Abstract
Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda requires the action of the protein Int, the product of the phage int gene. In this paper we show that highly purified Int relaxes supercoiled DNA. The association of this nicking-closing activity with Int is shown by: (i) the cosedimentation of nicking-closing and recombination activities of purified Int, (ii) the parallel inactivation of the two activities in purified Int by both heat and a specific antiserum, and (iii) the alteration of both activities in crude extracts of a strain expressing a mutant int gene. The nicking-closing activity of Int functions in the absence of divalent cations and in the absence of an apparent source of chemical energy. The activity displays no obvious sequence specificity and is inhibited by Mg2+, spermidine, and single-stranded DNA. Int relaxes positive as well as negative supercoils. We present a model for the mechanism of strand exchange that describes how the nicking-closing activity of Int might be used during recombination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Proteins that affect DNA conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:449–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Renaturation of complementary single-stranded DNA circles: complete rewinding facilitated by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5328–5332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Nash H., Weisberg R. A. Strand exchange in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. A genetic analysis of the att-int-xis region of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):97–120. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigman A., Hu S. L., Szybalski W. Regulation of integration by coliphage lambda: activation of int transcription by the cII and cIII proteins. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):542–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Wendel I. Stepwise relaxation of supercoiled SV40 DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):199–208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. The bacteriophage lambda int gene product. A filter assay for genetic recombination, purification of int, and specific binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7149–7157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
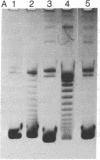
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda: requirement for supertwisted DNA in vivo and characterization of int. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1099–1109. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin S. Models of specifically paired like (homologous) nucleic acid structures. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 28;55(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Nash H. A. Involement of supertwisted DNA in integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda: in vitro study of the intermolecular reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1111–1114. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Nash H. A. Restriction assay for integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro: requirement for closed circular DNA substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3524–3528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. On the role of the bacteriophage lambda int gene product in site specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):627–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:171–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1072–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Dressler D. In vitro system from Escherichia coli that catalyzes generalized genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Genetic recombination: strand transfer and mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:847–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Lysogenization and curing by int-constitutive mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]