Abstract
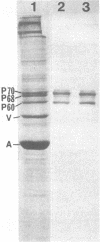
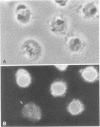
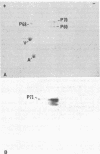
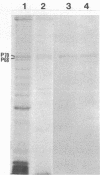
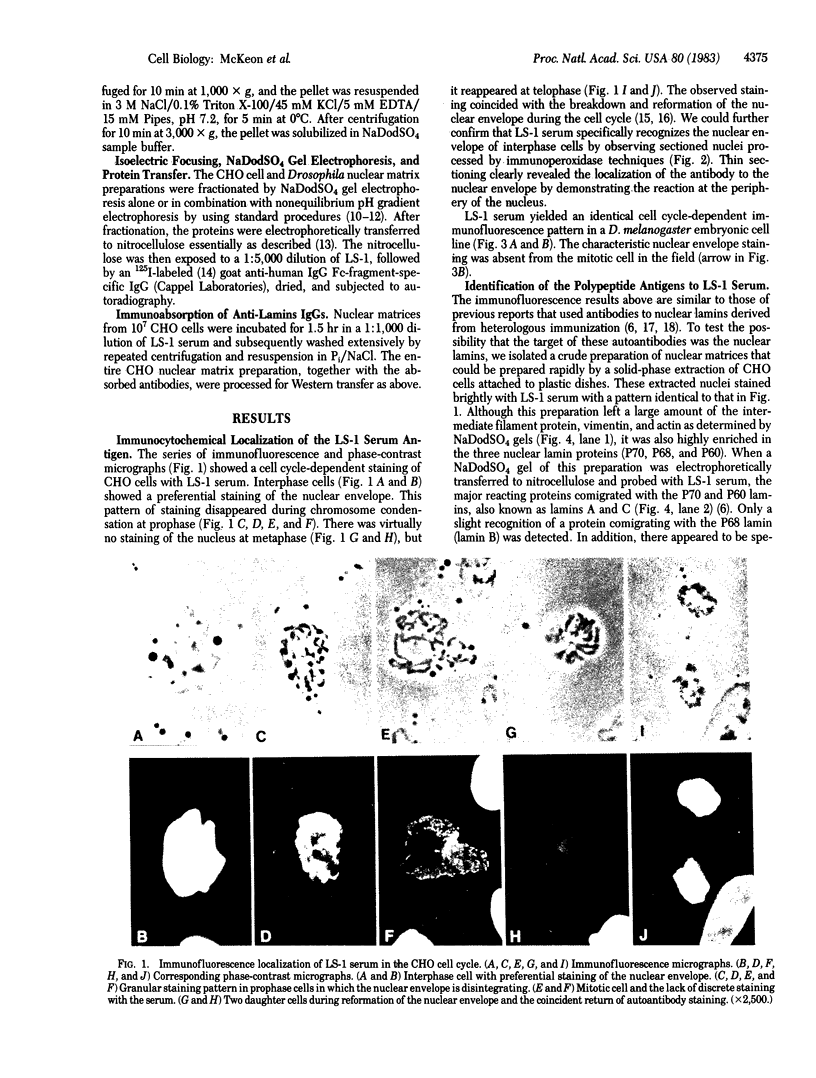
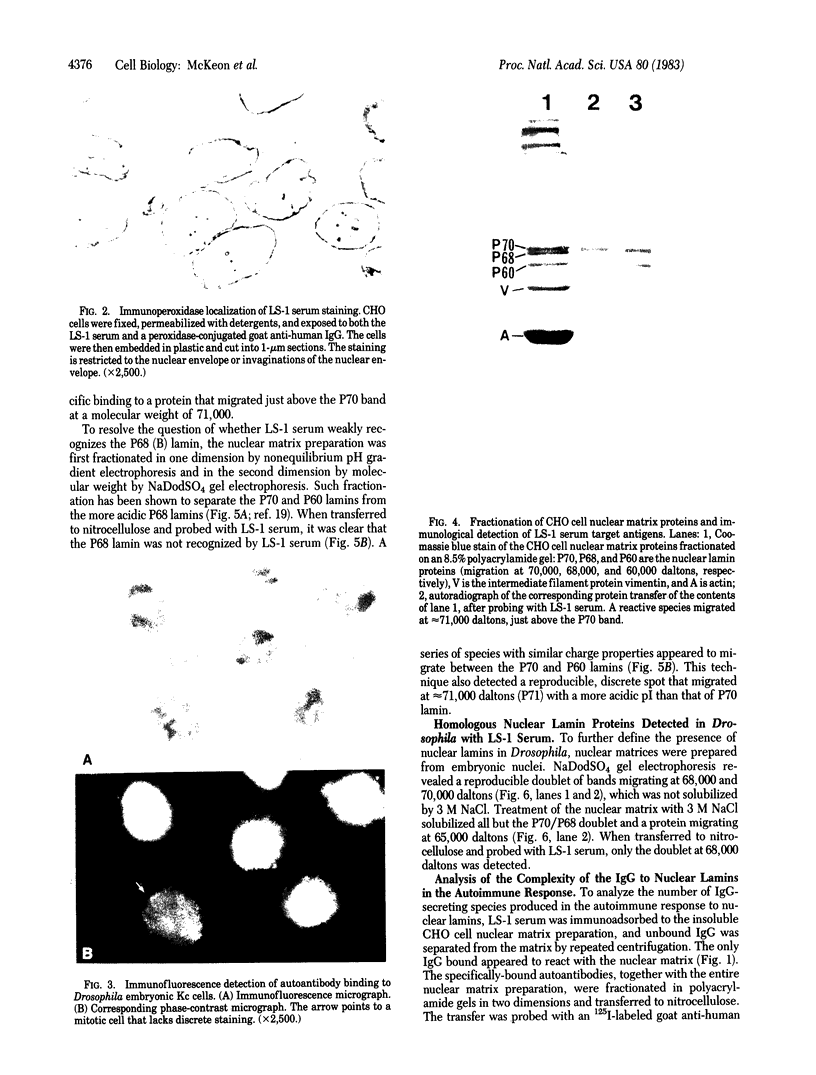
We have studied the autoantibodies in the serum of a patient with linear scleroderma that specifically recognize the nuclear envelope of cultured cells. These antibodies bind to conserved determinants of nuclear lamins, the predominant mammalian nuclear envelope proteins. Of the three mammalian nuclear lamin proteins (970, P68, and P60), only P70 and P60 bind the autoantibodies. In addition, two proteins of the Drosophila embryonic nuclear matrix, P70 and P68, bind these autoantibodies. We have used nuclear matrices to isolate the autoantibodies from the patient's serum that react to the nuclear lamins. At least three different IgG heavy chains were found to be involved in this autoimmune response to nuclear lamins, indicating that this response is not due to the expansion of a single B-cell clone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson R. P., Blobel G. Isolation of nuclear pore complexes in association with a lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1007–1011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. M., Steigerwald J. C., Tan E. M. Association of antinuclear and antinucleolar antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):43–51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely S., D'Arcy A., Jost E. Interaction of antibodies against nuclear envelope-associated proteins from rat liver nuclei with rodent and human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W. Structure, biochemistry, and functions of the nuclear envelope. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;Suppl 4:71–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. Nuclear lamina and the structural organization of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):967–978. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Dabauvalle M. C., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific differences in protein composition of nuclear pore complex-lamina structures in oocytes and erythrocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W., Ely S., D'Arcy A., Jost E. Localization of a nuclear envelope-associated protein by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies against a major polypeptide from rat liver fractions enriched in nuclear envelope-associated material. Cytobiologie. 