Abstract
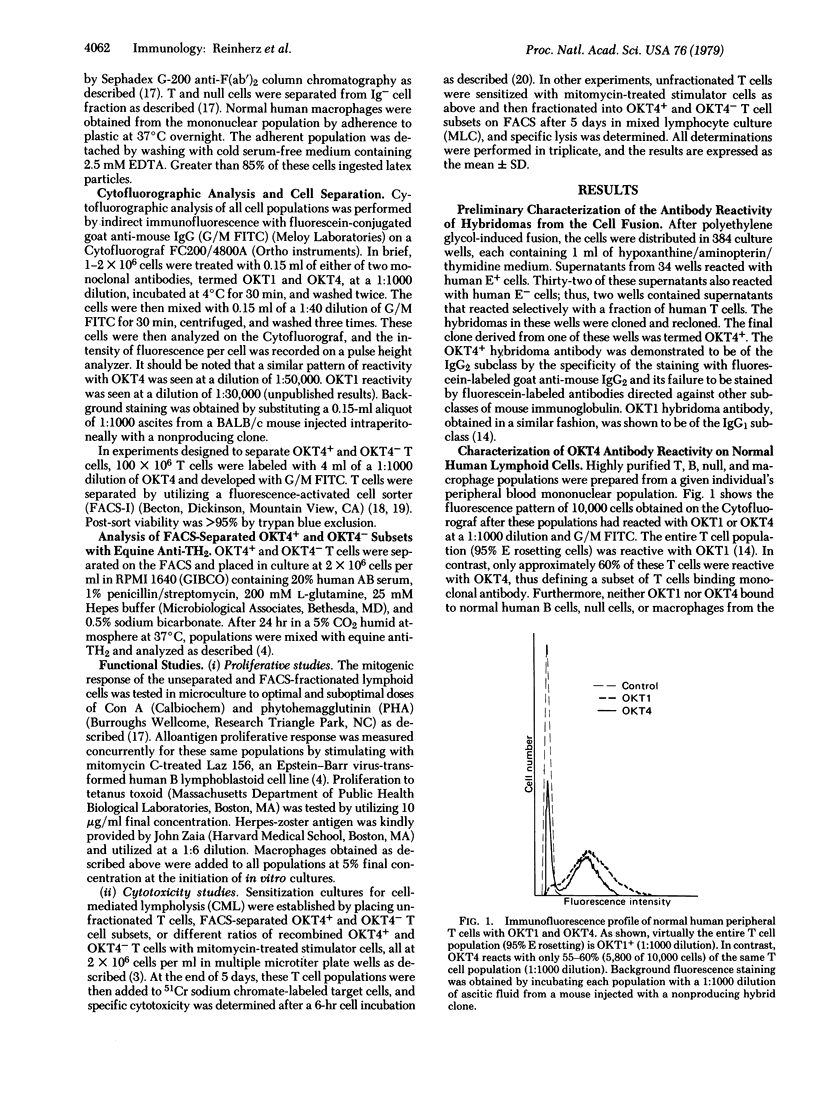
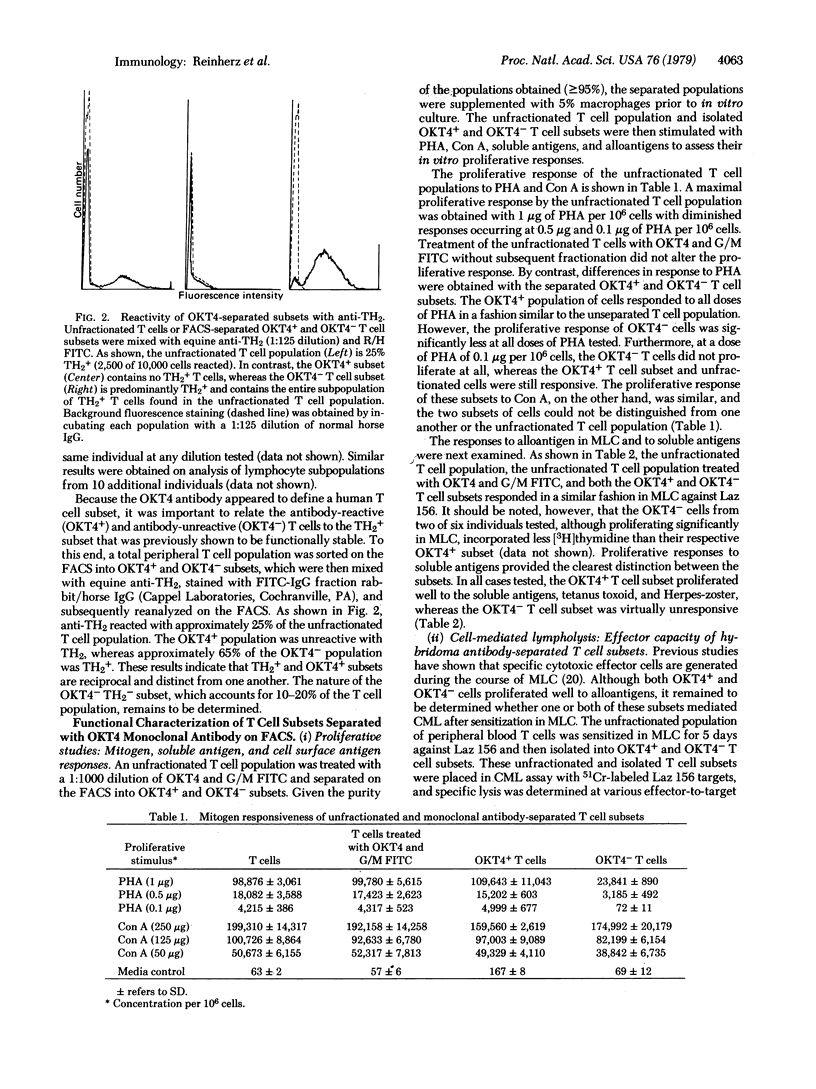
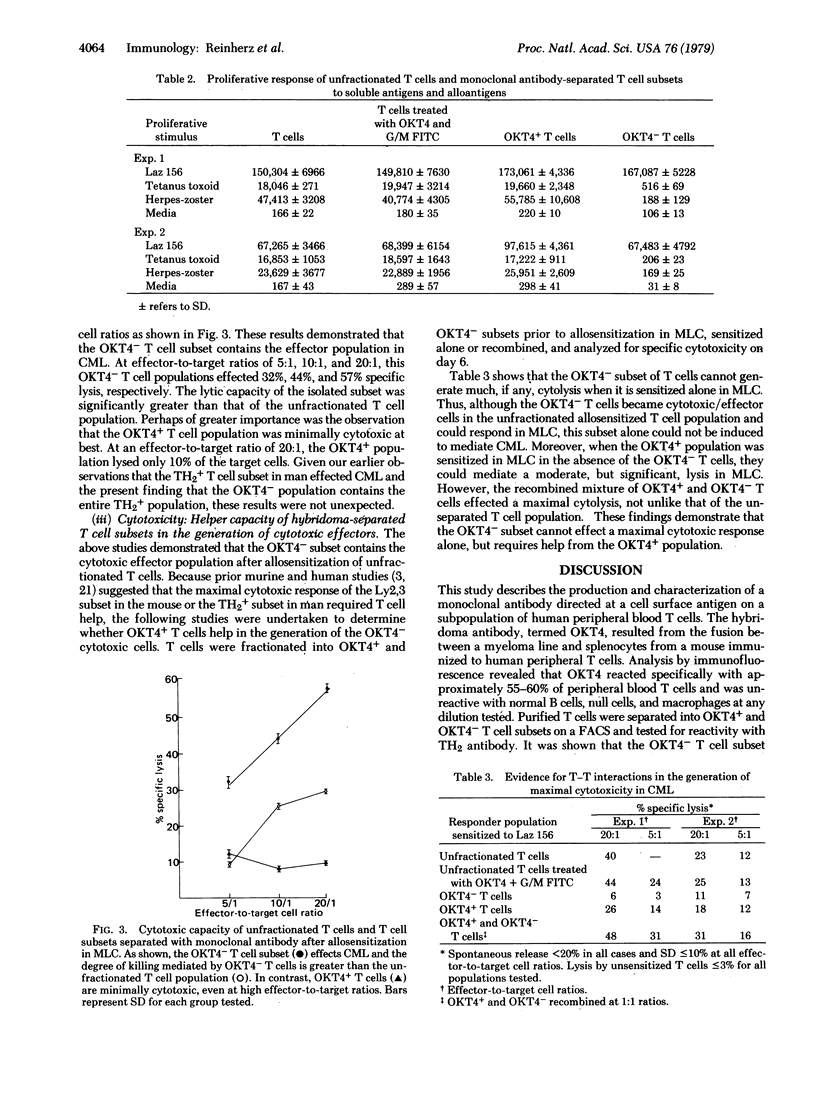
A monoclonal antibody was produced to human peripheral blood T cells. This hybridoma antibody, termed OKT4, was reactive by indirect immunofluorescence with only 55-60% of the peripheral blood T cell population (OKT4+) and unreactive with normal B cells, null cells, and macrophages. The OKT4- T cell population contained the previously described TH2+ subset that has been shown to contain cytotoxic/suppressor cells. With cell-sorter separation of OKT4+ and OKT4- cells, it was shown that these T cell subsets were functionally discrete. Both gave proliferative responses with concanavalin A, alloantigens, and phytohemagglutinin although OKT4+ cells were much more responsive to the latter. OKT4+ cells alone responded to soluble antigens whereas OKT4- cells alone were cytotoxic after alloantigenic sensitization of unfractionated T cells. However, both OKT4+ and OKT4- cells were required during sensitization for optimal development of cytotoxicity. These data suggest that the OKT4+ subset represents a helper population and that the OKT4- subset contains the cytotoxic effector population. OKT4 could be a valuable reagent for determining alterations of these functional subsets in human diseases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. A., Hulett H. R., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence activated cell sorting. Rev Sci Instrum. 