Abstract
Background
Abundant, indirect epidemiological evidence indicates that influenza contributes to all-cause mortality and cardiovascular hospitalisations with studies showing increases in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and death during the influenza season.
Objective
To investigate whether influenza is a significant and unrecognised underlying precipitant of AMI.
Design
Case-control study.
Setting
Tertiary referral hospital in Sydney, Australia, during 2008 to 2010.
Patients
Cases were inpatients with AMI and controls were outpatients without AMI at a hospital in Sydney, Australia.
Main outcome measures
Primary outcome was laboratory evidence of influenza. Secondary outcome was baseline self-reported acute respiratory tract infection.
Results
Of 559 participants, 34/275 (12.4%) cases and 19/284 (6.7%) controls had influenza (OR 1.97, 95% CI 1.09 to 3.54); half were vaccinated. None were recognised as having influenza during their clinical encounter. After adjustment, influenza infection was no longer a significant predictor of recent AMI. However, influenza vaccination was significantly protective (OR 0.55, 95% CI 0.35 to 0.85), with a vaccine effectiveness of 45% (95% CI 15% to 65%).
Conclusions
Recent influenza infection was an unrecognised comorbidity in almost 10% of hospital patients. Influenza did not predict AMI, but vaccination was significantly protective but underused. The potential population health impact of influenza vaccination, particularly in the age group 50–64 years, who are at risk for AMI but not targeted for vaccination, should be further explored. Our data should inform vaccination policy and cardiologists should be aware of missed opportunities to vaccinate individuals with ischaemic heart disease against influenza.
Keywords: Coronary Artery Disease, Infection
Background
Influenza is a cause of significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in the elderly, during the annual winter epidemics.1 Laboratory-confirmed influenza, which represents the ‘tip of the iceberg’ of seasonal influenza-like illness (ILI), causes more morbidity and mortality than any other infectious disease in Australia, with the highest hospitalisation rates for influenza at the extremes of age.2 In addition to ILI, influenza virus infection can cause a primary viral pneumonia and be complicated by secondary bacterial pneumonia, with severe disease and mortality higher in persons with underlying chronic diseases.3
There is abundant but indirect epidemiological evidence that influenza contributes to all-cause mortality4 5 and to cardiovascular and respiratory hospitalisations.6 Studies show an increase in rates of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and death during the annual influenza season.6 7 Acute infections in general have been shown to be associated with an increased risk of AMI in observational epidemiological studies.8 9 One study found the risk of myocardial infarction or stroke was more than four times higher after a respiratory tract infection, with the highest risk in the first 3 days.8
Despite the compelling observational epidemiological data, the role of infection in ischaemic events is rarely included in the burden of influenza disease estimates and in economic evaluations of influenza vaccination, nor weighed heavily in policy decisions. This is because direct, confirmatory evidence of the role of viruses and respiratory infections in the precipitation of ischaemic events is lacking. This study aimed to examine whether influenza is an unrecognised significant underlying precipitant of acute ischaemic cardiac events.
Methods
Study design
We conducted a case-control study during consecutive southern hemisphere winter seasons (2008–2010) at a tertiary referral hospital in Sydney, Australia. This hospital is also a district hospital for the surrounding community, serving a population of 1 114 020 people (2006).10 The influenza winter season was defined as commencing when ≥3 influenza cases were diagnosed within 1 week, as notified by participating laboratory staff (WHO National Influenza Centre). A sample size of 88 in each arm (ratio 1:1) was calculated to detect a difference in positive influenza test results of 20% versus 5% with a 95% CI and 80% power. Incidence estimates were based on Australian-specific excess influenza morbidity modelling.5 We aimed to recruit 300 cases and 300 controls over 3 years to allow for smaller differences in overall and seasonal rates. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the Sydney West Area Health Service (Westmead), New South Wales, Australia – HREC2007/2/4.8 (2533).
