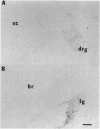
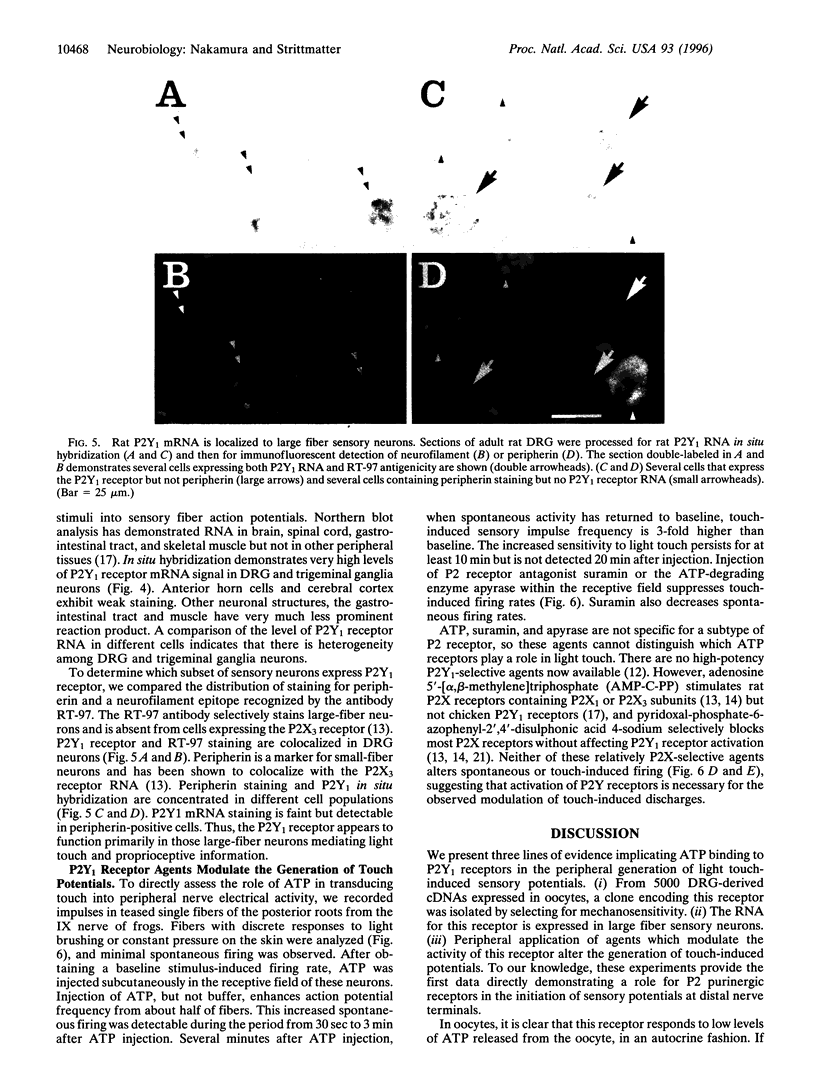
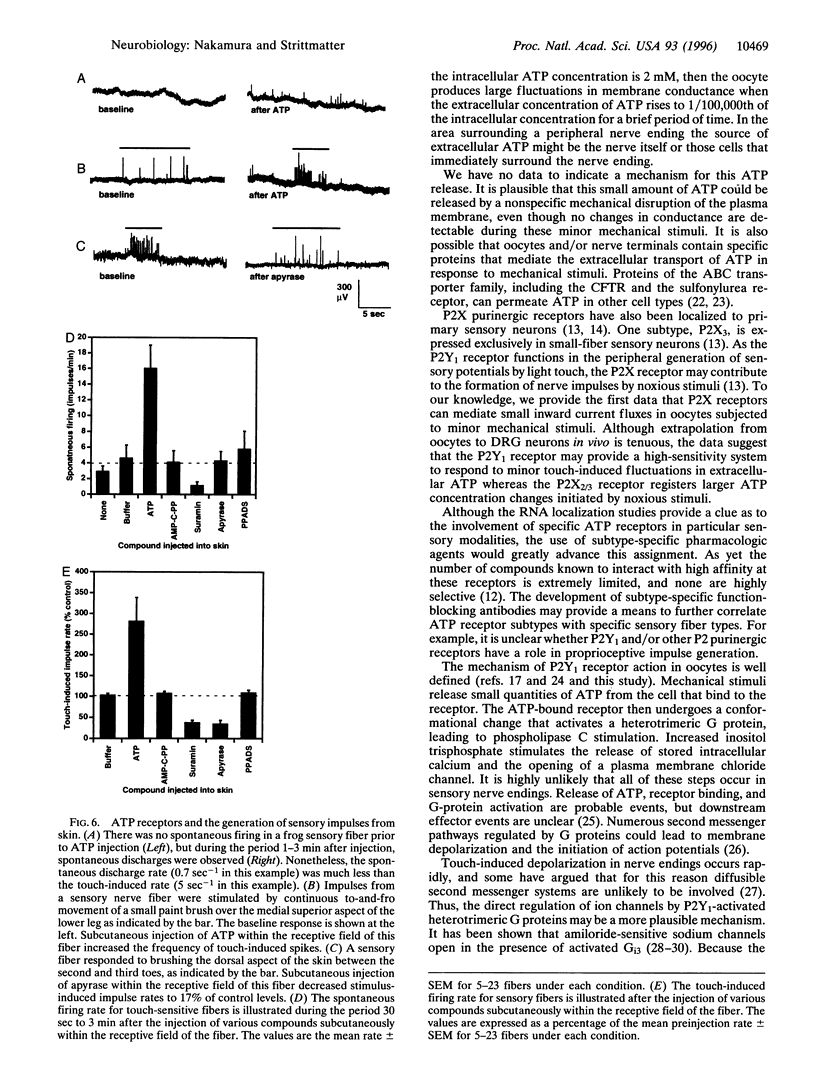
Abstract
Somatic sensation requires the conversion of physical stimuli into the depolarization of distal nerve endings. A single cRNA derived from sensory neurons renders Xenopus laevis oocytes mechanosensitive and is found to encode a P2Y1 purinergic receptor. P2Y1 mRNA is concentrated in large-fiber dorsal root ganglion neurons. In contrast, P2X3 mRNA is localized to small-fiber sensory neurons and produces less mechanosensitivity in oocytes. The frequency of touch-induced action potentials from frog sensory nerve fibers is increased by the presence of P2 receptor agonists at the peripheral nerve ending and is decreased by the presence of P2 antagonists. P2X-selective agents do not have these effects. The release of ATP into the extracellular space and the activation of peripheral P2Y1 receptors appear to participate in the generation of sensory action potentials by light touch.
Full text
PDF
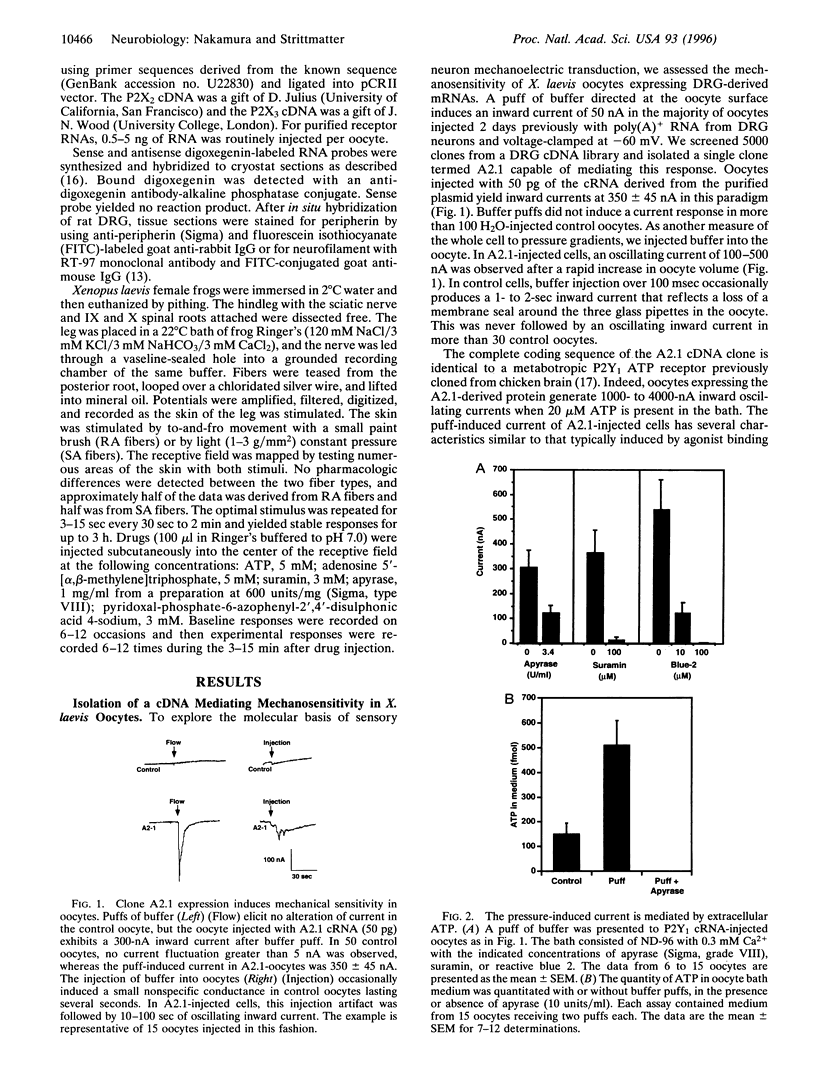
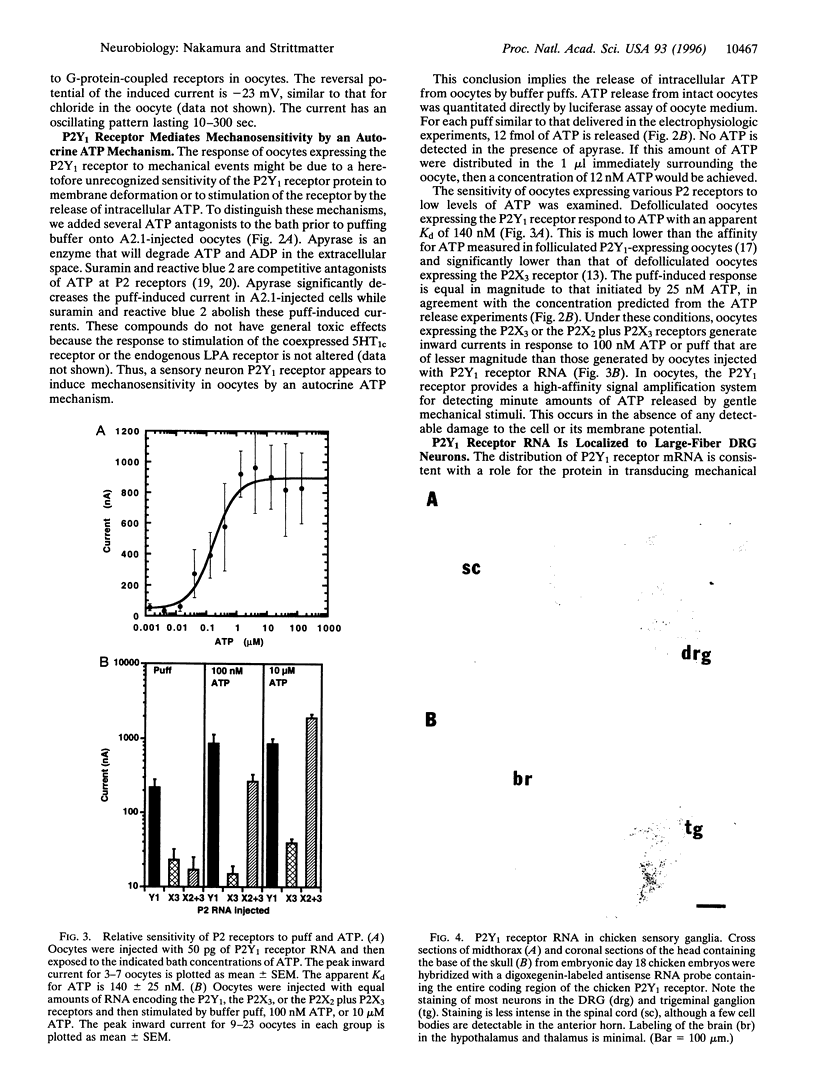

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman M. J., Wickman K. D., Clapham D. E. Hypotonicity activates a native chloride current in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):153–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Stow J. L., Cantiello H. F., de Almeida J. B., Benos D. J. Purified epithelial Na+ channel complex contains the pertussis toxin-sensitive G alpha i-3 protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4759–4765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: concentration dependence and kinetics. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Patenaude C. R., Ausiello D. A. G protein subunit, alpha i-3, activates a pertussis toxin-sensitive Na+ channel from the epithelial cell line, A6. