Abstract
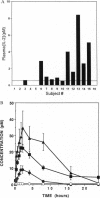
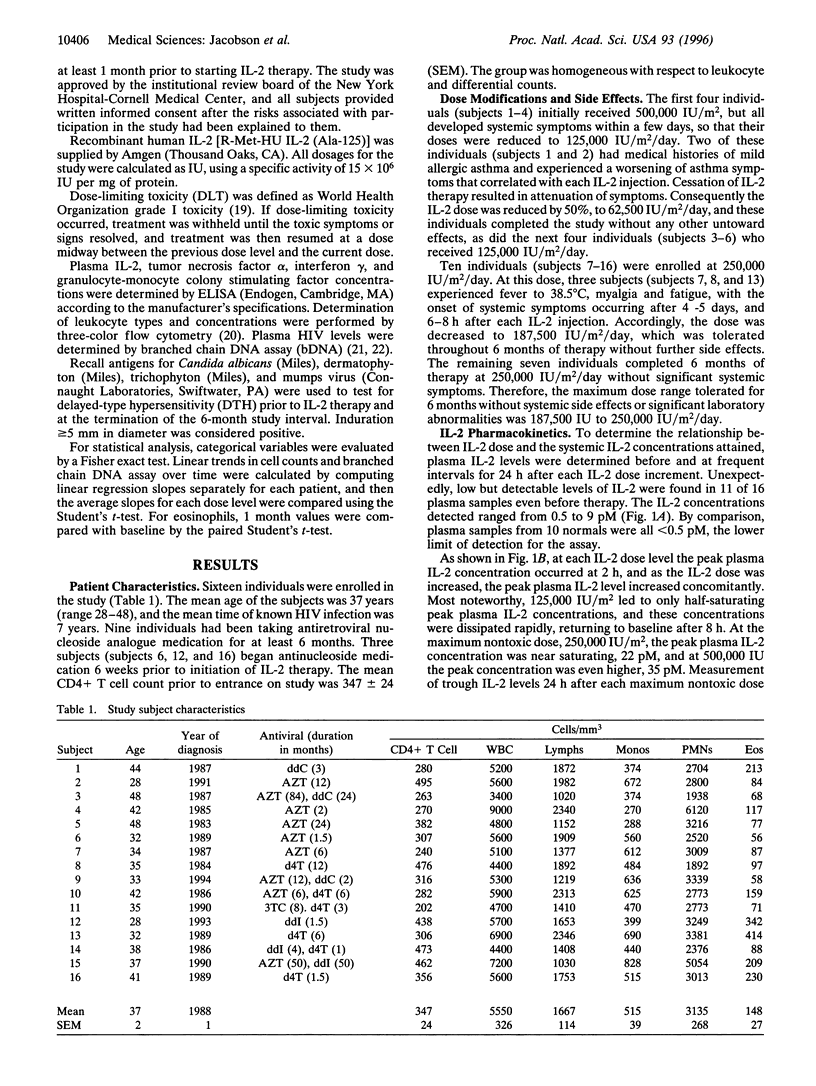
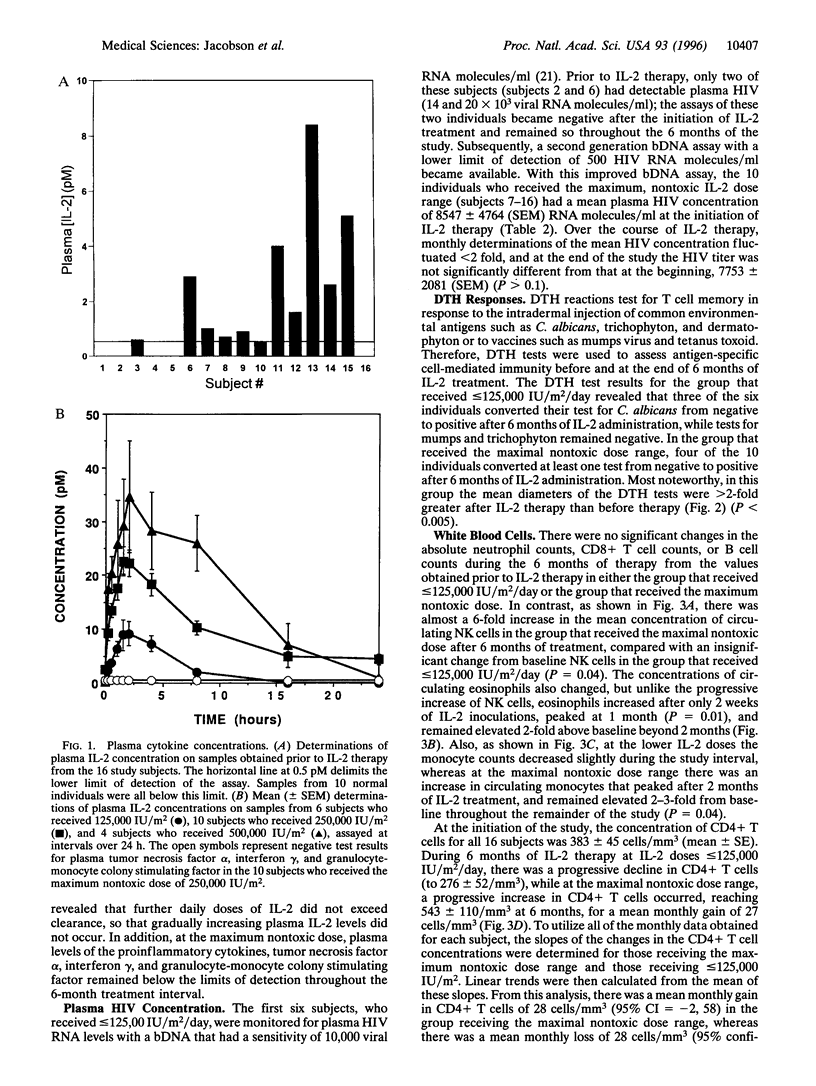
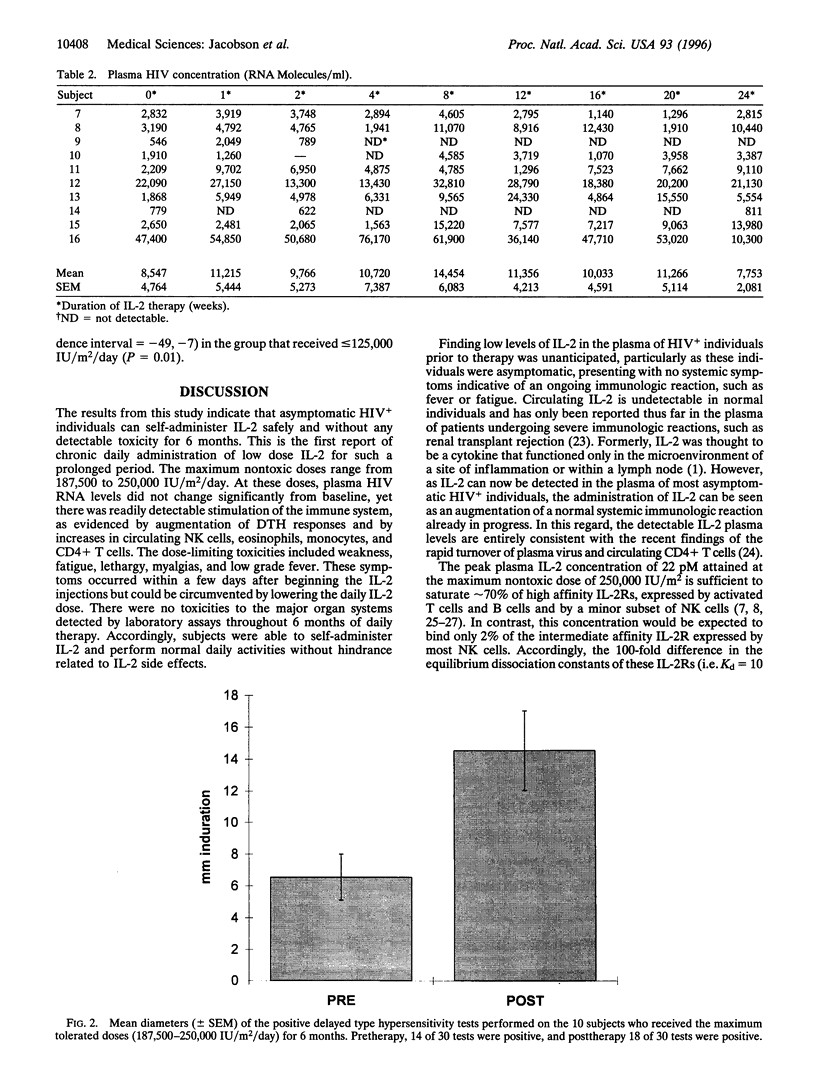
When administered in high doses to HIV positive (HIV+) individuals, interleukin 2 (IL-2) causes extreme toxicity and markedly increases plasma HIV levels. Integration of the information from the structure-activity relationships of the IL-2 receptor interaction, the cellular distribution of the different classes of IL-2 receptors, and the pharmacokinetics of IL-2 provides for the rationale that low IL-2 doses should circumvent toxicity. Therefore, to identify a nontoxic, but effective and safe IL-2 treatment regimen that does not stimulate viral replication, doses of IL-2 from 62,500 to 250,000 IU/m2/day were administered subcutaneously for 6 months to 16 HIV+ individuals with 200-500 CD4+ T cells/mm3. IL-2 was already detectable in the plasma of most HIV+ individuals even before therapy. Peak plasma IL-2 levels were near saturating for high affinity IL-2 receptors in 10 individuals who received the maximum nontoxic dose, which ranged from 187,500 to 250,000 IU/m2/day. During the 6 months of treatment at this dose range, plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines remained undetectable, and plasma HIV RNA levels did not change significantly. However, delayed type hypersensitivity responses to common recall antigens were markedly augmented, and there were IL-2 dose-dependent increases in circulating Natural Killer cells, eosinophils, monocytes, and CD4+ T cells. Expanded clinical trials of low dose IL-2 are now warranted, especially in combination with effective antivirals to test for the prevention of immunodeficiency and the emergence of drug-resistant mutants and for the eradication of residual virions.
Full text
PDF
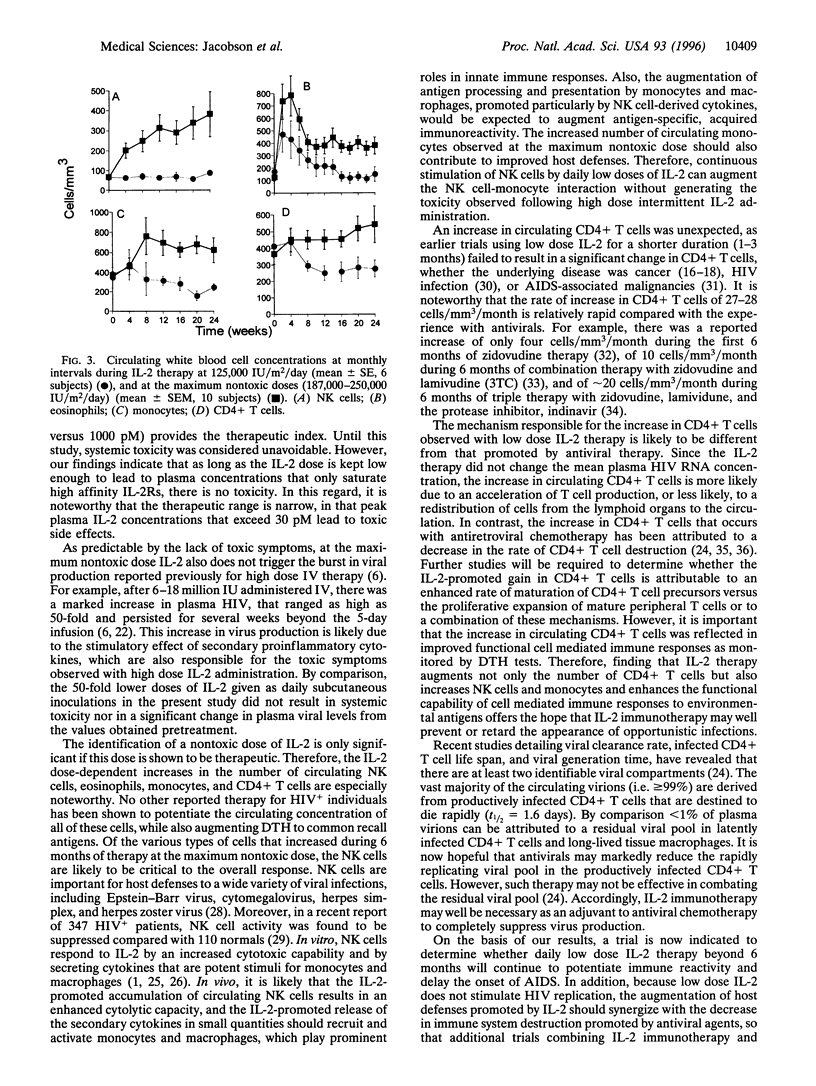