Study participants
Cases
Cases were patients aged ≥40 years of age admitted with an AMI, evolving or recent myocardial infarction to the cardiology unit during the influenza season. Eligible respondents were those able to provide samples within 72 h of the AMI event, resided in Sydney, available for follow-up and provided informed consent. Cases reporting a previous cardiovascular event were eligible. A diagnosis of AMI was defined as a typical rise and gradual fall in troponin or more rapid rise and fall in creatine kinase MB (CK-MB) biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis, with one or more of the following: ischaemic symptoms (chest or arm pain, nausea/vomiting, sweating, or shortness of breath); development of pathological Q waves on ECG; ECG changes indicative of ischaemia (ST segment elevation or depression); coronary artery intervention; or pathological findings of an AMI. Cases were recruited into the study period between 27th June and 20th October 2008, 18th May and 23rd October 2009 and 21st June and 28th October 2010.
Controls
Controls were persons aged ≥40 years of age attending the orthopaedic or ophthalmic outpatient clinics during the same time period. Respondents, residing in Sydney, available for follow-up and able to provide informed consent, were eligible. Controls were unmatched, except for the same age cut-off and recruitment period, to ensure similar level of exposure to circulating influenza. Controls were excluded if they reported a history of AMI, transient ischaemic attack or stroke in the previous 12 months. Stable angina was permissible if there had been no worsening of angina or AMI episodes or hospital admissions in the last year. Controls were recruited into the study period between 30th June and 31st October 2008, 19th May and 26th October 2009 and 23rd June and 29th October 2010.
Data collection and validation
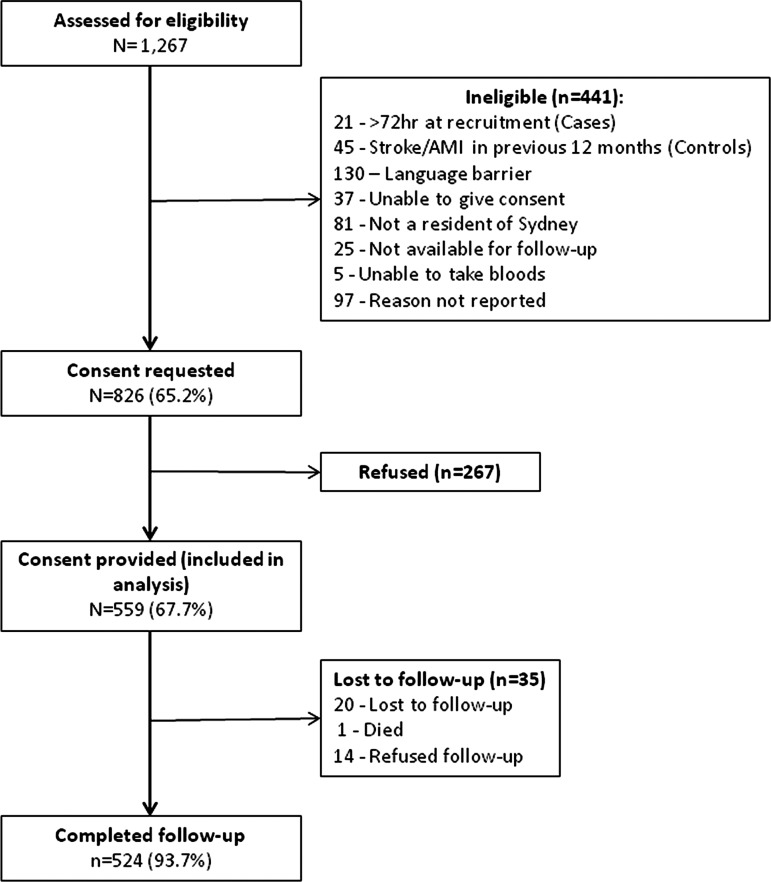
All eligible participants were identified daily and approached for consent (figure 1). Recruited subjects provided nasal and pharyngeal viral swabs at baseline and blood samples at baseline and 4–6 weeks postrecruitment and all were included in the final analysis, regardless of the collection of follow-up sera. A baseline structured interviewer-administered questionnaire collected detailed medical and vaccination history, socio-demographic data and current comorbidities. Self-reported respiratory symptoms were collected at baseline in 2009 and 2010 only. Influenza vaccination status was validated for current and previous influenza seasons from hospital and general practitioner (GP) records, with GPs contacted via facsimile or telephone. If discrepancies arose between GP and self-report, GP-reported vaccination status was considered correct. Self-reported vaccination status was considered sufficient in those individuals whose GP could not be contacted. Self-reported quality of life attributes of mobility, self-care, performing usual activities, pain and anxiety were collected using a three point scale: no problems, some problems or considerable problems.