1978 Oct;18(1):22–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Kasper C. B. Electrophoretic analysis of three major nuclear envelope polypeptides. Topological relationship and sequence homology. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11713–11720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Harlow E. Association of a murine 53,000-dalton phosphoprotein with simian virus 40 large-T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):213–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.213-224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Sep;16(9):557–560. doi: 10.1177/16.9.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton K. R., Cochran D. L. In vitro oxidation of intrinsic sulfhydryl groups yields polymers of the two predominant polypeptides in the nuclear envelope fraction. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1212–1216. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton K. R., Higgins L. L., Cochran D. L., Ruffolo J. J., Jr, Egle P. M. Nuclear lamins of erythrocyte and liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10978–10983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stick R., Krohne G. Immunological localization of the major architectural protein associated with the nuclear envelope of the Xenopus laevis oocyte. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Apr;138(2):319–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Reactions of systemic lupus erythematosus sera with histone fractions and histone-DNA complexes. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(4):485–492. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuffanelli D. L., Marmelzat W. L., Dorsey C. S. Linear scleroderma with hemiatrophy: report of three cases associated with collagen-vascular disease. Dermatologica. 1966;132(1):51–58. doi: 10.1159/000254396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. A., Witte O. N. Long-term culture of B lymphocytes and their precursors from murine bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]