1972 Mar;43(3):404–409. doi: 10.1063/1.1685647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. II. Cooperation between subclasses of Ly+ cells in the generation of killer activity. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1390–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. II. Activation by antigen: after immunization, antigen-specific suppressor and helper activities are mediated by distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1391–1340. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Quantitative isolation of human T and B cells and response to mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1113–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Lazarus H., Penta A. C., Schlossman S. F. Two functionally distinct subpopulations of human T cells that collaborate in the generation of cytotoxic cells responsible for cell-mediated lympholysis. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1423–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Budzko D. B. Identification and characterization of a new subset of rat T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes N. F., Tolnai M. E., Silveira N. P., Gilbertsen R. B., Metzgar R. S. Technical aspects of the rosette tests used to detect human complement receptor (B) and sheep erythrocyte-binding (T) lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Webb S. R. Subpopulations of human T cells identified by receptors for immunoglobulins and mitogen responsiveness. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2171–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Parkman R., Rappeport J., Rosen F. S., Schlossman S. F. Aberrations of suppressor T cells in human graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 10;300(19):1061–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905103001901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Con A-inducible suppression of MLC: evidence for mediation by the TH2 + T cell subset in man. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1335–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Strelkauskas A. J., O'Brien C., Schlossman S. F. Phenotypic and functional distinctions between the TH2+ and JRA+ T cell subsets in man. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondel P. M., Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. III. Specific allogeneic lympholysis mediated by human T cells alone. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):982–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelkauskas A. J., Callery R. T., McDowell J., Borel Y., Schlossman S. F. Direct evidence for loss of human suppressor cells during active autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5150–5154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelkauskas A. J., Schauf V., Wilson B. S., Chess L., Schlossman S. F. Isolation and characterization of naturally occurring subclasses of human peripheral blood T cells with regulatory functions. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1278–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