Figure 1.
Consort diagram of recruitment and follow-up.
Sample collection and laboratory testing for influenza
Trained staff collected blood samples at baseline and at 4–6 weeks. Influenza A- and B-specific antibody titres were determined on paired sera tested in parallel using a complement fixation assay. Trained staff collected nasopharyngeal swabs at recruitment. Rayon-tipped, plastic-shafted swabs were inserted separately into each nostril and the pharynx, and placed in single vial viral transport media. Swabs were transported immediately to the laboratory, or stored at 4°C if transport was delayed and combined in the laboratory. Nucleic acid testing (NAT) using inhouse PCRs assay tested for influenza.11 Other respiratory pathogens tested included parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, picornavirus (enterovirus, rhinovirus), adenovirus, coronaviruses 229E and OC43 and human metapneumovirus using a published method.12
Exposure measures
The primary explanatory variable was laboratory evidence of undiagnosed influenza, defined as a positive NAT or serological evidence of influenza A or B (defined as either a fourfold rise in titre between baseline and follow-up in any individual, or a single titre of ≥64 at baseline in an unvaccinated individual). Subjects with a positive baseline serology for influenza who had received influenza vaccine (GP verified) in the study year were not defined as having influenza as a single high serological titre cannot reliably differentiate between infection and vaccination. The additional exposure measure of a baseline acute respiratory tract infection (ARTI) (2009 and 2010 only) included self-reported ARTI in the past week.
Data analysis
The Pearson χ2 was used to test the association between a recent AMI and underlying influenza infection, with p≤0.05 considered statistically significant. The association between AMI and other risk factors including age, sex, smoking status, alcohol consumption and self-reported presence of hypertension, high cholesterol and diabetes were explored. The protective effect of influenza vaccination against both influenza and AMI was also investigated.
Unconditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate the association between AMI and influenza infection and to adjust for potential confounders. All plausible variables were included and a forced entry method initially considered all variables in the model. A model of best fit was determined using a manual iterative process of variable removal. Variables remaining in the model were assessed for significance and those variables resulting in significant model changes were explored for interaction effects. The final model reports the proportion of variation explained by the model using the Nagelkerke R squared statistic. IBM SPSS Statistics V.20 was used for all analyses.
Vaccine effectiveness (VE) is the risk reduction attributed to vaccination estimated from observational studies from measurements of the incidence of disease in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals.13 In a case-control study, the VE for the prevention of AMI is estimated from the Odds Ratio (OR) using the formula: (1- OR)×100.14 We used the adjusted OR of the association between influenza vaccination and AMI, obtained from the final logistic regression model. We also estimated the VE for the prevention of influenza. As recruitment into our case-control study was not based on the outcome of influenza infection, we are able to calculate the attack rate of influenza infection in our vaccinated and unvaccinated participants. VE was calculated for influenza using the formula: ((ARU−ARV)÷ARU)×100, where ARU is the attack rate in unvaccinated and ARV is attack rate in vaccinated participants. To calculate this VE, a stricter definition of influenza infection defined as either a positive NAT or serological evidence of influenza A or B defined as a fourfold rise in antibody titre between baseline and follow-up was used.
Results
A total of 559 participants were recruited across the three study years, 275 (49.2%) cases and 284 (50.8%) controls (table 1). The response rates and patient follow-up are shown in figure 1; 67% of eligible cases and controls participated in the study, with 524 (93.7%) completing follow-up.
Table 1.
