Abstract
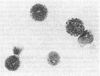
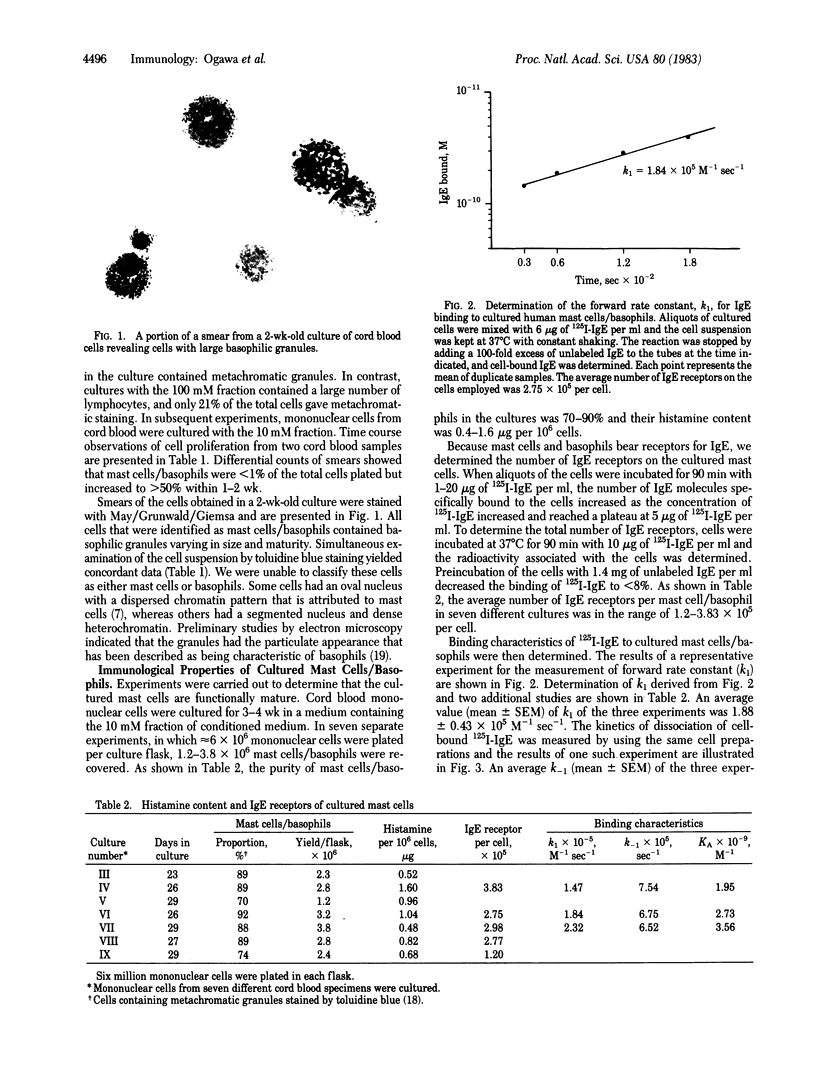
Selective growth of human mast cells/basophils was obtained in suspension cultures of mononuclear cells from umbilical cord blood. A fraction of culture supernatant of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated T cells, which lacked interleukin 2, was required for the selective growth of mast cells. When the mononuclear cells were cultured for 2-4 wk in the presence of the fraction, 50-90% of the total cells in the cultures contained metachromatic granules. Under the optimal culture conditions, the number of mast cells/basophils recovered from the cultures was 30-60% of the number of mononuclear cells plated. Cultured mast cells/basophils bear 1.2-3.83 X 10(5) IgE receptors per cell and contained 0.48-1.6 micrograms of histamine per 10(6) cells. The average forward rate constant, k1, and dissociation constant, k-1, for the binding of human IgE to IgE receptors on the cells were 1.9 X 10(5) M-1 sec-1 and 6.9 X 10(-5) sec-1, respectively (average equilibrium constant = 2.75 X 10(9) M-1). Specific binding of human IgE with high affinity indicates that the cells recovered in the suspension culture are human mast cells/basophils. Cultured cells sensitized with human IgE released a substantial amount of histamine upon exposure to anti-IgE. The results indicate that human mast cells/basophils obtained in the culture are functionally mature.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D. The nature and action of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):947–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H., Wingard J. R., Ishizaka T. The interaction of human and rodent IgE with the human basophil IgE receptor. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):327–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. In vitro generation of tumor-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes. Secondary allogeneic mixed tumor lymphocyte culture of normal murine spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):468–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Molina A., Spiegelberg H. L. A subpopulation of normal human peripheral B lymphcytes that bind IgE. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):616–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI108679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Lee E. H. Biologic function of the Fc fragments of E myeloma protein. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Conrad D. H., Schulman E. S., Sterk A. R., Ishizaka K. Biochemical analysis of initial triggering events of IgE-mediated histamine release from human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., De Bernardo R., Tomioka H., Lichtenstein L. M., Ishizaka K. Identification of basophil granulocytes as a site of allergic histamine release. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1000–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Soto C. S., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. 3. Number of IgE molecules and their receptor sites on human basophil granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):500–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Huff T. F., Uede T., Munoz J. J., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factor. II. Physicochemical properties and cell sources of glycosylation-enhancing factor. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1802–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Isersky C., Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. I. Evidence for specific binding of IgE. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):600–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. II. Quantitative aspects of the binding reaction. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1676–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M. The purification of human basophils. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2519–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malveaux F. J., Conroy M. C., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M. IgE receptors on human basophils. Relationship to serum IgE concentration. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):176–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI109103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Plummer J. M., Spiegelberg H. L. Comparison of the Fc receptors for IgE on human lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao K., Yokoro K., Aaronson S. A. Continuous lines of basophil/mast cells derived from normal mouse bone marrow. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):333–335. doi: 10.1126/science.7209531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Spicer S. S., Cantey J. R., Ogawa M. Clonal assay of mouse mast cell colonies in methylcellulose culture. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):352–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Cordon-Cardo C., Good R. A. Growth of a pure population of mouse mast cells in vitro with conditioned medium derived from concanavalin A-stimulated splenocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2559–2561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Stevens R. L., Lewis R. A., Liu F. T., Corey E., Austen K. F. IgE-mediated release of leukotriene C4, chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan, beta-hexosaminidase, and histamine from cultured bone marrow-derived mouse mast cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):189–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Rifkind A. B., Cordon-Cardo C., Good R. A. Selective growth of a population of human basophil cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5793–5796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Stevens R. L., Akiyama F., Schmid K., Austen K. F. Culture from mouse bone marrow of a subclass of mast cells possessing a distinct chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with glycosaminoglycans rich in N-acetylgalactosamine-4,6-disulfate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7229–7236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Clark-Lewis I. A T cell-derived factor stimulating multipotential hemopoietic stem cells: molecular weight and distinction from T cell growth factor and T cell-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):30–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W. In in vitro production and cloning of the P cell, a bone marrow-derived null cell that expresses H-2 and Ia-antigens, has mast cell-like granules, and is regulated by a factor released by activated T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Peters S. P., Schleimer R. P., Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Human lung mast cells: purification and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterk A. R., Ishizaka T. Binding properties of IgE receptors on normal mouse mast cells. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):838–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tertian G., Yung Y. P., Guy-Grand D., Moore M. A. Long-term in vitro culture of murine mast cells. I. Description of a growth factor-dependent culture technique. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):788–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung Y. P., Eger R., Tertian G., Moore M. A. Long-term in vitro culture of murine mast cells. II. Purification of a mast cell growth factor and its dissociation from TCGF. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung Y. P., Moore M. A. Long-term in vitro culture of murine mast cells. III. Discrimination of mast cells growth factor and granulocyte-CSF. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1256–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Ultrastructural evidence for the common origin of human mast cells and basophils. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]