 3 | 0.781 | 0.02119 | 0.1394 | 100 |
| securinine | −0.584 | 4 | −0.674 | 0.02524 | 0.1456 | 75 |
| proadifen | −0.584 | 4 | −0.671 | 0.02616 | 0.0261 | 75 |
| merbromin | −0.345 | 5 | −0.605 | 0.0272 | 0.1707 | 80 |
| anisomycin | −0.498 | 4 | −0.661 | 0.02988 | 0.1864 | 75 |
| digoxin | −0.549 | 4 | −0.659 | 0.03079 | 0.1122 | 75 |
| lycorine | −0.379 | 5 | −0.581 | 0.03827 | 0.28 | 60 |
| fluspirilene | 0.56 | 4 | 0.635 | 0.04372 | 0.1005 | 75 |
Mean score is the average connectivity score of control-treated pairs for a molecule in the CMAP database, n indicates the number such pairs. Enrichment indicates the relative connectivity of a particular set of instances compared against all other instances. Specificity indicates the relative uniqueness of connectivity by tallying the frequency at which the connectivity between the query and relevant instances is equaled or exceeded by the connectivity between the same instances and a large number of gene signatures from MSigDB. Non-null percentage refers to the number of instances that are scored in the same direction as the majority instances.
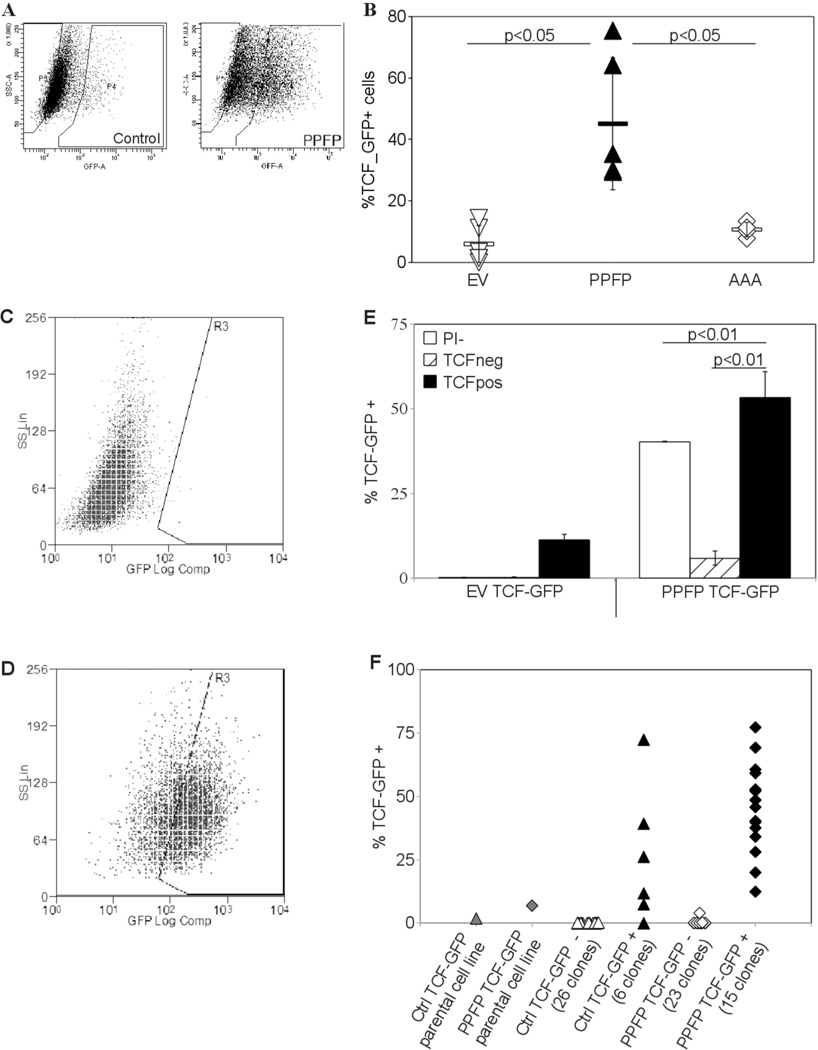
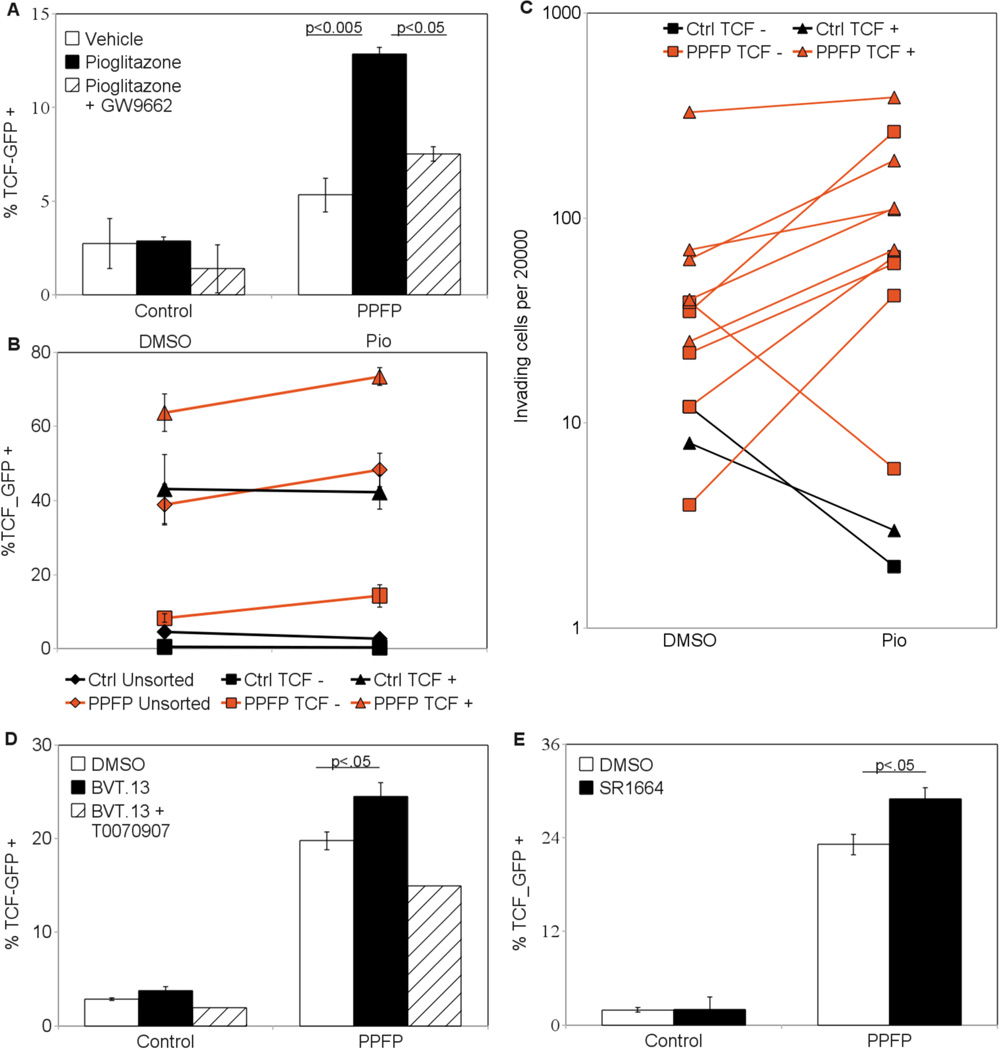
Based upon this, we delivered via lentivirus two independent Wnt/TCF responsive promoter constructs driving GFP expression into our cell lines to measure the extent of Wnt pathway activation. GFP positive cells were sorted and grown to generate new cell lines in which all of the cells were transduced. Upon expansion, a substantial fraction of the cells reverted to a TCF_GFP- phenotype. However, with either construct and 3 independent PPFP cell lines we found each time a 2–5 fold increase in the number of TCF_GFP+ cells relative to similarly-transduced PCCL3-EV control cells. As was the case with the functional assays, the DBD mutant PPFP-AAA did not effect an increase in TCF_GFP activation over control cells [Fig. 2A, 2B].
Figure 2.
(A) Increased TCF driven GFP expression in PCCL3-PPFP cells. Empty vector control PCCL3 and PCCL3-PPFP cells were infected with lentiviral constructs carrying a GFP gene driven by a TCF responsive promoter. Cells which expressed GFP after 5 days in culture were sorted out and expanded to create 100% transfected cell lines. These cell lines were analyzed for GFP expression by flow cytometry. Gates were set at the level of GFP expression in 99.5% of control cells expressing GFP under the control of the same promoter without TCF response elements. Test samples with GFP levels higher than gated were considered GFP positive and TCF responsive. (B) Increased TCF_GFP positivity in multiple PPFP cell lines versus empty vector control and AAA cells. Empty vector control PCCL3-EV, PCCL3-PPFP, and PCCL3-AAA cell lines were infected