Abstract
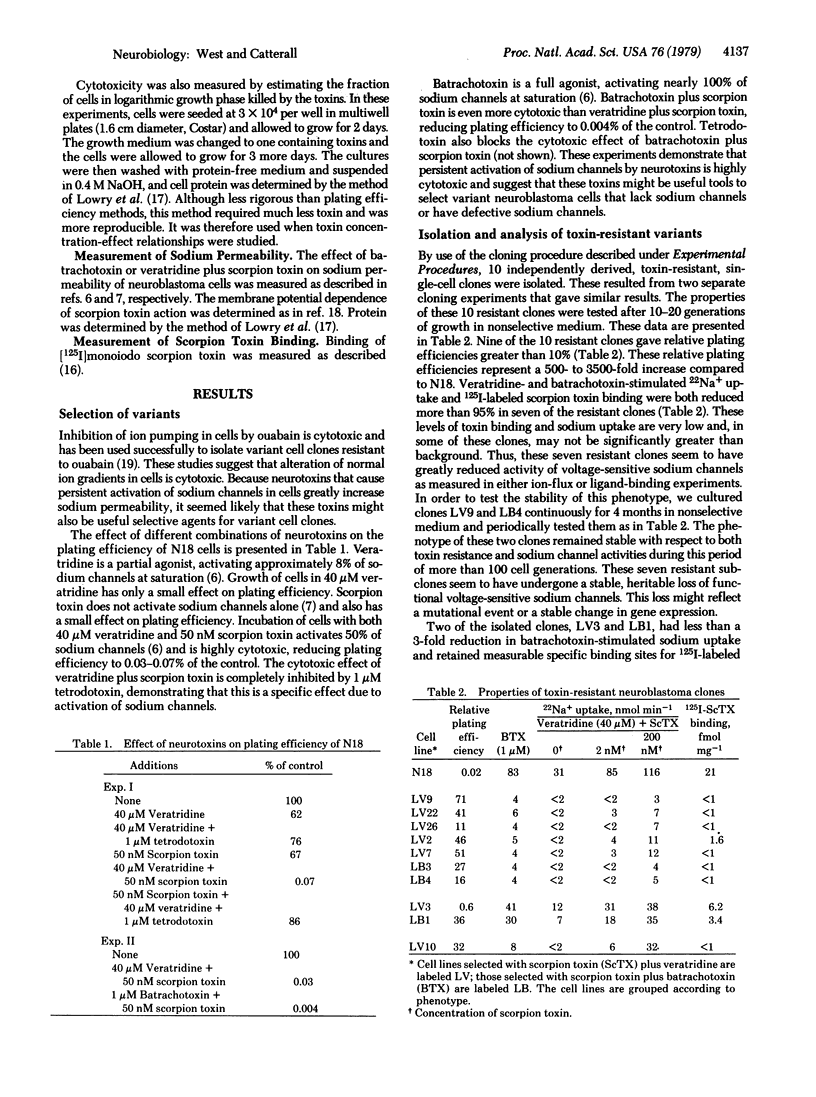
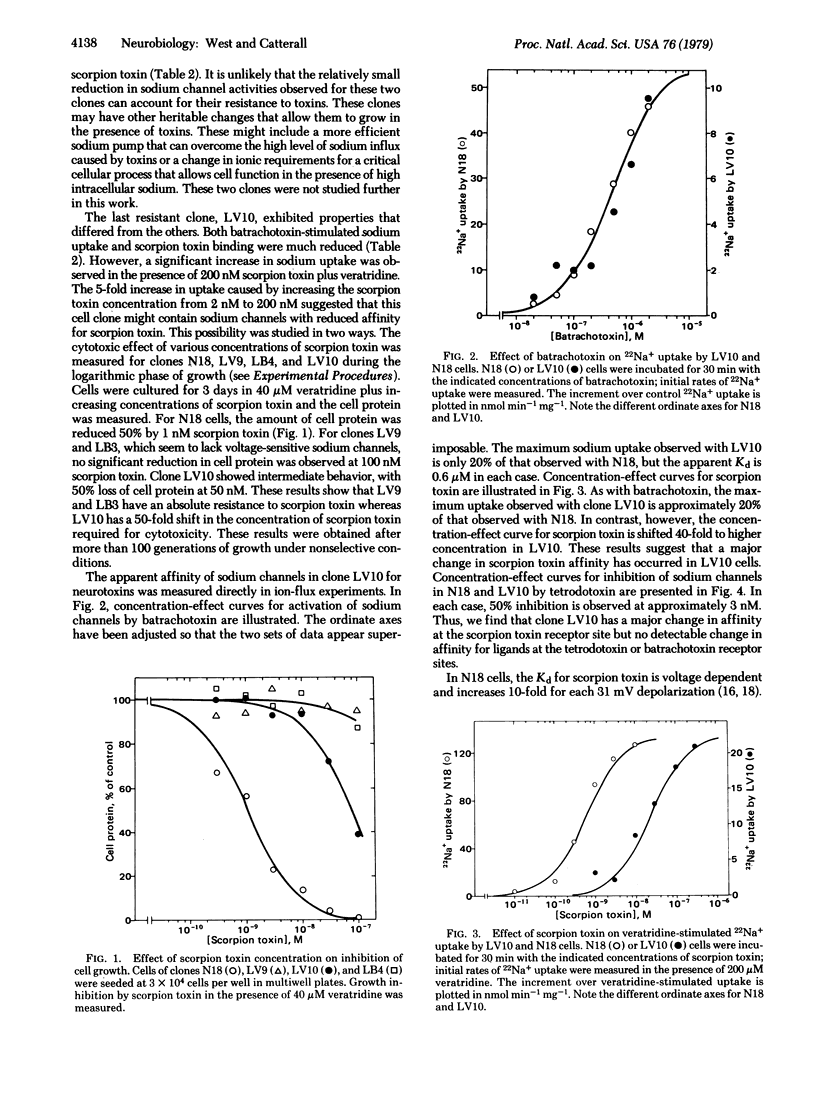
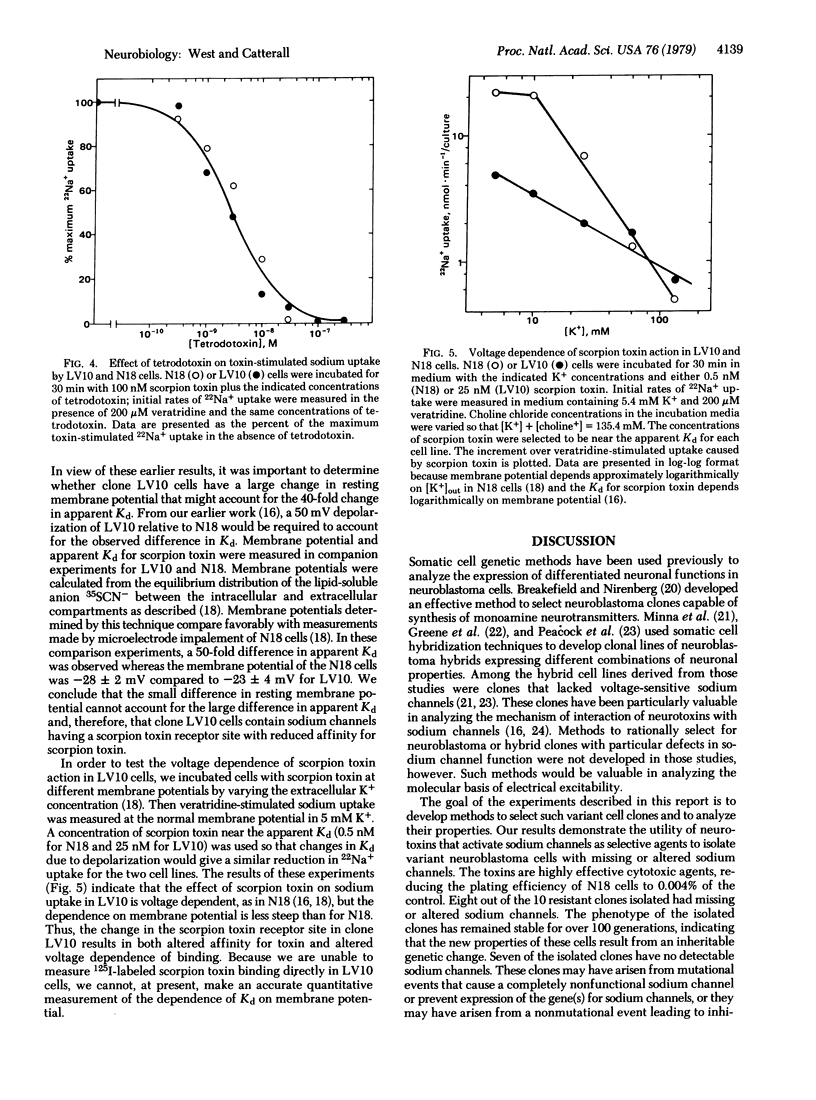
Neurotoxins that cause persistent activation of voltage-sensitive sodium channels are highly cytotoxic to electrically excitable neuroblastoma cells. These toxins were used as selective agents to isolate variant neuroblastoma clones with missing or altered sodium channels. Of ten resistant clones analyzed, seven lacked functional sodium channels and one had a specific 40-fold increase Kd for scorpion toxin and altered voltage dependence of scorpion toxin binding. The phenotypes of these cell clones were stable for more than 100 generations, indicating that they were the result of stable genetic change.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. Selection of a variant lymphoma cell deficient in adenylate cyclase. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):750–752. doi: 10.1126/science.163487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breakefield X. O., Nirenberg M. W. Selection for neuroblastoma cells that synthesize certain transmitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2530–2533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins. An allosteric model. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8669–8676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore of cultured neuroblastoma cells by veratridine and batrachotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4053–4059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Beress L. Sea anemone toxin and scorpion toxin share a common receptor site associated with