Baseline demographic characteristics of cases and controls
| Characteristic | Cases (n=275) | Controls (n=284) | p Value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recruitment year | |||
| 2008 | 98 (35.6%) | 103 (36.3%) | 0.9 |
| 2009 | 103 (37.5%) | 107 (37.8%) | |
| 2010 | 74 (26.9%) | 74 (26.1%) | |
| Sex (male) | 216 (78.5%) | 130 (45.8%) | <0.001 |
| Age group | |||
| 40–64 years | 176 (64.0%) | 72 (25.4%) | <0.001 |
| ≥65 years | 99 (36.0%) | 212 (74.6%) | |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Caucasian | 210 (76.4%) | 227 (80.5%) | 0.3 |
| Asian | 42 (15.3%) | 32 (11.3%) | |
| Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander | 5 (1.8%) | 2 (0.7%) | |
| Other | 18 (6.5%) | 21 (7.4%) | |
| Marital status | |||
| Married/de facto | 188 (72.6%) | 153 (57.5%) | <0.001 |
| Widowed/separated/divorced | 49 (18.9%) | 101 (38.1%) | |
| Never married | 22 (8.5%) | 11 (4.2%) | |
| Language other than English spoken at home | 51 (18.5%) | 37 (13.1%) | 0.08 |
| Household living arrangements (lives alone) | 55 (20.1%) | 92 (32.6%) | 0.001 |
| Smoker† | |||
| Current | 76 (27.9%) | 31 (11.2%) | <0.001 |
| Former | 103 (37.9%) | 102 (36.8%) | |
| Never | 93 (34.2%) | 144 (52.0%) | |
| Alcohol consumption‡ | |||
| Never | 104 (38.4%) | 142 (51.8%) | 0.005 |
| Sometimes | 134 (49.4%) | 110 (40.1%) | |
| Daily | 33 (12.2%) | 22 (8.0%) | |
| Any problems with¶ | |||
| Mobility | 77 (28.1%) | 101 (36.1%) | 0.05 |
| Self-care | 15 (5.5%) | 14 (5.0%) | 0.8 |
| Performing usual activities | 32 (11.7%) | 41 (14.7%) | 0.3 |
| Pain | 82 (30.1%) | 112 (40.0%) | 0.02 |
| Anxiety | 105 (38.6%) | 64 (23.1%) | <0.001 |
| Self-reported chronic diseases | |||
| None | 15 (5.5%) | 34 (12.0%) | 0.02 |
| 1 | 55 (20.0%) | 53 (18.7%) | |
| ≥2 | 205 (74.5%) | 197 (69.4%) | |
| Self-reported | |||
| COPD§ | 41 (14.9%) | 42 (14.8%) | 0.97 |
| Diabetes | 68 (24.7%) | 70 (24.6%) | 0.98 |
| Hypertension | 148 (53.8%) | 156 (54.9%) | 0.79 |
| High cholesterol | 150 (54.5%) | 128 (45.1%) | 0.03 |
*Pearson's χ2 test.
†Excludes 10 participants who refused.
‡Excludes 14 participants who refused.
§Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: defined as self-reported asthma or chronic bronchial disease.
¶Includes those reporting some problems and considerable problems.
Demographic characteristics
Cases and controls differed in a number of demographic and health-related characteristics (table 1). Overall, 285/559 (51.0%) participants reported receiving an influenza vaccine in the year of recruitment. GP verification was obtained for 428/559 (76.6%) participants with 276 (49.4%) considered vaccinated, including 223/311 (71.7%) aged ≥65 years and 53/248 (21.4%) aged 40–64 years. Significantly more controls (184/284, 64.8%) than cases (92/275, 33.5%) were vaccinated in the year of recruitment (OR 3.7 95% CI 2.6 to 5.2, p<0.001), with differences evident for all recruitment years.
Influenza infection and ARTI
Evidence of influenza infection was identified in 53 (9.5%) subjects. Table 2 shows the number of participants with positive results, by study arm, year and type of evidence. Of cases, 34/275 (12.4%) were influenza positive compared with 19/284 (6.7%) controls, with cases significantly more likely to have recent influenza (OR 1.97, 95% CI 1.09 to 3.54, p=0.022). VE against influenza was 83.6% (95% CI 27.6% to 96.3%), using the stricter definition of a positive influenza result. Of participants, 84/339 (24.8%) reported a baseline ARTI, comprising 52 (31.1%) cases and 32 (18.6%) controls. ARTI reported at baseline (measured in 2009 and 2010) was significantly associated with AMI (OR 1.98 95% CI 1.2 to 3.3, p=0.008) on univariate analysis. ARTI was reported in 38 (22.2%) of vaccinated and 46 (27.4%, p=0.3) of unvaccinated participants, and was more likely in current smokers (28, 40.0%) than non-smokers (56, 21.5%, OR 2.42 95% CI 1.4 to 4.3, p=0.002). Other viral pathogens were identified in 32 (5.7%) participants, with no difference between cases (15, 5.5%) and controls (17, 6.0%) (p=0.8).
