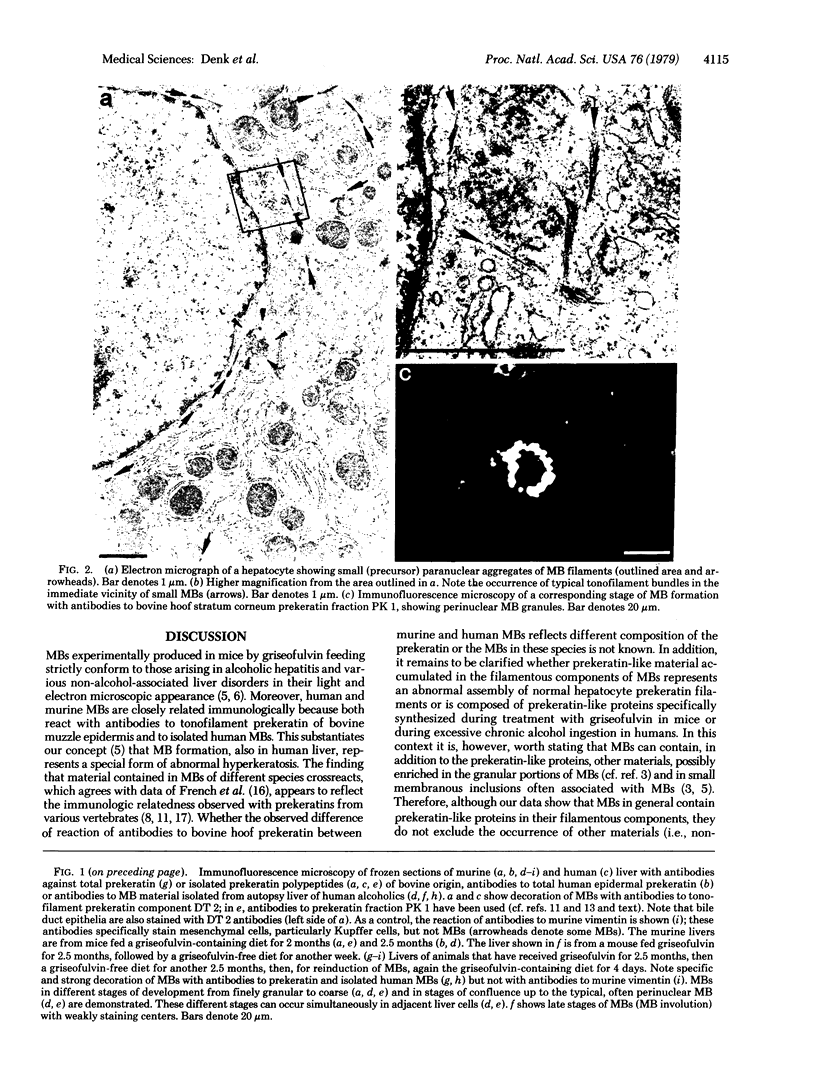
Abstract
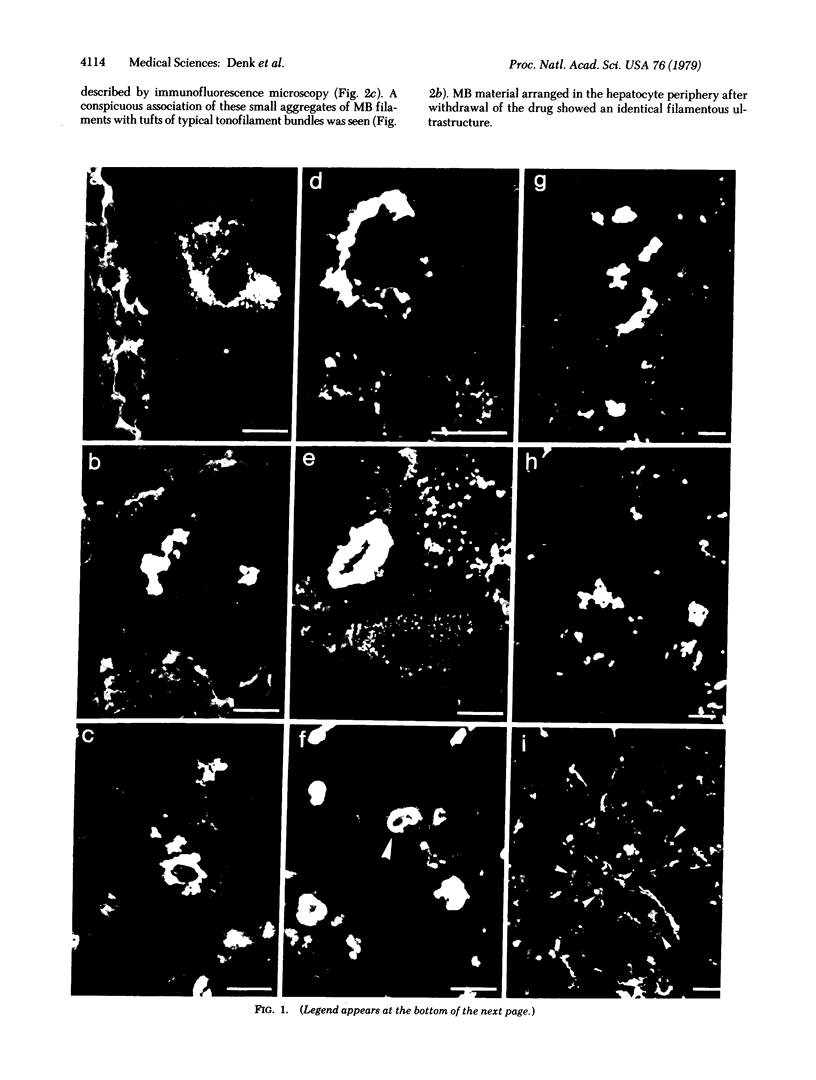
Antibodies raised against prekeratin intensely and specifically stain, in immunofluorescence microscopy, Mallory bodies ("alcoholic hyalin") present in livers of human alcoholics and griseofulyin-treated mice. The high sensitivity of this method allows the identification of small distinct cytoplasmic structures that are observed during early stages of Mallory body formation, especially frequent in the perinuclear cytoplasm, as well as during stages of Mallory body disintegration and disappearance, such as after withdrawal of the drug. In the latter situation, the prekeratin-containing small particles exhibit a characteristic pattern of arrangement in the hepatocyte periphery. Electron microscopy illustrates that such small bodies are heap-like aggregates of typical Mallory body filaments. Immunofluorescence studies with antibodies to isolated prekeratin polypeptides from bovine hoof or muzzle epidermis show that Mallory body filaments, in particular those in human liver, are immunologically more closely related to prekeratin of tonofilaments from living epidermal cells (stratum spinosum). The data indicate that Mallory bodies contain a pathologic form of prekeratin-like material. They also suggest that disorders of cytoskeletal structures of the intermediate-sized filament class are associated with specific diseases and can be visualized and characterized by immunofluorescence microscopy by using antibodies to constitutive proteins of such filaments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIAVA C. MALLORY ALCOHOLIC HYALIN: A HERETOFORE UNIQUE LESION OF HEPATOCELLULAR ERGASTOPLASM. Lab Invest. 1964 Apr;13:301–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Croop J. M., Otto J. J., Bryan J., Holtzer H. Differences among 100-A filamentilament subunits from different cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christoffersen P. Light microscopical features in liver biopsies with Mallory bodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1972;80(6):705–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Eckerstorfer R. Colchicine-induced Mallory body formation in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;36(6):563–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Eckerstorfer R., Gschnait F., Konrad K., Wolff K. Experimental induction of hepatocellular hyalin (Mallory bodies) in mice by griseofulvin treatment. 1. Light microscopic observation. Lab Invest. 