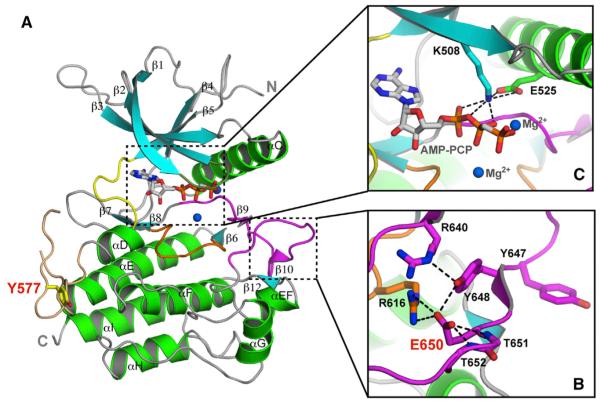
Figure 1. The Pathogenic K650E Mutation Drives the FGFR3 Kinase into the Active Conformation.
(A) Ribbon diagrams of the FGFR3KK650E structure. β strands and α helices are colored cyan and green, respectively. The A-loop, catalytic loop, nucleotide-binding loop, kinase insert, and kinase hinge are colored magenta, orange, smudge, wheat, and yellow, respectively. In all of the figures, the ATP analog (AMP-PCP) and magnesium ions are rendered as sticks and blue spheres, respectively.
(B) Close-up view of the catalytically critical salt bridge between K508 and E525 in the kinase N-lobe important for ATP coordination and hydrolysis.
(C) The carboxylate group of E650 introduces a network of intramolecular hydrogen bonds that tether the flexible A-loop to the rigid core of the C-lobe, thereby stabilizing the active-state conformation of the A-loop. Side chains of selected residues are shown as sticks. Atom colorings in this figure and the following figures are as follows: oxygens in red, nitrogens in blue, and coloring for carbons follow the coloring scheme of the specific region of the kinase to which they belong. The mutant residue E650 and kinase insert tyrosine Y577 are labeled in red; other residues are labeled in black. The hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines.
See also Figures S1–S3.