Table 2.
Evidence of influenza* infection in cases and controls, by type of evidence and study year
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Controls | Cases | Controls | Cases | Controls | Cases | Controls | |
| Baseline influenza A antibody titre ≥64 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 23 | 12 |
| Baseline influenza B antibody titre ≥64 | 1 | 1 | 2† | 1 | 1† | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| ≥Four fold rise influenza A | 0 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
| ≥Four fold rise influenza B | 4 | 2 | 1‡ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 |
| NAT positive influenza | 0 | 0 | 1‡ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Any positive result | 9 | 4 | 13 | 7 | 12 | 8 | 34 | 19 |
*Serological evidence of influenza is either a fourfold rise in titre between baseline and convalescent sera or a baseline titre of ≥64 in an unvaccinated individual. Vaccination status was validated by GP records.
†Also had a baseline antibody titre for influenza A ≥64 (only counted once) (1×2009 case and 1×2010 case).
‡Also had a >fourfold rise in influenza A antibody titre (counted once in total).
GP, general practitioner; NAT, nucleic acid testing.
Logistic regression and VE
In the multivariate analysis recent influenza was no longer a significant predictor of AMI (p=0.8); however, age, gender, smoking, high cholesterol and influenza vaccination were significantly associated with AMI (table 3). The overall model was statistically significant (χ2=148.7, df=6, p<0.001, Nagelkerke R square=0.316). Influenza vaccination was significantly protective, with a VE for the prevention of AMI of 45% (95% CI 15% to 65%). VE for the prevention of AMI in 40–64-year-olds was estimated as 45% (95% CI −15% to 73%) and 33% (95% CI −20% to 63%) for those aged ≥65 years.
Table 3.
Results of the multivariate logistic regression model for predictors of acute myocardial infarction
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evidence of recent influenza infection* | 1.07 | 0.53 to 2.19 | 0.849 |
| Age† | 0.96 | 0.94 to 0.97 | <0.001 |
| Sex (Male) | 3.83 | 2.54 to 5.78 | <0.001 |
| Self-reported high cholesterol | 2.00 | 1.35 to 2.97 | 0.001 |
| Current smoker | 2.11 | 1.25 to 3.56 | 0.005 |
| Influenza vaccine in study year‡ | 0.55 | 0.35 to 0.85 | 0.008 |
*Any evidence of influenza is either a fourfold rise in titre between baseline and convalescent sera or a baseline titre of ≥64 in an unvaccinated, GP-verified individual.
†Age as a continuous variable.
‡Vaccination status validated by GP records.
GP, general practitioner.
Discussion
We identified unrecognised recent influenza in almost 10% of participants, indicating that a clinical diagnosis of influenza may be missed in hospital patients with other presentations. A recent ARTI was more common in AMI cases, and increased the risk of AMI by twofold, highlighting the need for greater awareness of infection as an underlying or precipitating condition in hospital patients.
While influenza and ARTI significantly predicted AMI in unadjusted analysis, after adjustment for other factors, influenza and ARTI (data not shown) were no longer independent predictors of AMI. However, influenza vaccination in the study year was significantly protective against AMI, with unvaccinated subjects almost twice as likely as vaccinated subjects to have AMI. Our finding of vaccination being a protective factor is validated by the fact that other significant predictors of AMI in the model (age, gender, smoking, high cholesterol) are accepted risk factors for AMI. The estimated VE of influenza vaccine against AMI was 45% (95% CI 15% to 65%), suggesting potential population health benefits of vaccination in adults at risk of ischaemic heart disease. While other studies have looked at the association of influenza, influenza vaccination and AMI,15–20 none estimate influenza VE against AMI. A previous case-control study found influenza vaccination reduced the risk of recurrent AMI (OR 0.33, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.82).15 This equates to a VE of 67% (95% CI 18% to 87%) in the prevention of recurrent AMI, a finding which supports our own study.