1976 Oct;35(4):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drochmans P., Freudenstein C., Wanson J. C., Laurent L., Keenan T. W., Stadler J., Leloup R., Franke W. W. Structure and biochemical composition of desmosomes and tonofilaments isolated from calf muzzle epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):427–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Denk H., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Ultrastructural, biochemical, and immunologic characterization of Mallory bodies in livers of griseofulvin-treated mice. Fimbriated rods of filaments containing prekeratin-like polypeptides. Lab Invest. 1979 Feb;40(2):207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French S. W., Ihrig T. J., Norum M. L. A method of isolation of Mallory bodies in a purified fraction. Lab Invest. 1972 Mar;26(3):240–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenstein C., Franke W. W., Osborn M., Weber K. Reaction of tonofilament-like intermediate-sized filaments with antibodies raised against isolated defined polypeptides of bovine hoof prekeratin. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Nov;2(6):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Balzer D. R., Jr Specificity of desmin to avian and mammalian muscle cells. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezey E. Liver disease and nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):770–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. W., Jr, Law D. H., 4th, Sandstead H. H., Lanier V. C., Jr, Younger R. K. Jejunoileal shunt in surgical treatment of morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 1970 May;171(5):770–782. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197005000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Immunofluorescent staining of keratin fibers in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinberg H. M., Regan R. J., Geier E. A., Peterson G. E., French S. W. Mallory bodies: isolation of hepatocellular hyalin and electrophoretic resolution of polypeptide components. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):483–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggers K. D., French S. W., French B. A., Carr B. N. The ultrastructure of Mallory body filaments. Lab Invest. 1973 Dec;29(6):652–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo H., Minick O. T., Batti F., Kent G. Morphologic variants of alcoholic hyalin. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):25–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]