Abstract
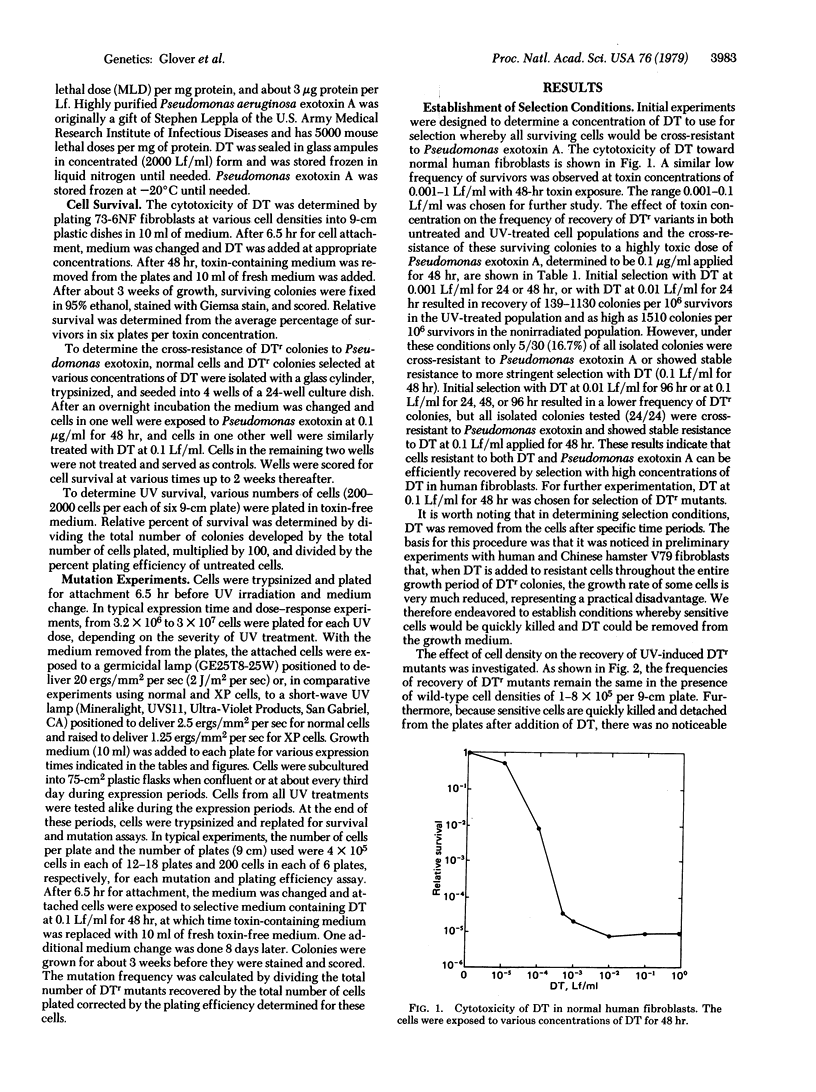
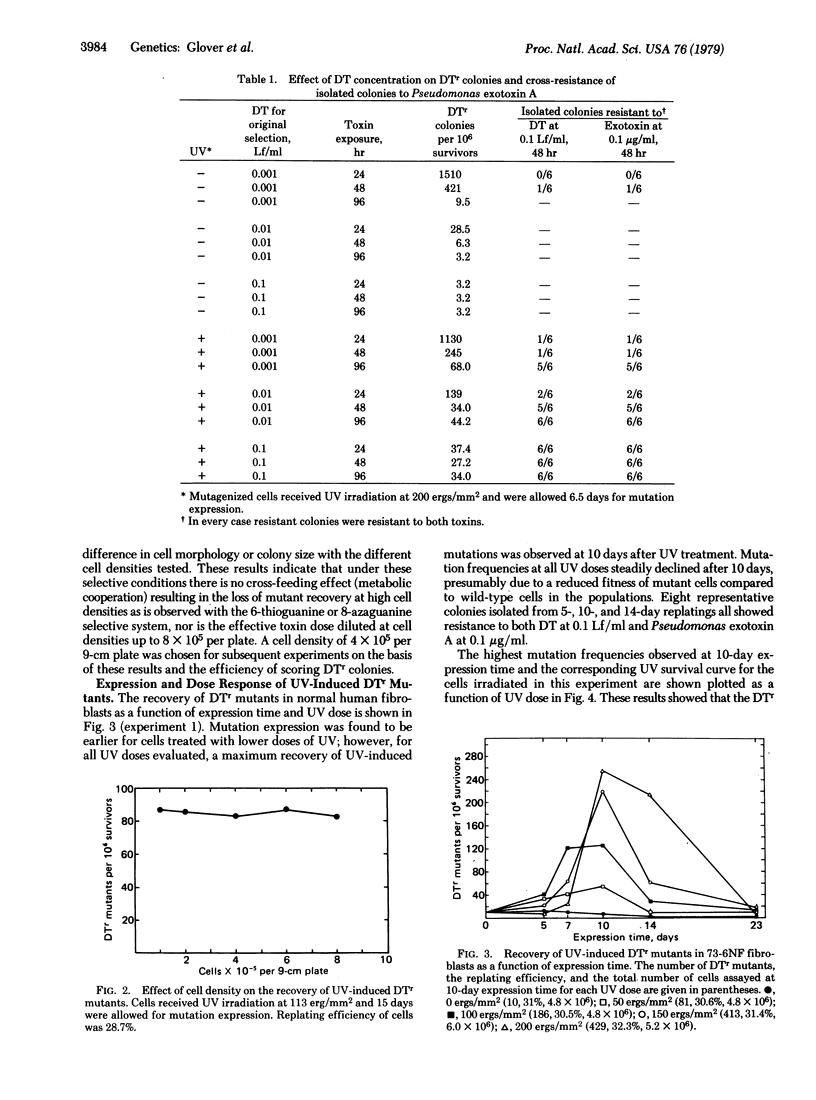
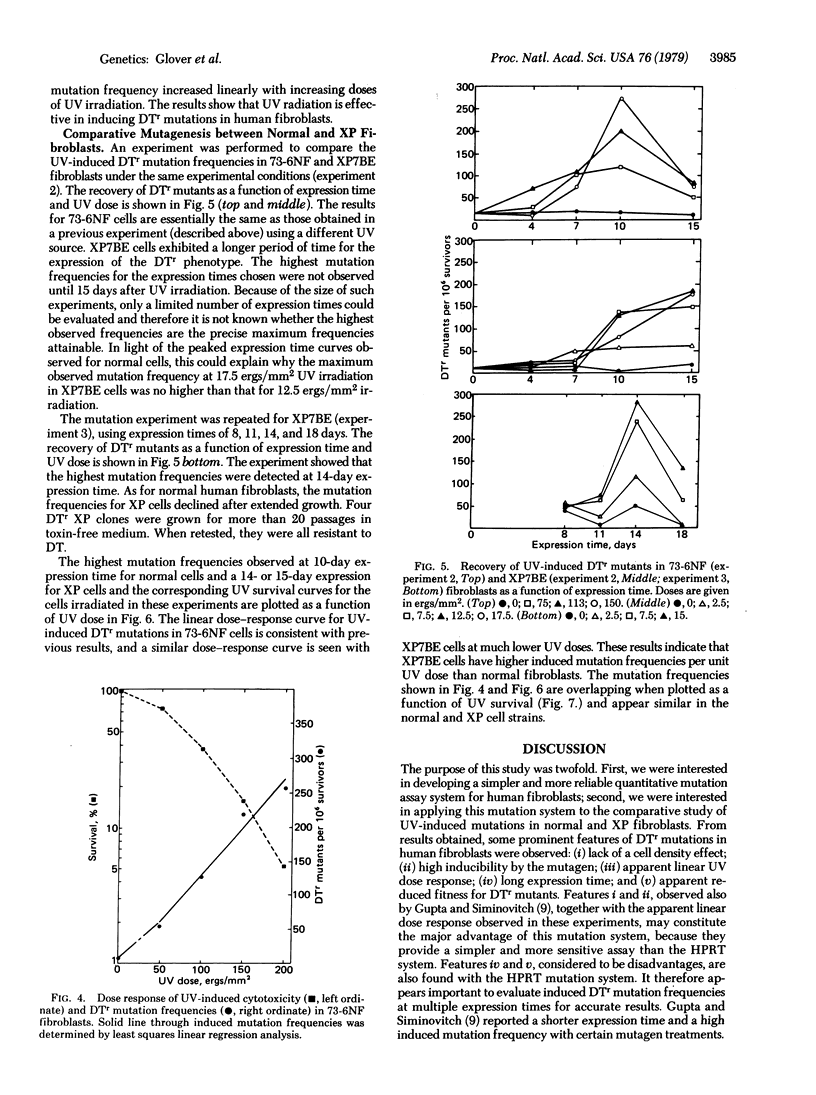
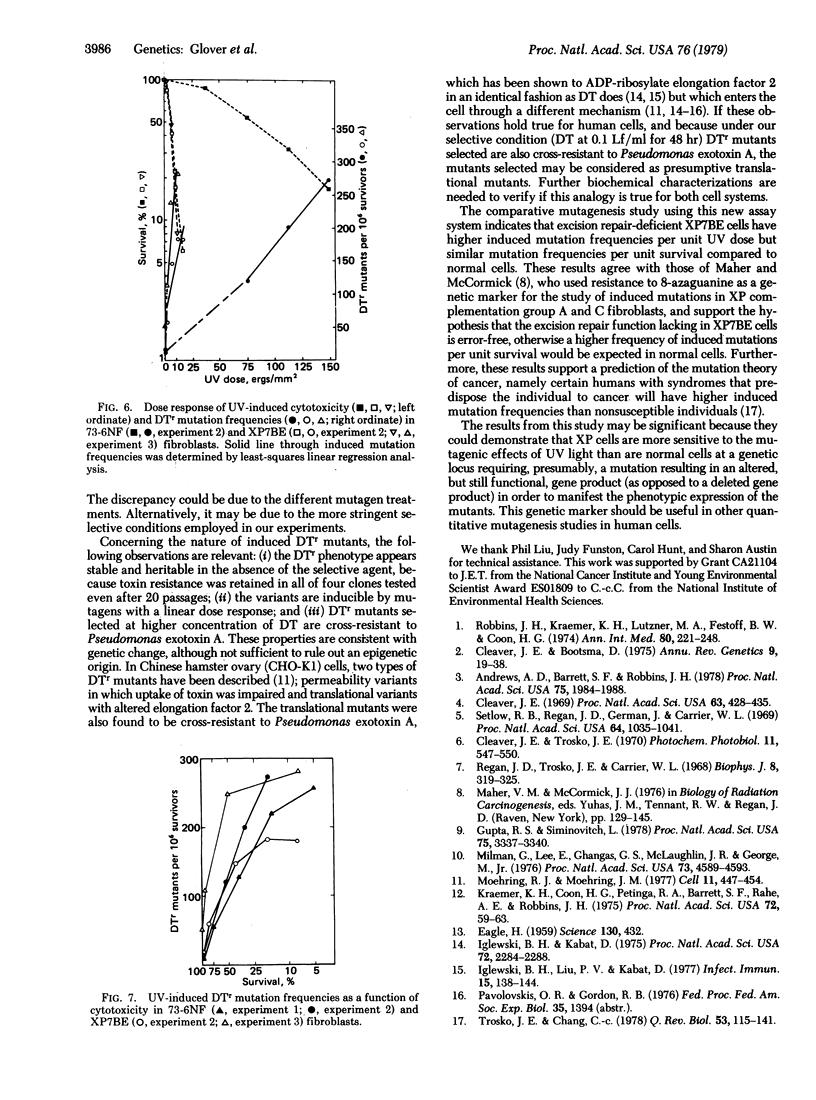
The UV induction of diphtheria toxin-resistant (DTr) mutants in normal and xeroderma pigmentosum human fibroblasts has been quantitatively characterized. A concentration of diphtheria toxin at which DTr cells are cross-resistant to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A was determined and used in the selection of resistant mutants. Recovery of mutants was not influenced by the presence of wild-type cell densities of 1-8 x 10(5) per 9-cm plate, indicating no metabolic cooperation exists, in contrast to what is seen in the selection of some other variant phenotypes. Expression periods for UV-induced mutations differed with the severity of mutagen treatment and cell strain used. A relatively long (10-15 days after UV treatment) expression period was required for the maximum recovery of DTr mutants. Maximum recovery was followed by a decrease in mutation frequency on subsequent days evaluated. An apparent linear dose response within the dose range used was observed for UV-induced mutations in both normal and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Our results indicate that xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts have higher UV-induced mutation frequencies per unit UV dose but similar frequencies per unit survival compared to normal cells within the range of UV doses tested.