While we showed a protective effect of influenza vaccination against AMI, we were unable to demonstrate a direct effect of influenza infection on AMI. This could reflect low statistical power, with laboratory-confirmed influenza being a much rarer event than vaccination, which showed significant association. Furthermore, the high vaccination rate in our participants likely reduced the risk of influenza and our ability to detect a difference between groups. However, other studies have shown an association among influenza, influenza vaccination and AMI. In a recent case-control study in China, serological evidence of influenza was found to significantly predict recent AMI.16 Other observational studies have found influenza vaccination to be protective against AMI, recurrent AMI and cardiac death.15 21 Three randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which patients with coronary artery disease or admitted with acute coronary syndrome were randomised to receive the influenza vaccine have shown reductions in recurrent events at 6 22 and 12 months,17 20 and cardiovascular death (HR 0.34, 0.17 to 0.71)20 and any coronary ischaemic event at 12 months19 compared with placebo.
Clinical and animal studies have identified an association among inflammation and atherosclerotic disease development, destabilisation of advanced disease and healing delay.23 It is postulated that infection precipitates inflammation by induction of a prothrombotic state or autoimmune reactions in already-diseased coronary vessels, causing critical obstruction. Given the animal, observational and RCT data suggesting the precipitation of ischaemic events by infection, the prevention of influenza by vaccination may have an important role in reducing ischaemic events. Influenza vaccination is efficacious in preventing severe influenza, reducing the incidence of pneumonia and death in the elderly24 and is also a cost-effective intervention25 recommended by national expert committees. Australia funds immunisation for adults aged ≥65 years and those with pre-existing risk conditions with both influenza and pneumococcal vaccines.26 Although estimated influenza vaccination levels are high (>70%) for the age group ≥65 years, uptake in younger at-risk groups is low.27 This was reflected in our study, with controls who were on average older and eligible to receive free influenza vaccination had higher rates of vaccination, whereas the AMI cases, despite being at risk were on average younger and therefore not eligible for free vaccination had much lower vaccination uptake.
Extension of vaccination programmes to include those aged 50–64 years has been suggested. However, cost-effectiveness studies of a targeted programme for this age group28 do not include the prevention of AMI. Cardiovascular disease is the second largest contributor to disease burden in Australia, accounting for 18% of the total disability-adjusted life years lost.29 As such, even a small effect of influenza vaccination in preventing AMI may have significant population health gains. The influenza VE in protecting against AMI (45%, 95% CI 15% to 65%) in our study and other similar studies indicates a substantial potential population health impact on ischaemic heart disease by vaccinating younger adults. Approximately 3.4 million Australians are affected by cardiovascular disease.30 Although two-thirds of the burden is in older adults, 19% of 45–54-year-olds and 5% of those aged under 45 years are affected.30 Influenza vaccination of people with an index AMI could also have a significant impact, with high rates of subsequent acute coronary events in patients with AMI. Death or re-infarction occurred in six of 100 patients within 1 month, and 27 within 1 year in unvaccinated AMI patients on standard treatment.20 Clinicians should consider vaccination of AMI patients before hospital discharge.
Ours is an observational study and is subject to the limitations of its non-randomised and its unmatched study design. The sample size, although adequate to detect a difference in influenza positive results, was small considering the number of vaccinated participants, but the study was intensive and difficult to conduct, and achieving final sample size required 3 years of recruitment. Australia has a funded influenza vaccination programme for people aged 65 years and older, with uptake rates >85%. Our controls were older than AMI cases, and therefore more likely to be vaccinated and more likely to be living alone, which could affect exposure status. Given the strong relationship between age and vaccination uptake, and the older age of controls, the study would have benefited from being individually age-matched. However, we adjusted for age in our model, and influenza vaccination remained significant. Further, controls were recruited from outpatient clinics and representative of community-acquired influenza. While there is the possibility that controls may have not attended due to severe influenza infection, the majority of participants found to have laboratory evidence of influenza did not report acute respiratory symptoms. The modelling adjusted for the factors which were unequally distributed between cases and controls. It is reassuring that known risk factors of age, current smoking and high cholesterol were found to be significant predictors of AMI in our model, the last being the two largest predictors of AMI in the INTERHEART study.31 Our study did not find a self-reported history of diabetes or hypertension or alcohol consumption to be predictors of AMI.31 While we did not control for all possible confounders, residual confounding is a concern for all case-control studies if confounding variables are not measured or adjusted for. For example, influenza vaccination was excluded from the INTERHEART study.31 We believe we have included all major confounders in our model. The low national influenza season in 2010 limited our statistical power and may explain why influenza infection did not significantly predict AMI. The number of vaccinated subjects was far greater than the number with documented influenza infection, therefore affording greater statistical power for examining the association of AMI with vaccination. Our study is strengthened by collection over a number of influenza seasons and the use of laboratory-confirmed influenza as a primary variable of interest, rather than self-reported ARTI, which is subject to biases. With a strict definition of AMI, it is unlikely that misclassification of AMI has occurred, which would unduly bias VE calculations. An overestimation of vaccination status would bias VE estimates; however, we have classified vaccination status based on GP verified reports, in which more than 75% of participants were able to be verified.