with the TCF reporter construct as described in (A) and analyzed via flow cytometry. Each point on the graph represents an independent cell line. Results are typical of many (>3) repeated experiments. (C, D) Re-establishment of TCF heterogeneity by TCF_GFP+ cells. The GFP+ and GFP- fractions were placed in culture and analyzed after 5 days. The fractions were analyzed for TCF_GFP expression: (C) was a typical GFP-fraction and (D) was a typical GFP+ fraction in culture, 5 days after sorting. (E) Cells were sorted according to their GFP expression status and analyzed after 5 days in culture as described in (C,D). A whole population sample for each cell line (gated on cell viability only, denoted PI-) was also sorted through the flow cytometer during the same sorting session and analyzed with the other fractions. Results are means ± SD and were repeated with independent cell lines. (F) Re-establishment of TCF heterogeneity in cell lines derived from single TCF_GFP+ cells. Single cells were sorted into each well of a 96 well plate based on their GFP status, and grown into cell lines which were analyzed by flow cytometry. Each point on the graph indicates a cell line derived from a single cell, the GFP status of which is indicated below the X-axis. The experiment was repeated and similar results obtained.
An apparent hierarchy exists in the cell lines defined by TCF activation status
We re-sorted the 100% transduced cell lines into TCF_GFP+ and TCF_GFP- fractions. The TCF_GFP+ fraction again generated both TCF_GFP+ and TCF_GFP- populations. The TCF_GFP- fraction also regenerated some TCF_GFP+ cells, but at a small fraction of the original level [Fig. 2C–E]. The TCF_GFP- fraction could have had a diminished but extant capacity to generate TCF_GFP+ cells, or the TCF_GFP+ cells could have come from contaminating, originally TCF_GFP+ cells. Clonal populations grown from single cells sorted into 96 well plates provided data which support the latter possibility. Out of 26 EV control clones and 23 PPFP clones grown from TCF_GFP- cells, only one contained a TCF_GFP+ fraction, which was still a small fraction of the TCF_GFP+ fraction of the parental cell line [Fig. 2F]. The ability to reconstitute the heterogeneity of the parental cell lines was clearly confined to the TCF_GFP+ populations of the EV control and PPFP cell lines.
A potential artifactual explanation for the appearance of TCF_GFP- cells could be loss of the TCF/GFP construct in the cellular genome. This was excluded by qPCR measurement of GFP DNA in three PPFP TCF_GFP- and three PPFP TCF_GFP+ clones. Setting the average GFP DNA content of the TCF_GFP+ clones at 1, the mean±SD GFP content of those clones was 1.00±0.16, and that of the TCF_GFP- clones was 1.07±0.26.