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20867–20870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Akopian A. N., Sivilotti L., Colquhoun D., Burnstock G., Wood J. N. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):428–431. doi: 10.1038/377428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake M. E., Petersen S. A. ATP overflow from the mouse isolated vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):825–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen B., Reimann W., Selve N., Friderichs E., Bültmann R. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecally administered P2-purinoceptor antagonists in rats. Brain Res. 1994 Dec 15;666(2):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90770-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., Williams M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):143–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshima Y., Nakamura F., Strittmatter P., Strittmatter S. M. Collapsin-induced growth cone collapse mediated by an intracellular protein related to UNC-33. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):509–514. doi: 10.1038/376509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründer S., Thiemann A., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):759–762. doi: 10.1038/360759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. G protein-coupled mechanisms and nervous signaling. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90158-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Chalfie M. Gene interactions affecting mechanosensory transduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):467–470. doi: 10.1038/367467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Gu G., Ferguson E. L., Chalfie M. A stomatin-like protein necessary for mechanosensation in C. elegans. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):292–295. doi: 10.1038/378292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Jessell T. M. ATP excites a subpopulation of rat dorsal horn neurones. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):730–733. doi: 10.1038/304730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernan M., Cowan D., Zuker C. Genetic dissection of mechanosensory transduction: mechanoreception-defective mutations of Drosophila. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1195–1206. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G. B., Ackerman M. J., Gordon E. A., Krapivinsky L. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular characterization of a swelling-induced chloride conductance regulatory protein, pICln. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C., Neidhart S., Holy C., North R. A., Buell G., Surprenant A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):432–435. doi: 10.1038/377432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Wurgler-Murphy S. M., Saito H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):242–245. doi: 10.1038/369242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat A. G., Ausiello D. A., Cantiello H. F. Vasopressin and protein kinase A activate G protein-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C218–C223. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert E. M., Egan M. E., Hwang T. H., Fulmer S. B., Allen S. S., Cutting G. R., Guggino W. B. CFTR regulates outwardly rectifying chloride channels through an autocrine mechanism involving ATP. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Excitation of rat locus coeruleus neurons by adenosine 5'-triphosphate: ionic mechanism and receptor characterization. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):894–899. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-00894.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Cannon S. C., Ross E. M., Higashijima T., Fishman M. C. GAP-43 augments G protein-coupled receptor transduction in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5327–5331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukharev S. I., Blount P., Martinac B., Blattner F. R., Kung C. A large-conductance mechanosensitive channel in E. coli encoded by mscL alone. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):265–268. doi: 10.1038/368265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde M. A., Díaz M., Sepúlveda F. V., Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F. Volume-regulated chloride channels associated with the human multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):830–833. doi: 10.1038/355830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Simon J., Krishek B. J., Bateson A. N., Smart T. G., King B. F., Burnstock G., Barnard E. A. Cloning and functional expression of a brain G-protein-coupled ATP receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81397-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziganshin A. U., Hoyle C. H., Bo X., Lambrecht G., Mutschler E., Bäumert H. G., Burnstock G. PPADS selectively antagonizes P2X-purinoceptor-mediated responses in the rabbit urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1491–1495. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Awqati Q. Regulation of ion channels by ABC transporters that secrete ATP. Science. 1995 Aug 11;269(5225):805–806. doi: 10.1126/science.7543697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]