There has been little international policy debate surrounding the use of influenza vaccination in the prevention of ischaemic cardiac disease morbidity in people less than 65 years of age. The current recommendations are for selective vaccination of people with known risk factors often at personal expense. However, this does not achieve adequate vaccination rates.27 Other studies which have looked at influenza and AMI in people aged <65 years have shown mixed results, but even a small reduction in AMI by prevention of influenza may have population health benefit.32 33 The role of an expanded vaccination programme for adults over 50 years of age, which would capture a significant proportion of people at risk of AMI, should be explored by further research. At the least, clinicians should be aware of influenza and infection as an underlying and poorly diagnosed precipitant or comorbidity in hospitalised patients and of the preventive benefit of influenza vaccine for patients at risk for AMI.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr Nicholas Wood, Professor Paul Mitchell, Professor John Fox and Ms Swati Ghotane for their contribution to this study.
Footnotes
Correction notice: This paper has been changed since it was first published online. Data has been updated in the Demographic characteristics section.
Contributors: CRM, PK, RL and DED conceived and designed the study. AEH, IR, HS and ZG contributed to protocol development and coordinated and conducted fieldwork with assistance from TT. ALK, HWDS and VL conducted fieldwork, developed substudy protocols and contributed to literature review of the manuscript. CRM, AEH and ZG interpreted data and performed the analyses. CRM and AEH wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all the mentioned coauthors critically revised the manuscript and provided final approval of the manuscript. The guarantor is CRM.
Funding: This work was supported by a grant from GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Belgium. Dr Iman Ridda and Dr Holly Seale are supported by Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Training Fellowships.
Competing interests: Professor CR Macintyre has received grant funds and/or support for investigator-driven research from GSK, CSL, Sanofi Pasteur, Merck and Pfizer. Dr Anita Heywood has received grant funds for investigator-driven research from GSK and Sanofi Pasteur. Dr Holly Seale has received grant funds for investigator-driven research from GSK, CSL and Sanofi Pasteur. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics approval: Human Research Ethics Committee of the Sydney West Area Health Service (Westmead), New South Wales, Australia–HREC2007/2/4.8 (2533).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Nielsen J, Mazick A, Glismann S, et al. Excess mortality related to seasonal influenza and extreme temperatures in Denmark, 1994–2010. BMC Infect Dis 2011;11:350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chiu C, Dey A, Wang H, et al. Vaccine preventable diseases in Australia, 2005 to 2007. Commun Dis Intell 2010;34(Supp):S1–167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fiore AE, Uyeki TM, Broder K, et al. Prevention and control of influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep 2010;59:1–62 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Reichert TA, Simonsen L, Sharma A, et al. Influenza and the winter increase in mortality in the United States, 1959–1999. Am J Epidemiol 2004;160:492–502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Newall AT, Wood JG, Macintyre CR. Influenza-related hospitalisation and death in Australians aged 50 years and older. Vaccine 2008;26:2135–41 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tillett HE, Smith JW, Gooch CD. Excess deaths attributable to influenza in England and Wales: age at death and certified cause. Int J Epidemiol 1983;12:344–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Warren-Gash C, Bhaskaran K, Hayward A, et al. Circulating influenza virus, climatic factors, and acute myocardial infarction: a time series study in England and Wales and Hong Kong. J Infect Dis 2011;203:1710–8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smeeth L, Thomas SL, Hall AJ, et al. Risk of myocardial infarction and stroke after acute infection or vaccination. N Engl J Med 2004;351:2611–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Meier CR, Jick SS, Derby LE, et al. Acute respiratory-tract infections and risk of first-time acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 1998;351:1467–71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sydney West Area Health Service Healthcare Services Plan 2005–2010—CAREFirst Strategic Health Investment Priorities. In: NSW Health, ed. 2006. http://www.wsahs.nsw.gov.au/services/dsdph/StPl/PUBLICAT/SWAHS-Healthcare-Services-Plan-final-April.pdf (accessed Oct 2012). [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kok J, Blyth CC, Foo H, et al. Comparison of a rapid antigen test with nucleic acid testing during cocirculation of pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 and seasonal influenza A/H3N2. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:290–1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Druce J, Tran T, Kelly H, et al. Laboratory diagnosis and surveillance of human respiratory viruses by PCR in Victoria, Australia, 2002–2003. J Med Virol 2005;75:122–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Last JM. A dictionary of epidemiology. 4th edn New York: Oxford University Press, 2001 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Torvaldsen S, McIntyre PB. Observational methods in epidemiologic assessment of vaccine effectiveness. Commun Dis Intell 2002;26:451–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Naghavi M, Barlas Z, Siadaty S, et al. Association of influenza vaccination and reduced risk of recurrent myocardial infarction. Circulation 2000;102:3039–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guan X, Yang W, Sun X, et al. Association of influenza virus infection and inflammatory cytokines with acute myocardial infarction. Inflamm Res 2012;61:591–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Phrommintikul A, Kuanprasert S, Wongcharoen W, et al. Influenza vaccination reduces cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Eur Heart J 2011;32:1730–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hung IF, Leung AY, Chu DW, et al. Prevention of acute myocardial infarction and stroke among elderly persons by dual pneumococcal and influenza vaccination: a prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2010;51:1007–16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ciszewski A, Bilinska ZT, Brydak LB, et al. Influenza vaccination in secondary prevention from coronary ischaemic events in coronary artery disease: FLUCAD study. Eur Heart J 2008;29:1350–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gurfinkel EP, Leon de la Fuente R, Mendiz O, et al. Flu vaccination in acute coronary syndromes and planned percutaneous coronary interventions (FLUVACS) Study. Eur Heart J 2004;25:25–31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nichol KL, Nordin J, Mullooly J, et al. Influenza vaccination and reduction in hospitalizations for cardiac disease and stroke among the elderly. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1322–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gurfinkel EP, de la Fuente RL, Mendiz O, et al. Influenza vaccine pilot study in acute coronary syndromes and planned percutaneous coronary interventions: the FLU Vaccination Acute Coronary Syndromes (FLUVACS) Study. Circulation 2002;105:2143–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Libby P, Egan D, Skarlatos S. Roles of infectious agents in atherosclerosis and restenosis: an assessment of the evidence and need for future research. Circulation 1997;96:4095–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gross PA, Hermogenes AW, Sacks HS, et al. The efficacy of influenza vaccine in elderly persons. A meta-analysis and review of the literature. Ann Intern Med 1995;123:518–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hampson AW, Irving LB. Influenza vaccination: cost-effective health care for the older adult? J Qual Clin Pract 1997;17:3–11 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.National Health and Medical Research Council The Australian immunisation handbook. 9th edn. Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, 2008 [Google Scholar]
- 27.Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) 2009 Adult vaccination Survey. Summary results. Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, 2011. http://www.aihw.gov.au (accessed Oct 2012) [Google Scholar]
- 28.Newall AT, Kelly H, Harsley S, et al. Cost effectiveness of influenza vaccination in older adults: a critical review of economic evaluations for the 50- to 64-year age group. Pharmacoeconomics 2009;27:439–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Begg SJ, Vos T, Barker B, et al. Burden of disease and injury in Australia in the new millennium: measuring health loss from diseases, injuries and risk factors. Med J Aust 2008;188:36–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) Australia's health 2010. Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, 2010. http://www.aihw.gov.au (accessed Oct 2012). [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ôunpuu S, et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. The Lancet 2004;364:937–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fleming DM, Cross KW, Pannell RS. Influenza and its relationship to circulatory disorders. Epidemiol Infect 2005;133:255–62 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Warren-Gash C, Hayward AC, Hemingway H, et al. Influenza infection and risk of acute myocardial infarction in England and Wales: a CALIBER Self-Controlled Case Series Study. J Infect Dis 2012;206:1652–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]