The TCF responsive cell fraction is enriched for anchorage independent and invasive cells
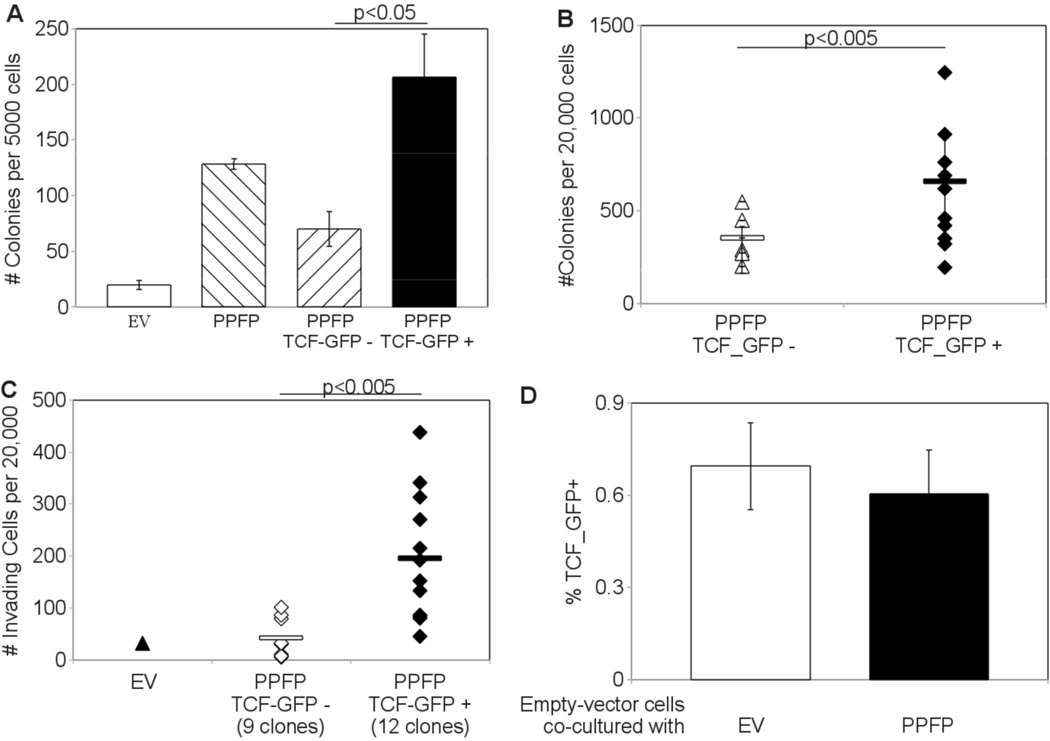
Bulk populations of TCF_GFP+ cells formed more colonies in soft agar than TCF_GFP- cells [Fig. 3A]. Clones derived from TCF_GFP+ cells also formed more colonies than clones of TCF_GFP- cells, though overlap was observed [Fig. 3B]. Furthermore, clones of TCF_GFP+ cells were on average 5 times more invasive than clones of TCF_GFP- cells [Fig. 3C].
Figure 3.
(A) Increased Soft agar colony formation in TCF_GFP+ cells. PCCL3-PPFP cells were sorted via FACS into 3 separate samples: whole population (gated on viability only, labeled PPFP on graph), TCF-GFP-, and TCF-GFP+ (gated on viability and GFP). 5000 cells from each sample were suspended and cultured in 0.33% agarose and analyzed for colony formation after 21 days. (B) Increased soft agar colony formation in cell lines derived from single TCF_GFP+ cells. Cell lines were established from individual cells. The TCF status of the founding cells is indicated below the X-axis. 20,000 cells from each clonal cell line were suspended and cultured in 0.33% agarose and analyzed for colony formation. (C) Increased invasion through Matrigel by cell lines derived from individual TCF_GFP+ cells. The TCF status of the founding cells is indicated below the X-axis. 20,000 cells from each clonal cell line were placed in a Matrigel-coated transwell and analyzed for invasion after 36 hours. (D) No increase in TCF activation despite co-culture with PPFP cells. Empty vector control PCCL3-EV cells were co-cultured with 4 fold excess PCCL3-EV or PCCL3-PPFP constitutive-DsRed cells. After 5 days in culture the cells were analyzed for GFP status by flow cytometry. During analysis, DsRed positive cells were excluded so that the % TCF_GFP+ reported is from the DsRed negative PCCL3-EV cells only. Columns represent means ± SD; the experiment was repeated and similar results obtained.
A potential artifactual explanation for the lower colony forming and invasive capacities of the TCF_GFP- cells could be the loss of PPFP expression, which also would result in lower TCF-driven GFP expression. This was excluded by RT-qPCR measurement of PPFP expression in three TCF_GFP-and three TCF_GFP+ clones. The average PPFP expression normalized to beta actin was set at 1 for the GFP_TCF- cells, resulting in a mean±SD PPFP expression of 1.00±0.07 in the TCF_GFP- cells and 1.05±0.08 in the TCF_GFP+ cells.
TCF activation in PCCL3-PPFP cells involves a cell autonomous process
The signaling cascade leading to TCF activation typically originates from exogenous Wnt ligands, but exogenous factors were not sufficient to account for TCF activation in PCCL3-PPFP cells. PCCL3-EV control cells transduced with TCF_GFP were co-cultured with 4-fold excess PCCL3-EV or PCCL3-PPFP cells constitutively expressing DsRed for 5 days, then analyzed via flow cytometry. After removing DsRed cells from the data, the level of GFP positivity was unchanged [Fig. 3D]. PCCL3-PPFP cells co-cultured with 4-fold excess control cells also did not lose GFP positivity (data not shown). We conclude that hypothetical activating or inhibiting exogenous ligands are not sufficient for TCF activation, and PPFP activation of TCF pathways occurs via a cell autonomous process.
