Abstract
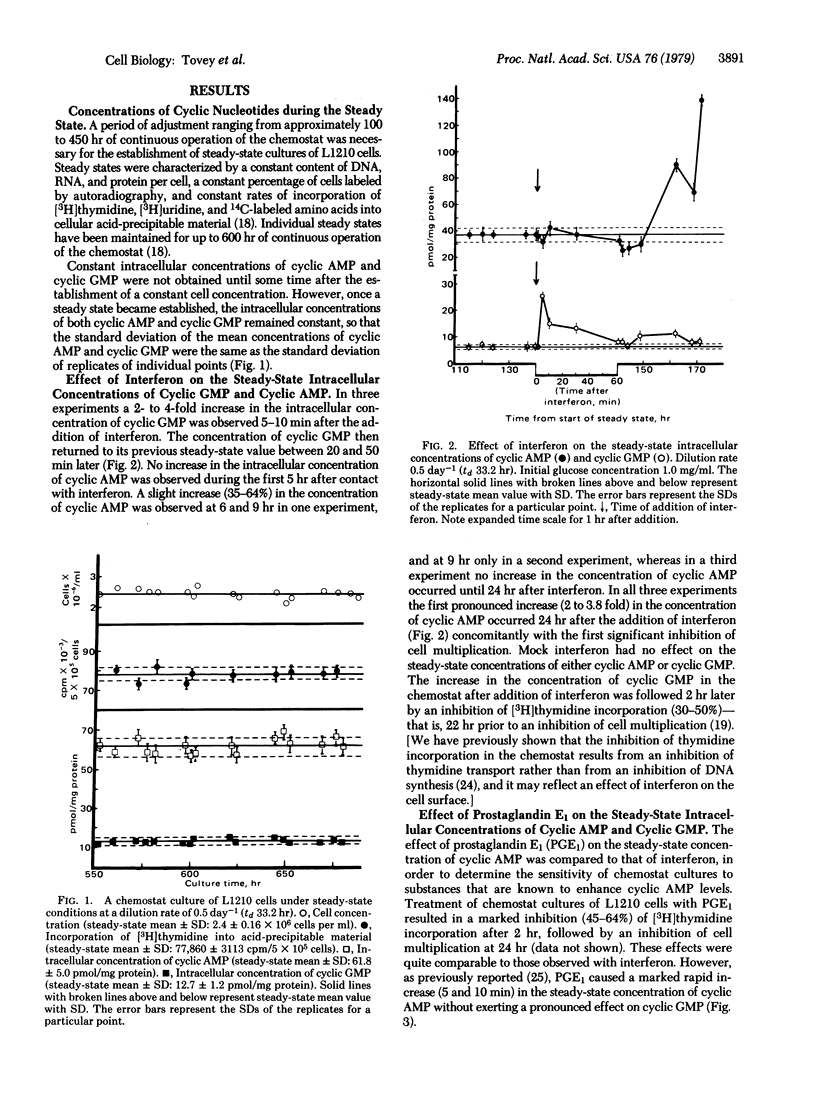
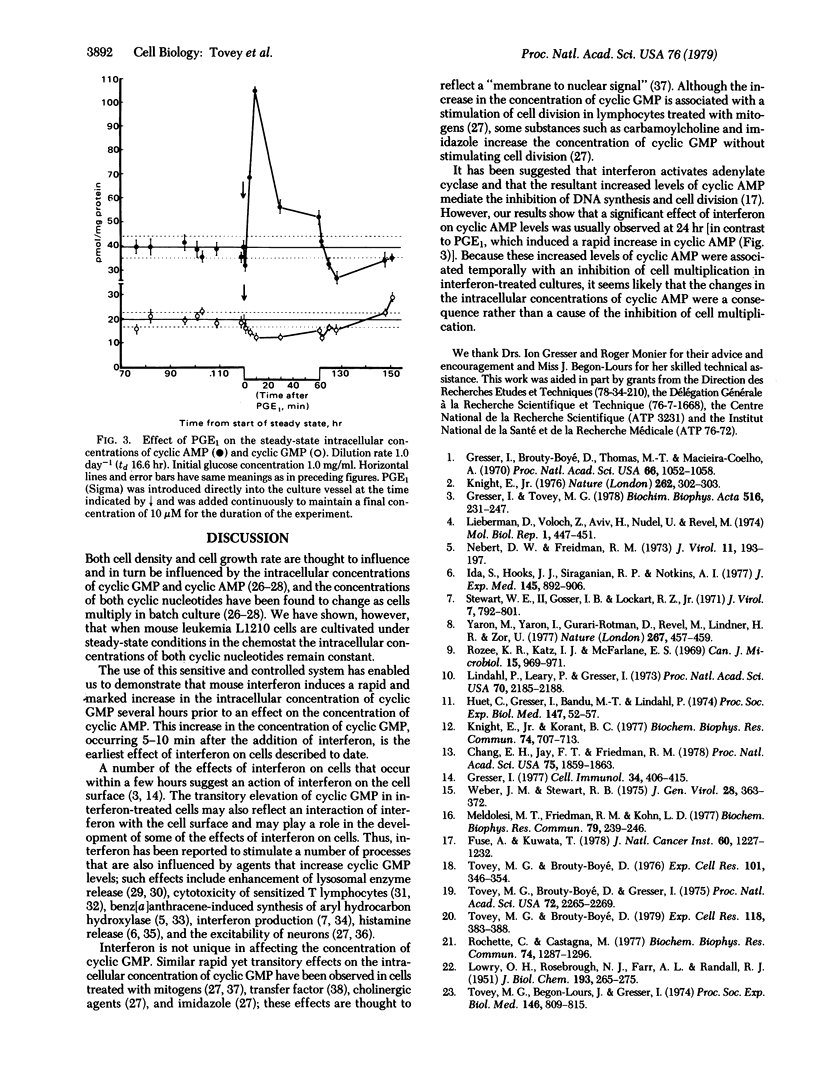
Constant intracellular concentrations of both adenosine 3',5'-cyclic-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) and guanosine 3',5'-cyclic-monophosphate (cyclic GMP) were obtained when leukemia L1210 cells were cultivated under steady-state conditions in the chemostat. In this sensitive and controlled system addition of mouse interferon resulted in a rapid (5-10 min) increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic GMP, which preceded by several hours an increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP. In contrast to the effect of interferon, addition of prostaglandin E1 induced a rapid increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP without markedly affecting the intracellular concentration of cyclic GMP. It is suggested that the rapid effect of interferon on cyclic GMP plays a role in mediating some of the effects of interferon on cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn H. S., Horowitz S. G., Eagle H., Makman M. H. Effects of cell density and cell growth alterations on cyclic nucleotide levels in cultured human diploid fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Tovey M. G. Inhibition by interferon of thymidine uptake in chemostat cultures of L1210 cells. Intervirology. 1978;9(4):243–252. doi: 10.1159/000148942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet M. C., Gresser I. Interferon enhances the excitability of cultured neurones. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):558–560. doi: 10.1038/278558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. H., Jay F. T., Friedman R. M. Physical, morphological, and biochemical alterations in the membrane of AKR mouse cells after interferon treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1859–1863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlapowski F. J., Kelly L. A., Butcher R. W. Cyclic nucleotides in cultured cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:245–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse A., Kuwata T. Inhibition of DNA synthesis and alteration of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in RSa cells by human leukocyte interferon. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jun;60(6):1227–1232. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garovoy M. R., Strom T. B., Kaliner M., Carpenter C. B. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity mechanism and modulation by cyclic nucleotides. Cell Immunol. 1975 Dec;20(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Haddox M. K. Cyclic GMP metabolism and involvement in biological regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:823–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Brouty-Boyé D., Thomas M. T., Macieira-Coelho A. Interferon and cell division. I. Inhibition of the multiplication of mouse leukemia L 1210 cells in vitro by interferon preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1052–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. On the varied biologic effects of interferon. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):406–415. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G. Antitumor effects of interferon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 27;516(2):231–247. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Haddox M. K., Goldberg N. D. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate: a possible intracellular mediator of mitogenic influences in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3024–3027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbach M., Koschel K., Jungwirth Ch. Interferon enhances the fragility of lysosomes in L-929 mouse fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):387–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Lindahl P. Increased binding of concanavalin A to interferon-treated murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):52–57. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ida S., Hooks J. J., Siraganian R. P., Notkins A. L. Enhancement of IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils by viruses: role of interferon. