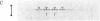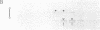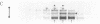Abstract
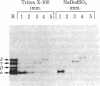
We have examined the sedimentation behavior, on sucrose density gradients, of acetylcholine receptor (AcChoR) subunits synthesized in vitro and integrated into heterologous rough microsomal membranes. In media containing nondenaturing detergents such as Triton X-100 or deoxycholate, the subunits appear to self-associate although, as previously reported, no heterologous interactions were detected. The sedimentation profiles assume a broad distribution in the region of 7-13 S. However, the peak fractions occupy the same region of the gradient as does native AcChoR, run in parallel. Such large homo-oligomers were not observed for another membrane protein, opsin, studied in the same way. This indicated that the associations are indeed between the AcChoR subunits and not simply between all newly synthesized membrane proteins. The homologous associations are interpreted to suggest a mechanism for maintaining the ionophore surfaces of the subunits in an energetically preferred, but metastable, configuration during the lengthy period of post-translational assembly.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. In vitro synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane insertion of the four subunits of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition protein is required for the integration of acetylcholine receptor delta subunit, a transmembrane glycoprotein, into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):501–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. The size and detergent binding of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5459–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Devreotes P. N. Newly synthesized acetylcholine receptors are located in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):237–244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. O., Jr, Richards F. M. A voltage-gated ion channel model inferred from the crystal structure of alamethicin at 1.5-A resolution. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):325–330. doi: 10.1038/300325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman B. M., Blobel G. In vitro biosynthesis, core glycosylation, and membrane integration of opsin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):236–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Garoff H., Simons K. Solubilization of the Semliki Forest virus membrane with sodium deoxycholate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Gilula N. B. Isolation and characterization of gap junctions from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2138–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M., Klymkowsky M. W., Lalancette R. A., Fairclough R. H. Structure and function of an acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):371–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84685-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Heuser J. E., Stroud R. M. Protease effects on the structure of acetylcholine receptor membranes from Torpedo californica. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):823–838. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor subunits transit a precursor pool before acquiring alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3605–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Krodel E. K., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):690–694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Karlin A. Affinity-labeling of purified acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):997–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Oswald R., Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Dissection of the 66 000-dalton subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2492–2497. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise D. S., Karlin A., Schoenborn B. P. An analysis by low-angle neutron scattering of the structure of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica in detergent solution. Biophys J. 1979 Dec;28(3):473–496. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85194-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise D. S., Wall J., Karlin A. Relative locations of the beta and delta chains of the acetylcholine receptor determined by electron microscopy of isolated receptor trimer. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12624–12627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]