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein Z. P., Porter M. M., Gould M., Lipman B., Bluman E. M., Stewart C. C., Hewitt R. G., Fyfe G., Poiesz B., Caligiuri M. A. Prolonged administration of low-dose interleukin-2 in human immunodeficiency virus-associated malignancy results in selective expansion of innate immune effectors without significant clinical toxicity. Blood. 1995 Nov 1;86(9):3287–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligiuri M. A. Low-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy: rationale and potential clinical applications. Semin Oncol. 1993 Dec;20(6 Suppl 9):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligiuri M. A., Murray C., Robertson M. J., Wang E., Cochran K., Cameron C., Schow P., Ross M. E., Klumpp T. R., Soiffer R. J. Selective modulation of human natural killer cells in vivo after prolonged infusion of low dose recombinant interleukin 2. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):123–132. doi: 10.1172/JCI116161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligiuri M. A., Murray C., Soiffer R. J., Klumpp T. R., Seiden M., Cochran K., Cameron C., Ish C., Buchanan L., Perillo D. Extended continuous infusion low-dose recombinant interleukin-2 in advanced cancer: prolonged immunomodulation without significant toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Dec;9(12):2110–2119. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.12.2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligiuri M. A., Zmuidzinas A., Manley T. J., Levine H., Smith K. A., Ritz J. Functional consequences of interleukin 2 receptor expression on resting human lymphocytes. Identification of a novel natural killer cell subset with high affinity receptors. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1509–1526. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concorde: MRC/ANRS randomised double-blind controlled trial of immediate and deferred zidovudine in symptom-free HIV infection. Concorde Coordinating Committee. Lancet. 1994 Apr 9;343(8902):871–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewar R. L., Highbarger H. C., Sarmiento M. D., Todd J. A., Vasudevachari M. B., Davey R. T., Jr, Kovacs J. A., Salzman N. P., Lane H. C., Urdea M. S. Application of branched DNA signal amplification to monitor human immunodeficiency virus type 1 burden in human plasma. J Infect Dis. 1994 Nov;170(5):1172–1179. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.5.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron J. J., Benoit S. L., Jemsek J., MacArthur R. D., Santana J., Quinn J. B., Kuritzkes D. R., Fallon M. A., Rubin M. Treatment with lamivudine, zidovudine, or both in HIV-positive patients with 200 to 500 CD4+ cells per cubic millimeter. North American HIV Working Party. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 21;333(25):1662–1669. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512213332502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Baseler M., Dewar R. J., Vogel S., Davey R. T., Jr, Falloon J., Polis M. A., Walker R. E., Stevens R., Salzman N. P. Increases in CD4 T lymphocytes with intermittent courses of interleukin-2 in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A preliminary study. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 2;332(9):567–575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503023320904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutukculer N., Clark K., Rigg K. M., Forsythe J. L., Proud G., Taylor R. M., Shenton B. K. The value of posttransplant monitoring of interleukin (IL)-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and soluble CD23 in the plasma of renal allograft recipients. Transplantation. 1995 Feb 15;59(3):333–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Ettinghausen S. E., Rayner A. A., Sharrow S. O., Seipp C. A., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin 2. II. Half life, immunologic effects, and expansion of peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo with recombinant IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2865–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Vachino G., Klempner M. S., Aronson F. R., Noring R., Smith S., Brandon E. P., Laird W., Atkins M. B. Inhibition of interleukin-2-induced tumor necrosis factor release by dexamethasone: prevention of an acquired neutrophil chemotaxis defect and differential suppression of interleukin-2-associated side effects. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):1933–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Vachino G., van der Meer J. W., Numerof R. P., Adams S., Cannon J. G., Bernheim H. A., Atkins M. B., Parkinson D. R., Dinarello C. A. Induction of circulating tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) as the mechanism for the febrile response to interleukin-2 (IL-2) in cancer patients. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Nov;8(6):426–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00916947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B., Hoogstraten B., Staquet M., Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981 Jan 1;47(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<207::aid-cncr2820470134>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakarai T., Robertson M. J., Streuli M., Wu Z., Ciardelli T. L., Smith K. A., Ritz J. Interleukin 2 receptor gamma chain expression on resting and activated lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):241–251. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Todd J. A., Kern D. G., Sheridan P. J., Fong S. J., Stempien M., Hoo B., Besemer D., Yeghiazarian T., Irvine B. Rapid and precise quantification of HIV-1 RNA in plasma using a branched DNA signal amplification assay. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Apr 15;8(5):446–454. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199504120-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Neumann A. U., Markowitz M., Leonard J. M., Ho D. D. HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1582–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perno C. F., Cooney D. A., Gao W. Y., Hao Z., Johns D. G., Foli A., Hartman N. R., Caliò R., Broder S., Yarchoan R. Effects of bone marrow stimulatory cytokines on human immunodeficiency virus replication and the antiviral activity of dideoxynucleosides in cultures of monocyte/macrophages. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):995–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Bressler P., Kinter A., Duh E., Timmer W. C., Rabson A., Justement J. S., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Interleukin 6 induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in infected monocytic cells alone and in synergy with tumor necrosis factor alpha by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):151–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr Review important concepts of receptor theory. J Auton Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;2(4):277–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1982.tb00520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1169–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.3131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Lowest dose interleukin-2 immunotherapy. Blood. 1993 Mar 15;81(6):1414–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soiffer R. J., Murray C., Gonin R., Ritz J. Effect of low-dose interleukin-2 on disease relapse after T-cell-depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1994 Aug 1;84(3):964–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. C., Stewart S. J. Cell preparation for the identification of leukocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;41:39–60. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61708-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppler H., Kaplan G., Smith K., Cameron P., Montana A., Meyn P., Cohn Z. Efficacy of low doses of the polyethylene glycol derivative of interleukin-2 in modulating the immune response of patients with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):291–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullum H., Gøtzsche P. C., Victor J., Dickmeiss E., Skinhøj P., Pedersen B. K. Defective natural immunity: an early manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):789–799. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Regulation of virus infections by natural killer cells. A review. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1986;5(4):169–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]