PPFP also activates Wnt/TCF signaling in vivo
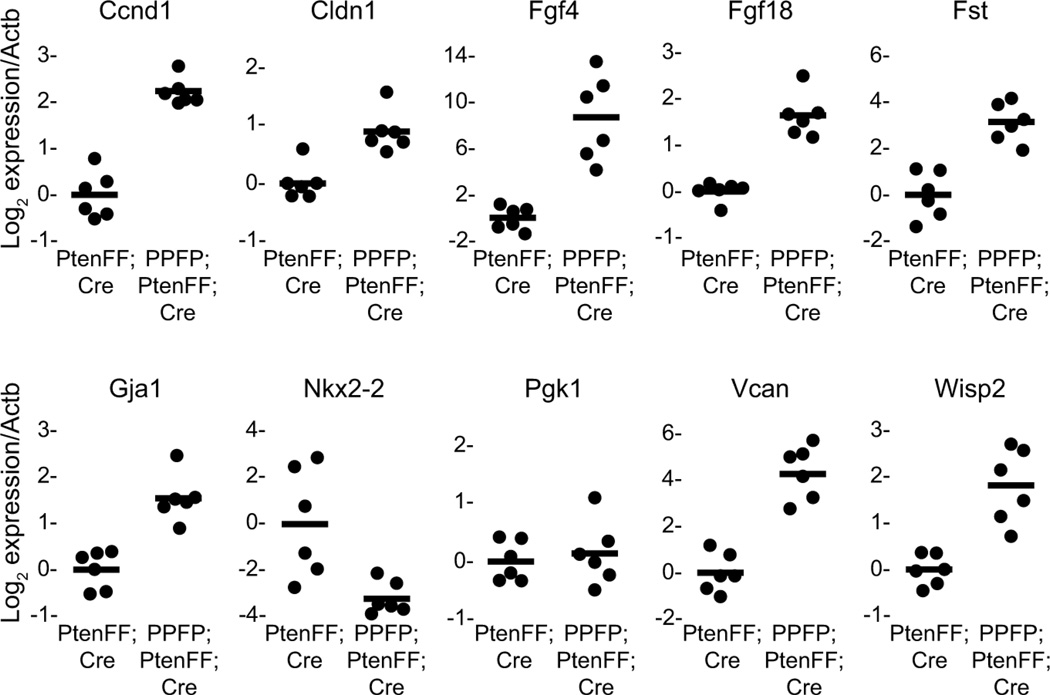
Mice with thyroid-specific expression of PPFP combined with thyroid-specific deletion of the tumor suppressor Pten (denoted PPFP;PtenFF;Cre) develop FTC, whereas mice with just thyroid-specific deletion of Pten (PtenFF;Cre) develop thyroid hyperplasia but no neoplasia (Dobson et al. 2011). We performed gene expression studies of thyroid RNA from mice of these two genotypes to determine whether this in vivo model of PPFP thyroid carcinoma is associated with Wnt/TCF activation. Initially a comparison was made by Affymetrix microarray analysis. The results of that study will be reported elsewhere, but the GeneChips included 30 genes known to be direct Wnt/TCF targets in other mammalian cell types, 27 of which have been reported to be induced by Wnt/TCF and 3 repressed (www.stanford.edu/group/nusselab/cgi-bin/wnt/target_genes). The microarray analysis indicated that 12 of the 27 potentially inducible genes were induced, and 2 of the 3 potentially repressible genes were repressed (data not shown). We selected 8 of the induced genes, one repressed gene, and two neutral control genes to evaluate by RT-qPCR in an independent set of 6 PPFP;PtenFF;Cre mice and 6 PtenFF;Cre control mice. As shown in Fig. 4, all 8 genes expected to be induced were induced, and the gene expected to be repressed was repressed. Thus, PPFP also activates Wnt/TCF signaling in a mouse model of FTC.
Figure 4.
Wnt/TCF target genes are induced in a mouse model of PPFP thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid RNA was prepared from 6 PPFP;PtenFF;Cre mice and 6 PtenFF;Cre control mice, and gene expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR. All of the genes analyzed are known to be induced by Wnt/TCF in other mammalian cell types, except for Nkx2-2 which is known to be repressed, and Pgk1 which is a neutral control gene used in addition to the normalization control gene Actb. For each gene, the average normalized expression in the PtenFF;Cre mice was set at 1. Each circle represents the data from one mouse, and the solid lines mark the average expression. For all genes the difference between PPFP;PtenFF;Cre and PtenFF;Cre is significant at P<0.001 except Nkx2-2 P=0.009, and Pgk1 P=0.57 (not significant).
The PPARG agonist pioglitazone increases TCF activation
PCCL3-PPFP cells treated with pioglitazone increased their number of TCF_GFP+ cells by more than two fold [Fig. 5A]. Total changes in cell number were insignificant and not a factor in the increased GFP+ percentage (data not shown). Co-treatment with the PPARG antagonist GW9662 negated the effects of pioglitazone, indicating PPARG specificity of pioglitazone action. PCCL3-EV control cells were not affected by the treatment. Cells treated with other PPARG agonists (CAY10410, GW1929) and another PPARG antagonist (T0070907) yielded similar results (data not shown).
Figure 5.
(A) Increased TCF activation after pioglitazone treatment. PCCL3-EV and PCCL3-PPFP cells were treated with the PPARG agonist pioglitazone (1 µM) with or without the PPARG antagonist GW9662 (0.1 µM) for 5 days. The cells were then analyzed via flow cytometry for GFP status. (B) Increased TCF activation in each pioglitazone treated fraction of the PCCL3-PPFP cell line. PCCL3-EV and PCCL3-PPFP cells were sorted via FACS into whole population, TCF_GFP-, and TCF_GFP+ samples. The sorted cells were cultured for 5 days in the presence of pioglitazone (1 µM) or vehicle (DMSO). Cells were then analyzed via flow cytometry for GFP status. (C) Increased invasiveness of pioglitazone treated PPFP cell lines. Cell lines each derived from a single TCF_GFP- or TCF_GFP+ cell were treated with pioglitazone (1 µM) for 5 days. Cells were then placed in Matrigel-coated transwells and their invasive capacities were analyzed. PPFP expressing cells were more invasive with pioglitazone treatment regardless of whether they were from a GFP- or GFP+ cell. (D) Increased TCF activation by a selective PPARG agonist. Empty vector control and PCCL3-PPFP cells were treated for 5 days with the selective PPARG agonist BVT.13 (1 µM) with or without the PPARG antagonist T0070907 (1 µM). Cells were then recovered and analyzed via flow cytometry for GFP status. (E) Increased TCF activation by non-adipogenic selective PPARG agonist. PCCL3-EV and PCCL3-PPFP cells were treated for 5 days with the non-adipogenic selective PPARG agonist SR1664 (1 µM). Cells were then recovered and analyzed via flow cytometry for GFP status.