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. D., Barrett S. F., Robbins J. H. Xeroderma pigmentosum neurological abnormalities correlate with colony-forming ability after ultraviolet radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum: biochemical and genetic characteristics. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:19–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Trosko J. E. Absence of excision of ultraviolet-induced cyclobutane dimers in xeroderma pigmentosum. Photochem Photobiol. 1970 Jun;11(6):547–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1970.tb06025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Xeroderma pigmentosum: a human disease in which an initial stage of DNA repair is defective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):428–435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Isolation and characterization of mutants of human diploid fibroblasts resistant to diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3337–3340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Coon H. G., Petinga R. A., Barrett S. F., Rahe A. E., Robbins J. H. National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20014, USA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Lee E., Ghangas G. S., McLaughlin J. R., George M., Jr Analysis of HeLa cell hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase mutants and revertants by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: evidence for silent gene activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4589–4593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Selection and characterization of cells resistant to diphtheria toxin and pseudomonas exotoxin A: presumptive translational mutants. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. D., Trosko J. E., Carrier W. L. Evidence for excision of ultraviolet-induced pyrimidine dimers from the DNA of human cells in vitro. Biophys J. 1968 Mar;8(3):319–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86490-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Kraemer K. H., Lutzner M. A., Festoff B. W., Coon H. G. Xeroderma pigmentosum. An inherited diseases with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):221–248. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Regan J. D., German J., Carrier W. L. Evidence that xeroderma pigmentosum cells do not perform the first step in the repair of ultraviolet damage to their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1035–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trosko J. E., Chang C. C. Environmental carcinogenesis: an integrative model. Q Rev Biol. 1978 Jun;53(2):115–141. doi: 10.1086/410451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