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):892–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Krassikoff N., Slywka J. Release of enzymes from a rat liver lysosome fraction: inhibition by catecholamines and cyclic3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate, stimulation by cholinergic agents and cyclic 3', 5'-guanosine monophosphate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jul;186(1):86–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliner M., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Immunological release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):556–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Antiviral and cell growth inhibitory activities reside in the same glycoprotein of human fibroblast interferon. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):302–303. doi: 10.1038/262302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. A cell surface alteration in mouse L cells induced by interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):707–713. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D., Voloch Z., Aviv H., Nudel U., Revel M. Effects of interferon on hemoglobin synthesis and leukemia virus production in Friend cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Dec;1(8):447–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00360670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Leary P., Gresser I. Enhancement by interferon of the specific cytotoxicity of sensitized lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi M. F., Friedman R. M., Kohn L. D. An interferon-induced increase in cyclic AMP levels precedes the establishment of the antiviral state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 7;79(1):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Friedman R. M. Stimulation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in cell cultures by interferon. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):193–197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.193-197.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette C., Castagna M. A simultaneous protein-binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in biological materials. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1287–1296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91658-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozee K. R., Katz L. J., McFarlane E. S. Interferon stimulation of methylase activity in L-cells. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Aug;15(8):969–971. doi: 10.1139/m69-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddon R. W., Lundeen D. E., Rikans L. E. Induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in mouse 3T3 cells: relationship to the state of cell proliferation and guanosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;9(5):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Gosser L. B., Lockart R. Z., Jr Priming: a nonantiviral function of interferon. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):792–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.792-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Begon-Lours J., Gresser I. A method for the large scale production of potent interferon preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):809–815. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Brouty-Boyé D. The use of the chemostat to study the relationship between cell growth rate, viability, and the effect of interferon on L 1210 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Feb;118(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M., Brouty-Boye D. Characteristics of the chemostat culture of murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Sep;101(2):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M., Brouty-Boyé D., Gresser I. Early effect of interferon on mouse leukemia cells cultivated in a chemostat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. M., Stewart R. B. Cyclic AMP potentiation of interferon antiviral activity and effect of interferon on cellular cyclic AMP levels. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):363–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaron M., Yaron I., Gurari-Rotman D., Revel M., Lindner H. R., Zor U. Stimulation of prostaglandin E production in cultured human fibroblasts by poly(I)-poly(C) and human interferon. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):457–459. doi: 10.1038/267457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida I., Azuma M., Suenaga T., Mizuno F. Regulation of interferon production by dibutyryl cyclic GMP in serum-free human diploid cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):303–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