Sorted bulk populations of TCF_GFP- PCCL3-PPFP cells, but not those of PCCL3-EV control cells, saw their TCF_GFP + population increased by pioglitazone to a similar extent as TCF_GFP+ and unsorted populations [Fig. 5B]. To address the possibility of contaminating TCF_GFP+ cells being responsible for the re-appearance of TCF_GFP+ cells in the TCF_GFP- population, we also treated clonal populations derived from TCF_GFP- cells. These clones had remained TCF unresponsive, previously containing an average of 0.30% TCF_GFP + cells. After treatment with pioglitazone, the clones contained an average of 0.90% TCF_GFP+ cells (n=4, p=0.09), suggestive of a small but real induction of TCF_GFP+ cells from the TCF_GFP- population.
The invasiveness of PCCL3-PPFP cells is increased by pioglitazone
Clonal populations grown from individual cells sorted by their TCF status were treated with pioglitazone or DMSO. Compared to the vehicle treated cells, the pioglitazone treated cells were more invasive, whether derived from TCF_GFP+ or TCF_GFP- cells [Fig. 5C]. The increase was seen in all but 1 of the PCCL3-PPFP clones (n=10). In contrast the two PCCL3-EV control clones tested did not become more invasive with pioglitazone.
The effects of full versus selective PPARG agonists on PPFP differ in cell culture versus in vivo
The pioglitazone results suggest that exposure of PPFP carcinomas to this drug would likely increase tumor growth and aggressiveness. However, we previously reported that pioglitazone reduces growth and metastases of tumors in PPFP;PtenFF;Cre mice, a transgenic model of PPFP thyroid carcinoma (Dobson et al. 2011). A remarkable feature of those tumors is that pioglitazone caused them to differentiate toward adipocytes, with the cells accumulating large intracellular lipid droplets and expressing a broad array of PPARG-inducible adipocyte genes.
We hypothesized that the adipogenic response to pioglitazone and other PPARG agonists is separable from the increased TCF responsiveness and invasiveness. This hypothesis is potentially testable due to the existence of selective PPARG modulators (SPPARMs). These small molecules effect the insulin sensitization response of full PPARG agonists with little to no adipogenesis and other associated side effects of classic agonists such as pioglitazone (Doshi et al. 2010).
We found that SPPARMs also increased the activation of TCF. BVT.13 increased the percentage of TCF responsive cells, and the PPARG antagonist T0070907 blocked this increase [Fig. 5D]. Similar results were obtained for FMOC-L-Leucine and nTZDpa (data not shown). Each of these reagents was identified as a PPARG selective agonist with weak adipogenic activity (Rocchi et al. 2001; Östberg et al. 2004; Lacroix et al. 2005; Choi et al. 2010). The maximal effects of the SPPARMs were volatile despite repeated experiments. We present here experiments demonstrating conservative but statistically significant increases in TCF activation. Other experiments with identical parameters demonstrated increases in TCF_GFP+ percentage similar to pioglitazone treatment.
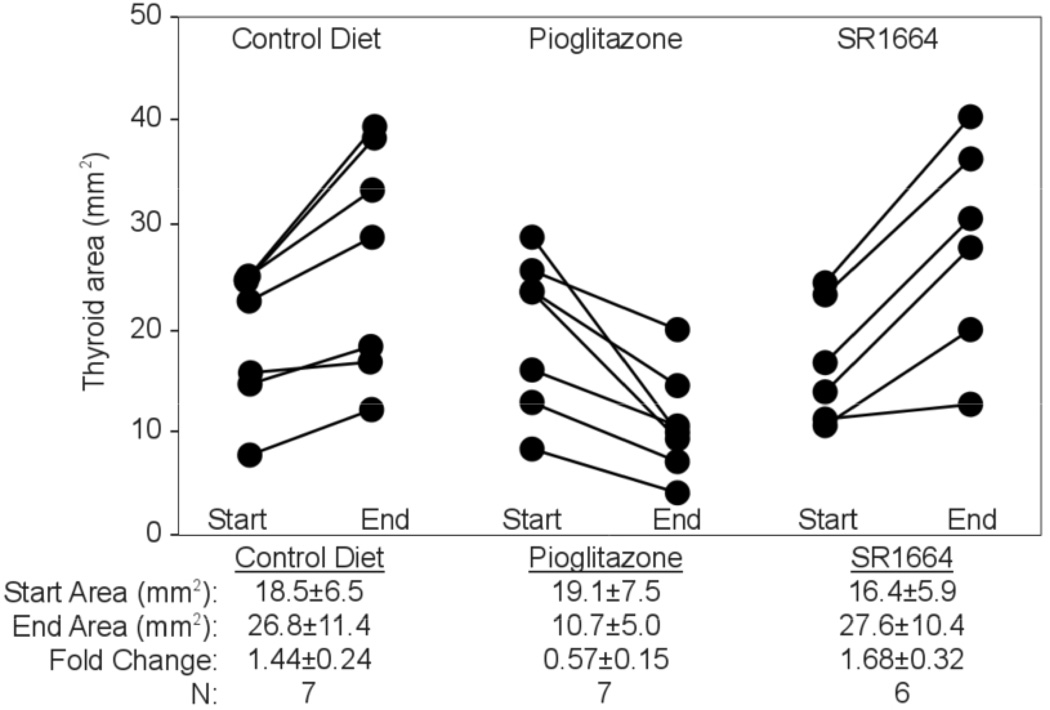
SR1664 was recently identified as a selective PPARG agonist with no detectable adipogenic activity (Choi et al. 2011). It also increased TCF_GFP positivity in PCCL3-PPFP cells [Fig. 5E]. However, PPFP;PtenFF;Cre transgenic mice treated with SR1664 received none of the antitumor effect of pioglitazone [Fig. 6], suggesting that the TCF-activating and antitumor effects of PPARG ligands are indeed due to different activities of PPFP.
Figure 6.
SR1664 does not inhibit thyroid tumor growth in vivo. Mice with thyroid-specific expression of PPFP and Pten deletion were treated with control diet, pioglitazone, or the selective PPARG agonist SR1664 for two weeks starting at age 8 weeks. Thyroid size was measured by ultrasound at the start and end of treatment. Each line represents one mouse. Thyroid area of wild type mice is 1.9 mm2 and does not change over the two week period (data not shown).