the action potential sodium ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7393–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cooperative activation of action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Membrane potential-dependent binding of scorpion toxin to the action potential Na+ ionophore. Studies with a toxin derivative prepared by lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8660–8668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Morrow C. S. Binding to saxitoxin to electrically excitable neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):218–222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Nirenberg M. Sodium uptake associated with activation of action potential ionophores of cultured neuroblastoma and muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3759–3763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Purification of a toxic protein from scorpion venom which activates the action potential Na+ ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5528–5536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Ray R., Morrow C. S. Membrane potential dependent binding of scorpion toxin to action potential Na+ ionophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2682–2686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couraud F., Rochat H., Lissitzky S. Binding of scorpion and sea anemone neurotoxins to a common site related to the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1525–1530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shain W., Chalazonitis A., Breakfield X., Minna J., Coon H. G., Nirenberg M. Neuronal properties of hybrid neuroblastoma X sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4923–4927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Molecular properties of the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Interactions with neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7383–7392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Kaslow H. R., Bourne H. R. Genetic evidence that cholera toxin substrates are regulatory components of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7120–7123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J., Nelson P., Peacock J., Glazer D., Nirenberg M. Genes for neuronal properties expressed in neuroblastoma x L cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):234–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J. H., Amano T., Minna J. Electrogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Jun;77(3):337–352. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P., Ruffner W., Nirenberg M. Neuronal tumor cells with excitable membranes grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock J. H., McMorris F. A., Nelson P. G. Electrical excitability and chemosensitivity of mouse neuroblastoma X mouse or human fibroblast hybrids. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):199–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector I., Kimhi Y., Nelson P. G. Tetrodotoxin and cobalt blockade of neuroblastoma action potentials. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 28;246(152):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio246124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


