Abstract
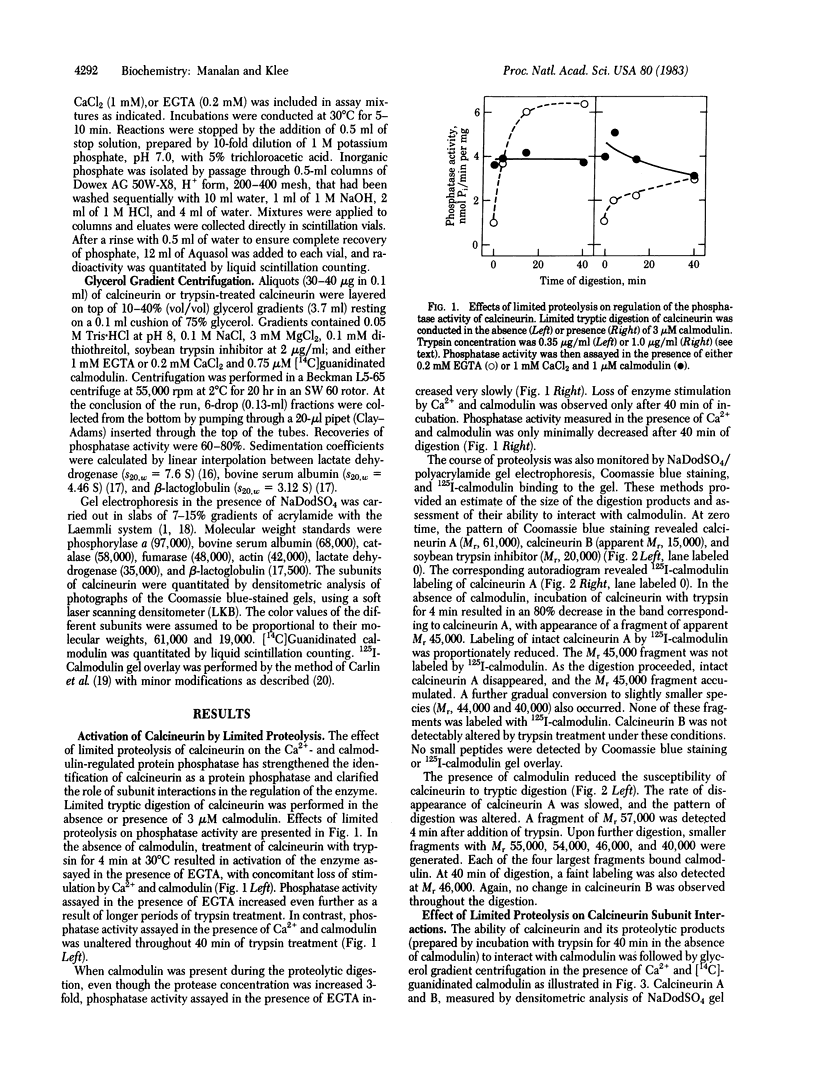
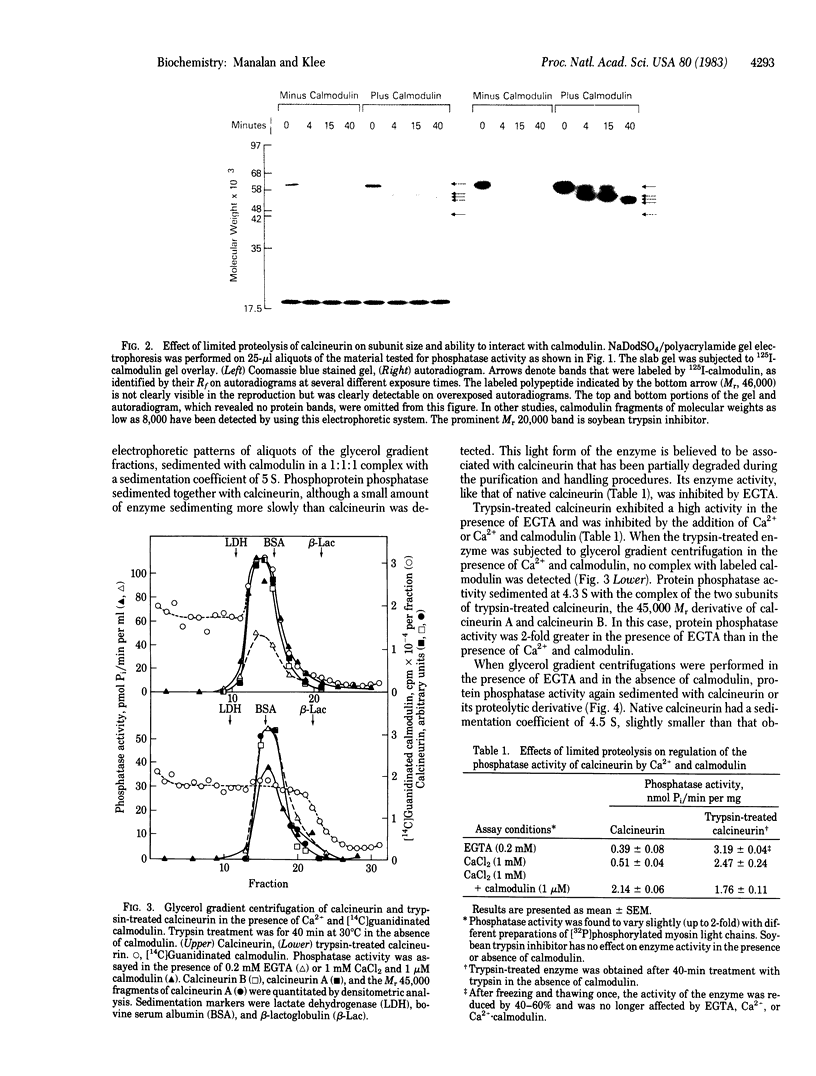
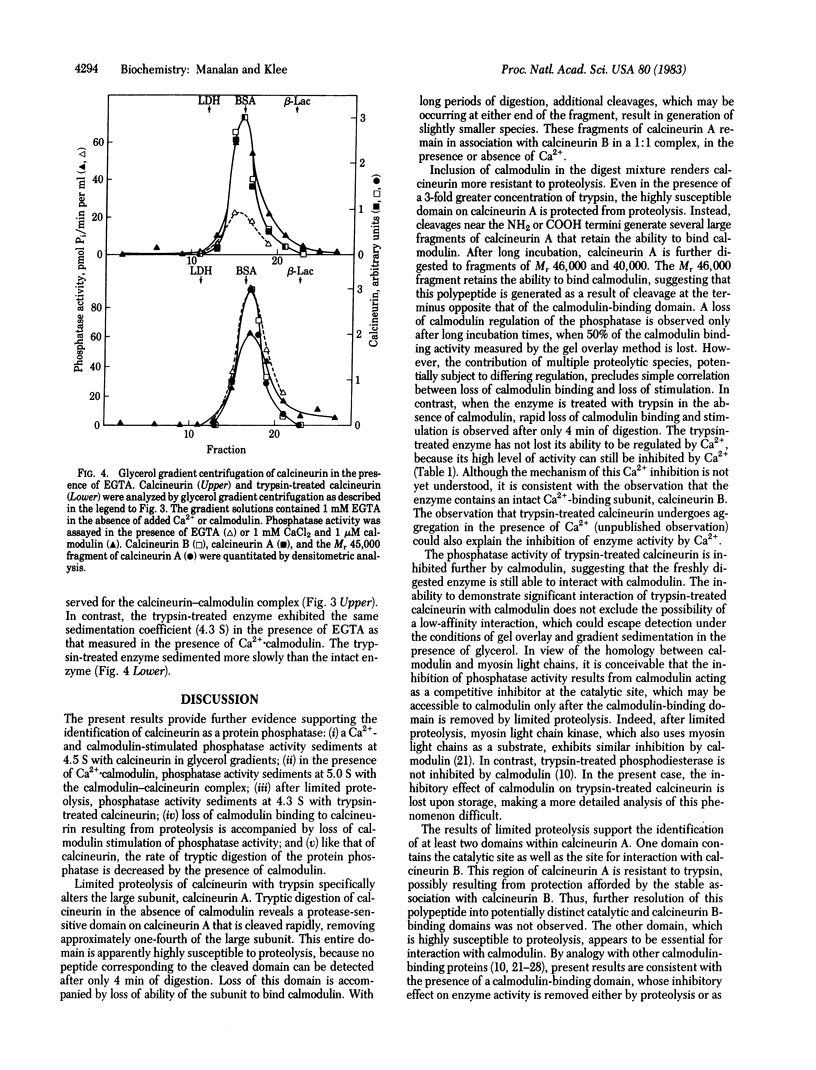
Calcineurin, a heterodimer of calcineurin B, a 19,000 Mr Ca2+-binding subunit, and calcineurin A, a 61,000 Mr calmodulin-binding subunit, was previously proposed to be a calmodulin- and Ca2+-regulated protein phosphatase. Like other calmodulin-stimulated enzymes, calcineurin can be activated and rendered calmodulin- and Ca2+-independent by limited proteolysis. By glycerol gradient centrifugation, the native enzyme has a s20,w of 4.5 S in EGTA and 5 S in the presence of Ca2+-calmodulin. Under the same conditions, the s20,w of the trypsin-activated enzyme (4.3 S) is not affected by Ca2+ and calmodulin. The trypsin-treated enzyme is a heterodimer of calcineurin B and a 45,000 Mr fragment of calcineurin A that has lost its ability to interact with calmodulin. Phosphatase activity sediments with calcineurin or its proteolytic fragments, providing further evidence that calcineurin is indeed a protein phosphatase. Calmodulin protects calcineurin against tryptic digestion; proteolysis occurs more slowly, yielding fragments with Mr 57,000, 55,000, and 54,000 that have preserved their ability to interact with calmodulin. After trypsin treatment in the presence of calmodulin, the protein phosphatase activity of calcineurin is still regulated by calmodulin. Prolonged trypsin treatment in the presence of calmodulin produces a 46,000 Mr fragment. Unlike the fragments generated in the absence of calmodulin, this 46,000 Mr fragment still interacts weakly with calmodulin. Thus, calcineurin, like other calmodulin-regulated enzymes, consists of a catalytic domain resistant to proteolysis and a calmodulin-binding regulatory domain susceptible to protease action in the absence of calmodulin but not in its presence. In the absence of calmodulin, the regulatory domain exerts an inhibitory effect on the catalytic domain; the inhibition is relieved upon calmodulin binding to or tryptic degradation of the regulatory