Taken together, our results suggest the following: 1) PPFP's contribution to malignant transformation depends on its PPARG DNA and ligand binding domains. 2) PPFP increases the number of TCF responsive PCCL3 cells, a population whose progeny effect the transformed phenotype of PCCL3-PPFP cells. 3) The effects of PPFP are amplified by actions common to PPARG agonists and non-adipogenic selective agonists in vitro. 4) Only the full PPARG agonist has anti-tumor effects in vivo, suggesting that the associated adipocyte transdifferentiation of cancer thyrocytes is more than a coincidental effect.
DISCUSSION
PPFP was one of the first carcinoma-related translocations to be identified, but the molecular mechanisms underlying its role in thyroid carcinogenesis remain imperfectly understood. PPFP transforms cells in vitro and induces metastatic FTC in mice in conjunction with Pten deletion (Diallo-Krou et al. 2009; Dobson et al. 2011), but it also can inhibit growth in already-malignant cell lines and in mouse xenografts of cell lines (Reddi et al. 2011). PPFP stimulates or inhibits targets of PAX8 and PPARG depending on the particular gene and cellular context (Kroll et al. 2000; Powell et al. 2004; Au et al. 2006; Espadinha et al. 2007).
Here we report that PPFP via its PPARG domains activates the Wnt/TCF pathway and that this is an essential step in the transformation effected by PPFP.
Rat thyroid PCCL3 cells expressing PPFP demonstrated higher anchorage-independence and invasive potential. These result are consistent with past reports in other cell lines of the pro-oncogenic effects of PPFP (Kroll et al. 2000; Powell et al. 2004; Au et al. 2006; Li et al. 2012). PPFP retains the ability to bind PPAR response elements (PPREs) (Au et al. 2006; Giordano et al. 2006) and our data indicate that a functional PPARG DNA binding domain is required for these actions of PPFP.
We reported previously that PPFP is a potent driver of the PPARG transcriptional program in the presence of the classic PPARG agonist pioglitazone (Dobson et al. 2011). We report here that full and selective PPARG agonists enhance the effects of PPFP while PPARG antagonists block them, suggesting an important role for PPARG domains in PPFP biology.
We speculate that the oncogenic targets of PPFP are part of a distinct transcriptional program activated by both full and selective PPARG agonists, rather than the adipogenic program that responds only to full agonists. In vivo in the absence of exogenous ligands the oncogenic action of PPFP dominates and patients or mice develop FTC, but the presence of a strong full agonist such as pioglitazone allows the adipogenic and anti-tumor activities of PPFP to prevail.
Based upon CMAP data, we hypothesized that the Wnt/TCF pathway may be a target of PPFP. Wnt/TCF pathways have a central role in cancer and stem cell biology which is best illustrated by studies in the intestine, where Wnt/TCF activity identifies stem cells that maintain healthy tissues and drive the progression of malignant disease (Korinek et al. 1997, 1998; Barker et al. 2009). Wnt pathway activation also is observed in all forms of thyroid malignancy but is more common and well studied in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas than FTC (Garcia-Rostan et al. 1999, 2001; Helmbrecht et al. 2001; Zhang et al. 2012).
Expression of PPFP increased the fraction of cells that is Wnt active/TCF responsive, and this fraction is enriched in invasive and colony forming cells. The TCF responsive and unresponsive fractions are hierarchically organized with the former being able to recapitulate the original heterogeneity in TCF reporter activity while the latter remains wholly unresponsive. This hierarchy suggests the TCF responsive fraction may harbor PPFP thyroid cancer stem cells, an hypothesis that requires confirmation. Our data suggest that PPFP exerts its oncogenic effects on the small fraction of stem and progenitor-like cells in thyroid cancer, effects that may be obscured in studies where only the bulk population is examined. Our data also suggest that Wnt/TCF activity in PPFP thyroid cancer stem cells may be modulated by small molecules directed at the PPARG domains within PPFP.
Published data on thyroid cancer stem cells are very limited, and no data exist from PPFP carcinomas. However, MET and AKT, both of which can induce TCF/β -catenin-mediated transcription, are reportedly activated in stem cells cultured from undifferentiated thyroid cancers, and this population also has increased nuclear β-catenin (Todaro et al. 2010). Thus, the Wnt/TCF reporter assays we used to identify a functionally significant subpopulation of thyroid cancer cells are promising tools for future use in the study of thyroid stem cells and cancer.
The mechanism of Wnt/TCF pathway activation by PPFP is unclear, except that it requires the PPARG DNA binding domain within PPFP. Activation of this pathway usually is mediated by transcription factors of the LEF/TCF7 family. We found that expression of TCF7L2 RNA is induced by PPFP (data not shown). However, shRNA knockdown of TCF7L2 failed to block Wnt/TCF pathway activation (data not shown), indicating that TCF7L2 either is non-essential or is not involved in the process. Further studies will be required to understand the mechanism by which PPFP regulates Wnt/TCF signaling.
In conclusion, we identified the Wnt/TCF pathway as a major positively regulated target of PPFP in stably transfected PCCL3 thyroid cells. PPFP activation of the TCF pathway depends on its functional PPARG DNA and ligand binding domains and can be modulated by small molecules in a PPARG like manner. The Wnt/TCF activated population is enhanced in the ability to invade through Matrigel and to form colonies in anchorage independent conditions, and may be a novel therapeutic target in patients with PPFP thyroid carcinomas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Anna Eliassen and Habib Khan for technical assistance.
FUNDING
This work was supported by NIH grants R01CA151842, R01CA166033, R01CA129765 and T32GM007315; and a Taubman Research Institute award.
Footnotes
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTION
Conceived and designed the experiments: DVP RK MW. Performed the experiments: DVP VG JY LC RK. Analyzed the data: DVP VG JY RK MW. Wrote the paper: DVP RK MW.
References
- Aldred MA, Morrison C, Gimm O, Hoang-Vu C, Krause U, Dralle H, Jhiang S, Eng C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is frequently downregulated in a diversity of sporadic nonmedullary thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene. 2003;22:3412–3416. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au AYM, McBride C, Wilhelm KG, Koenig RJ, Speller B, Cheung L, Messina M, Wentworth J, Tasevski V, Learoyd D, et al. PAX8-Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) Disrupts Normal PAX8 or PPARγ Transcriptional Function and Stimulates Follicular Thyroid Cell Growth. Endocrinology. 2006;147:367–376. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ, Clevers H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature. 2009;457:608–611. doi: 10.1038/nature07602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Bostrom P, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Bluher M, Griffin PR, et al. Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPAR[ggr] by Cdk5. Nature. 2010;466:451–456. doi: 10.1038/nature09291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JH, Banks AS, Kamenecka TM, Busby SA, Chalmers MJ, Kumar N, Kuruvilla DS, Shin Y, He Y, Bruning JB, et al. Antidiabetic actions of a non-agonist PPARγ ligand blocking Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation. Nature. 2011;477:477–481. doi: 10.1038/nature10383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diallo-Krou E, Yu J, Colby LA, Inoki K, Wilkinson JE, Thomas DG, Giordano TJ, Koenig RJ. Paired Box Gene 8-Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Fusion Protein and Loss of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Synergistically Cause Thyroid Hyperplasia in Transgenic Mice. Endocrinology. 2009;150:5181–5190. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson ME, Diallo-Krou E, Grachtchouk V, Yu J, Colby LA, Wilkinson JE, Giordano TJ, Koenig RJ. Pioglitazone Induces a Proadipogenic Antitumor Response in Mice with PAX8-PPARγ Fusion Protein Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrinology. 2011;152:4455–4465. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doshi LS, Brahma MK, Bahirat UA, Dixit AV, Nemmani KVS. Discovery and development of selective PPAR gamma modulators as safe and effective antidiabetic agents. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2010;19:489–512. doi: 10.1517/13543781003640169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espadinha C, Cavaco BM, Leite V. PAX8PPARgamma stimulates cell viability and modulates expression of thyroid-specific genes in a human thyroid cell line. Thyroid: Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association. 2007;17:497–509. doi: 10.1089/thy.2006.0263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito C, Miccadei S, Saiardi A, Civitareale D. PAX 8 activates the enhancer of the human thyroperoxidase gene. Biochemical Journal. 1998;331:37. doi: 10.1042/bj3310037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbro D, Pellizzari L, Mercuri F, Tell G, Damante G. Pax-8 protein levels regulate thyroglobulin gene expression. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology. 1998;21:347–354. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0210347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusco A, Berlingieri MT, Di Fiore PP, Portella G, Grieco M, Vecchio G. One- and two-step transformations of rat thyroid epithelial cells by retroviral oncogenes. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1987;7:3365–3370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Rostan G, Tallini G, Herrero A, D’Aquila TG, Carcangiu ML, Rimm DL. Frequent mutation and nuclear localization of beta-catenin in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Research. 1999;59:1811–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Rostan G, Camp RL, Herrero A, Carcangiu ML, Rimm DL, Tallini G. β-Catenin Dysregulation in Thyroid Neoplasms. The American Journal of Pathology. 2001;158:987–996. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64045-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou KR, King TJ, Scherer MA, Zhou H, Foster BK, Xian CJ. Attenuated Wnt/β-catenin signalling mediates methotrexate chemotherapy-induced bone loss and marrow adiposity in rats. Bone. 2012;50:1223–1233. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano TJ, Au AYM, Kuick R, Thomas DG, Rhodes DR, Wilhelm KG, Vinco M, Misek DE, Sanders D, Zhu Z, et al. Delineation, Functional Validation, and Bioinformatic Evaluation of Gene Expression in Thyroid Follicular Carcinomas with the PAX8-PPARG Translocation. Clinical Cancer Research. 2006;12:1983–1993. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass CK, Franco R, Weinberger C, Albert VR, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG. A c-erb-A binding site in rat growth hormone gene mediates trans-activation by thyroid hormone. Nature. 1987;329:738–741. doi: 10.1038/329738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmbrecht K, Kispert A, Wasielewski Rvon, Brabant G. Identification of a Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Human Thyroid Cells. Endocrinology. 2001;142:5261–5266. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.12.8554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato Y, Ying H, Zhao L, Furuya F, Araki O, Willingham MC, Cheng S-Y. PPARgamma insufficiency promotes follicular thyroid carcinogenesis via activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25:2736–2747. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinghoffer RA, Frazier J, Annis J, Berndt JD, Roberts BS, Arthur WT, Lacson R, Zhang XD, Ferrer M, Moon RT, et al. A lentivirus-mediated genetic screen identifies dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) as a modulator of beta-catenin/GSK3 signaling. PloS One. 2009;4:e6892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, Wichen Dvan, Weger Rde, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Clevers H. Constitutive Transcriptional Activation by a β-Catenin-Tcf Complex in APC−/− Colon Carcinoma. Science. 1997;275:1784–1787. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5307.1784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korinek V, Barker N, Moerer P, van Donselaar E, Huls G, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Depletion of epithelial stem-cell compartments in the small intestine of mice lacking Tcf-4. Nature Genetics. 1998;19:379–383. doi: 10.1038/1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll TG, Sarraf P, Pecciarini L, Chen C-J, Mueller E, Spiegelman BM, Fletcher JA. PAX8-PPARγ1 Fusion in Oncogene Human Thyroid Carcinoma. Science. 2000;289:1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5483.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix L, Lazar V, Michiels S, Ripoche H, Dessen P, Talbot M, Caillou B, Levillain J-P, Schlumberger M, Bidart J-M. Follicular Thyroid Tumors with the PAX8-PPARγ1 Rearrangement Display Characteristic Genetic Alterations. The American Journal of Pathology. 2005;167:223. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62967-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW, Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, Lerner J, Brunet J-P, Subramanian A, Ross KN, et al. The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2006;313:1929–1935. doi: 10.1126/science.1132939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Wang Z, Liu J, Tang C, Duan C, Li C. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in normal human thyroid cells transfected with PPFP. Endocrine-related Cancer. 2012;19:681–694. doi: 10.1530/ERC-12-0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C-L, Cheng H, Tung C-W, Huang W-J, Chang P-J, Yang J-T, Wang J-Y. Simvastatin reverses high glucose-induced apoptosis of mesangial cells via modulation of Wnt signaling pathway. American Journal of Nephrology. 2008;28:290–297. doi: 10.1159/000111142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui W-O, Zeng L, Rehrmann V, Deshpande S, Tretiakova M, Kaplan EL, Leibiger I, Leibiger B, Enberg U, Höög A, et al. CREB3L2-PPARγ Fusion Mutation Identifies a Thyroid Signaling Pathway Regulated by Intramembrane Proteolysis. Cancer Research. 2008;68:7156–7164. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia PE, Lapi P, Krude H, Pirro MT, Missero C, Chiovato L, Souabni A, Baserga M, Tassi V, Pinchera A, et al. PAX8 mutations associated with congenital hypothyroidism caused by thyroid dysgenesis. Nature Genetics. 1998;19:83–86. doi: 10.1038/ng0598-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magliano MPdi, Lauro RD, Zannini M. Pax8 has a key role in thyroid cell differentiation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2000;97:13144–13149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.240336397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri A, Chowdhury K, Gruss P. Follicular cells of the thyroid gland require Pax8 gene function. Nature Genetics. 1998;19:87–90. doi: 10.1038/ng0598-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques AR, Espadinha C, Frias MJ, Roque L, Catarino AL, Sobrinho LG, Leite V. Underexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ in PAX8/PPARγ-negative thyroid tumours. British Journal of Cancer. 2004;91:732–738. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T, Cepko CL. Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:16–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2235688100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M, Zannini M, Levy O, Carrasco N, Lauro Rdi. The Paired-Domain Transcription Factor Pax8 Binds to the Upstream Enhancer of the Rat Sodium/Iodide Symporter Gene and Participates in Both Thyroid-Specific and Cyclic-AMP-Dependent Transcription. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1999;19:2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.3.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Östberg T, Svensson S, Selén G, Uppenberg J, Thor M, Sundbom M, Sydow-Bäckman M, Gustavsson A-L, Jendeberg L. A New Class of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Agonists with a Novel Binding Epitope Shows Antidiabetic Effects. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:41124–41130. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401552200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J-W, Zarnegar R, Kanauchi H, Wong MG, Hyun WC, Ginzinger DG, Lobo M, Cotter P, Duh Q-Y, Clark OH. Troglitazone, the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Agonist, Induces Antiproliferation and Redifferentiation in Human Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Thyroid. 2005;15:222–231. doi: 10.1089/thy.2005.15.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell JG, Wang X, Allard BL, Sahin M, Wang X-L, Hay ID, Hiddinga HJ, Deshpande SS, Kroll TG, Grebe SK, et al. The PAX8/PPARγ fusion oncoprotein transforms immortalized human thyrocytes through a mechanism probably involving wild-type PPARγ inhibition. Oncogene. 2004;23:3634–3641. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiao LJ, Kang KL, Heo JS. Simvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells via canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Molecules and Cells. 2011;32:437–444. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-0107-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu W, Chen L, Kassem M. Activation of non-canonical Wnt/JNK pathway by Wnt3a is associated with differentiation fate determination of human bone marrow stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2011;413:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi HV, Madde P, Milosevic D, Hackbarth JS, Algeciras-Schimnich A, McIver B, Grebe SKG, Eberhardt NL. The Putative PAX8/PPARγ Fusion Oncoprotein Exhibits Partial Tumor Suppressor Activity through Up-Regulation of Micro-RNA-122 and Dominant-Negative PPARγ Activity. Genes & Cancer. 2011;2:46–55. doi: 10.1177/1947601911405045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi S, Picard F, Vamecq J, Gelman L, Potier N, Zeyer D, Dubuquoy L, Bac P, Champy M-F, Plunket KD, et al. A Unique PPAR[gamma] Ligand with Potent Insulin-Sensitizing yet Weak Adipogenic Activity. Molecular Cell. 2001;8:737–747. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafino A, Moroni N, Psaila R, Zonfrillo M, Andreola F, Wannenes F, Mercuri L, Rasi G, Pierimarchi P. Anti-proliferative effect of atrial natriuretic peptide on colorectal cancer cells: evidence for an Akt-mediated cross-talk between NHE-1 activity and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2012;1822:1004–1018. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang D, Liu Y, Xu X, Han T, Tian Y. 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine enhances susceptibility of renal cell carcinoma to paclitaxel by decreasing LEF1/phospho-β-catenin expression. Cancer Letters. 2011;311:230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim JS, Kim DH, Kwon HJ. Plakoglobin is a new target gene of histone deacetylase in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:1704–1711. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro M, Iovino F, Eterno V, Cammareri P, Gambara G, Espina V, Gulotta G, Dieli F, Giordano S, De Maria R, et al. Tumorigenic and Metastatic Activity of Human Thyroid Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Research. 2010;70:8874–8885. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz P, Spiegelman BM. Fat and Beyond: The Diverse Biology of PPARγ. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2008;77:289–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061307.091829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K, Evans RM. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989;57:1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood WM, Sharma V, Bauerle KT, Pike LA, Zhou Q, Fretwell DL, Schweppe RE, Haugen BR. PPARγ Promotes Growth and Invasion of Thyroid Cancer Cells. PPAR Research. 2011;2011:171765. doi: 10.1155/2011/171765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y, Yuan H, Wang C, Pattabiraman N, Rao M, Pestell RG, Glazer RI. 3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase-1 Activates the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-{gamma} and Promotes Adipocyte Differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:268–278. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y, Yuan H, Zeng X, Kopelovich L, Glazer RI. Inhibition of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Increases Estrogen Receptor–Dependent Tumor Specification. Cancer Research. 2009;69:687–694. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Gill AJM, Issacs JD, Atmore B, Johns A, Delbridge LW, Lai R, McMullen TPW. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway drives increased cyclin D1 levels in lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer. Human Pathology. 2012;43:1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]