domain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Purification and characterization of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7501–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelstein R. S., Pato M. D., Sellers J. R., de Lanerolle P., Conti M. A. Regulation of actin-myosin interaction by reversible phosphorylation of myosin and myosin kinase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):921–928. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autric F., Ferraz C., Kilhoffer M. C., Cavadore J. C., Demaille J. G. Large-scale purification and characterization of calmodulin from ram testis: its metal-ion-dependent conformers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 1;631(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin R. K., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Function of a calmodulin in postsynaptic densities. III. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the postsynaptic density. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):449–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Sadorf I., Bader H. A model for the regulation of the calmodulin-dependent enzymes erythrocyte Ca2+-transport ATPase and brain phosphodiesterase by activators and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj2070541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R., Knof S. Molecular weight and quaternary structure of lactic dehydrogenase. 3. Comparative determination by sedimentation analysis, light scattering and osmosis. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr 3;4(2):157–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEE W. A., RICHARDS F. M. The reaction of O-methylisourea with bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):489–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Krinks M. H. Calcineurin: a calcium- and calmodulin-binding protein of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6270–6273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H., Manalan A. S., Cohen P., Stewart A. A. Isolation and characterization of bovine brain calcineurin: a calmodulin-stimulated protein phosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:227–244. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. ACTIVATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE BY CA. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1033–1039. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Carafoli E. Acidic phospholipids, unsaturated fatty acids, and limited proteolysis mimic the effect of calmodulin on the purified erythrocyte Ca2+ - ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8588–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Desai R., Waisman D. M., Wang J. H. Purification and subunit structure of bovine brain modulator binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4276–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 5. Purification and properties of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase (2B) from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Manalan A., Klee C. B., Cohen P. Discovery of a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: probable identity with calcineurin (CaM-BP80). FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker M. M., Robinson J. B., Jr, Stellwagen E. The effect of proteolysis on the calmodulin activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9051–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. High levels of a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in bovine neostriatum. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1831–1837. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Dabrowska R., Hinkins S., Hartshorne D. J. Calcium-independent myosin light chain kinase of smooth muscle. Preparation by limited chymotryptic digestion of the calcium ion dependent enzyme, purification, and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1919–1925. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Hofmann F. Purification of myosin light chain kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5852–5855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




